What Is An Ecosystem? | Liste Ökosysteme
Di: Everly
What is an Ecosystem? Types of Ecosystem Teaching Wiki
An ecosystem may seem like a large term, but these systems can range greatly in size. The entire Earth is made up of connected ecosystems, each which fits together with the
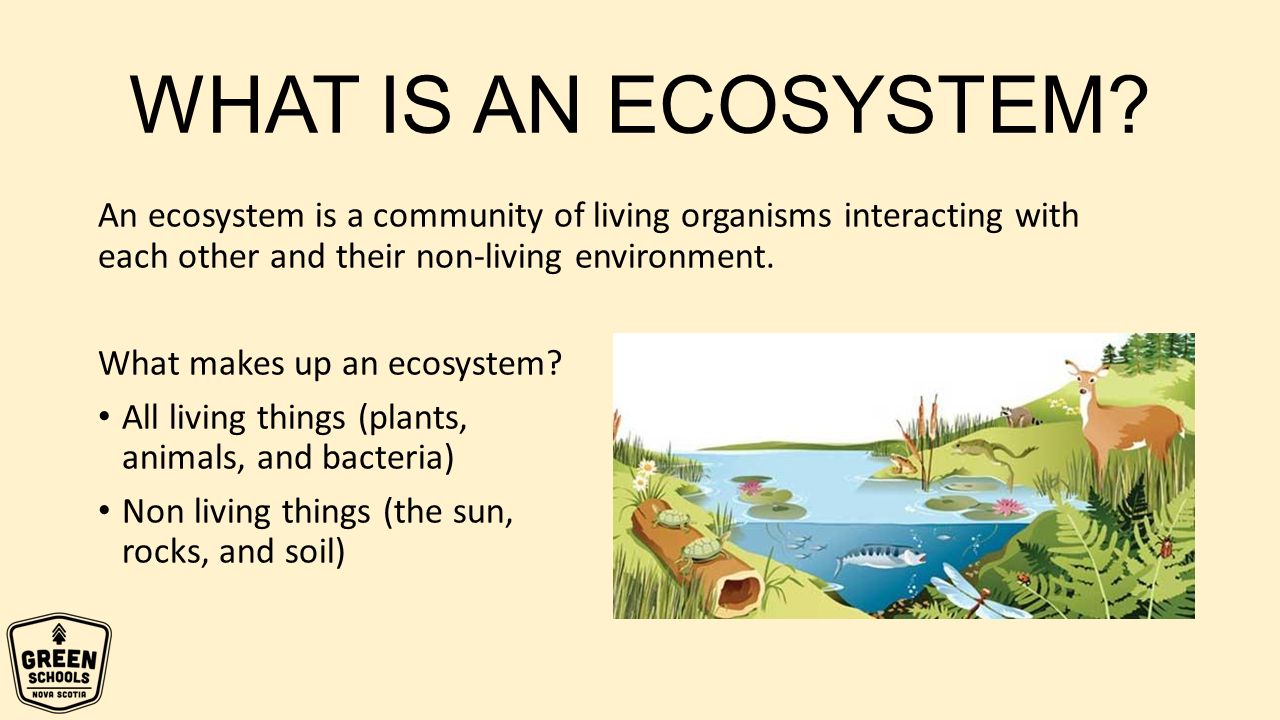
An ecosystem is a natural environment where everything interacts to support life. Ecosystems are made up of living – or biotic – organisms, like plants and animals;which rely on nonliving
Understand what an ecosystem is. Explore ecosystem examples, read an ecosystem definition, and discover the various types of ecosystems on water
Function of Ecosystem The function of ecosystem is to keep all its living and non-living components running in a balance. So, we can say that the functions of the ecosystem
- Ähnliche Suchvorgänge für What is an ecosystem?Science KS2: How do ecosystems work?
- What is an ecosystem? erkunden
- 10.1: Ecosystems and ecological interactions
- Ecosystem: Definition, Structure, Types & Function
Ecosystems are made up of two primary components: biotic and abiotic elements, which together create a self-sustaining environment that supports entire communities of
The
The Ecosystem. Ecology is the study of how living things interact with each other and with their environment. It is a major branch of biology, but has areas of overlap with geography, geology,
What Is An Ecosystem? An ecosystem is where a community of living organisms (such as plants and animals) live together in conjunction with non-living aspects of their
A variety of ecosystems are spread across the world, each with distinctive interacting characteristics and components. They range from small (eg a freshwater pond) to global (eg the desert biome).
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and includes a variety of other elements in the environment they inhabit. Keep reading for more information on ecosystems and processes for
An ecosystem, in the realm of ecological studies, represents a cohesive unit where living entities and their non-living environment engage in intricate interactions.
The ability of an ecosystem to remain at equilibrium in spite of disturbances is called resistance. The speed at which an ecosystem recovers equilibrium after being disturbed, called its
An ecosystem is a functional unit of nature where a community of living organisms interact among themselves and with the surrounding physical environment. Learn about the abiotic and biotic components, natural and
“ Ecosystems are the life-support systems of our planet, connecting every species and resource in a complex balance. These natural networks do much more than support
An ecosystem is a complex system of living and non-living things that work in union. Learn about the natural and artificial ecosystems, their components, biomes, and their roles in the
- What is Ecosystem? Definition, Structure, Types, and Functions
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- 1. Ecosystem Structure and Function
- What is an Ecosystem? Types of Ecosystem Teaching Wiki
- Biotic Factors: Definition, Types, Examples
The non-living abiotic factors control which organisms live in an ecosystem, where they live, and how many of them are there. Even slight changes in abiotic factors can have a