Where To Find Server Certificate In A Tls1.3 Handshake Capture
Di: Everly
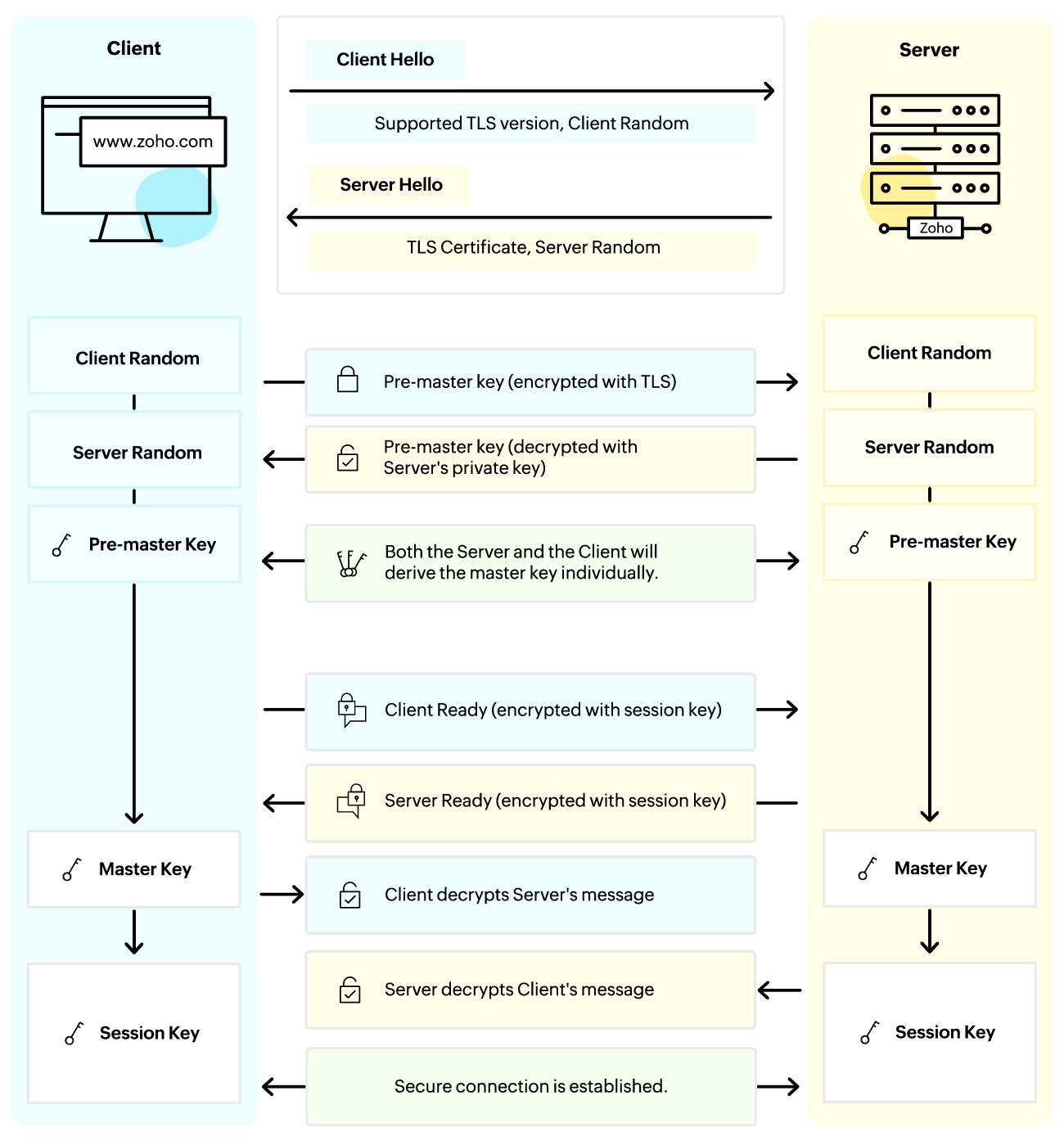
A walkthrough of a TLS 1.3 handshake
Management: PKI provides processes for managing certificates throughout their lifecycle, including issuance, renewal, revocation, and expiration. Obtain the packet capture.
Wireshark is a powerful tool for understanding or troubleshooting TLS/SSL connections, as it allows you to capture, filter, and analyze network traffic to diagnose issues in
In the “Certificate” message, the Server sends its SSL certificate chain (which includes its leaf certificate and intermediate certificates) to the client. To provide authentication
The server does not send any certificate in the ServerHello message; it sends certificates in the aptly-named Certificate message.. As indicated in the standard, the server is
- A Developer Guide to Performing a TLS Handshake
- Extracting certificates from SSL/TLS handshake packet capture
- How do I list the SSL/TLS cipher suites a particular website offers?
If you want to view only the Server Hello packets for TLS1.3 handshakes, you can type the following in the Display Filter field: tls.handshake.type==2 and
Find “Certificate, Server Hello” (or Client Hello if it is a client-side certificate that you are interested in obtaining. In the packet detail pane, expand the Secure Sockets Layer protocol; Expand the “TLSv1 Record Layer:
To tell in short, TCP handshake is a three-step process. First, the client sends the SYN packet to the server. Second, the server sends SYN + ACK in response to the client. At last, the client sends the acknowledgment to the
Overview and Dissection of TLS 1.3 Handshake using Wireshark
2. Server Hello To acknowledge the client, the server sends back a “hello” message as well. The server verifies that it supports the client’s TLS version and chooses the most
Certificate contains the server’s digital certificate and any per-certificate extensions. Certificate verify : the entire handshake is signed using the private key of the
Server Certificate – Originated by the server. Contains the public certificate chain that the client will authenticate. Certificate Request – Originated by the server. This message is only sent if the server also needs to
The CertificateVerify message is omitted if the client is not authenticating with a certificate. The client and server can now securely send application data to each other. Key exchange The key
So, the first steps of the TLS handshake require the client and server to share their capabilities so they can find the cryptographic features they mutually support. Once a client
Step 3: Server Certificate (Server → Client) The server now sends a signed TLS/SSL certificate that proves its identity to the client. It also contains the public key of the
where to find server certificate in a TLS1.3 handshake capture
Certificate contains the server’s digital certificate and any per-certificate extensions. Certificate verify : the entire handshake is signed using the private key of the
Certificate: The server sends its X.509 Certificate which contains the server’s public key and identity information to authenticate itself to the client. This could be a chain of
Capturing SSL/TLS handshake traffic with TCPdump can be done in a few simple steps. Let’s explore the process in detail. 1. Identify the Network Interface. First, determine which network
If the server’s certificate is issued by a trusted root CA or immediate CA, then the browser trust the server’s certificate. I will tell you how to find these root CAs in your web browser at the end of this article.
Server Certificate: The server sends its SSL certificate, which contains the server’s public key. Key Exchange: For example, to capture traffic where SSL v3 or TLS v1.0 is used, you could
The TLS handshake is basically a back-and-forth dialogue between your web server and the site visitor’s client. In a traditional TLS handshake, the browser is the one that
How do you use Wireshark to analyse SSL/TLS handshakes?
In the TLS connection common causes and troubleshooting guide (microsoft.com) and TLS connection common causes and troubleshooting guide (microsoft.com), the
The server’s randomly generated number, the server random. A session ID to identify the connection. This response confirms that the server can proceed with the
In TLS 1.3 everything after the server hello packet is encrypted including certificate exchange. We can’t use tcpdump to see the message exchange. We should require programs
techkluster.com
This time, then, instead of capturing packets with tcpdump, I’ll use openssl ’s helpful s_client command with the -msg option to see the actual exchange that occurred
I’m analyzing a TLS1.3 handshake using latest version of wireshark and I can’t find the certificate in the handshake (I know that the certificate in TLS1.3 is sent encrypted). In
To simplify things a little more I’ve lumped a few of these steps together. Step 1: The entire connection/handshake begins with the client sending a “client hello” message to the
The TLS 1.3 handshake also begins with the “Client Hello” message as in the case of TLS 1.2. So far, this doesn’t look surprised, See the next information. Now, it’s unexpected
Nmap with ssl-enum-ciphers. There is no better or faster way to get a list of available ciphers from a network service. Plus, nmap will provide a strength rating of strong,
When troubleshooting, it can be very helpful to view encrypted SSL connections in order to inspect the messages within. There is a relatively simple way to do this with Wireshark. Please note that TLS is intended for the confidential
- Cogas : Air Treatment
- Glasflasche Eckig 100 Ml
- Schokoladenfabrik Dortmund Brackel
- Commercial Office Space
- Moasure One Dachmessgerät _ Moasure X2 Datenblatt
- Gelöst: Kabel Widerruf: Vodafone Widerrufsfristen
- How To Shrink Rubber: Shrinking Rubber
- Metallbau Schmitt E.k, Donnersdorf
- Chirurgen In Remscheid _ Dr Stephan Remscheid
- Behind The Korean Broadcasting Boom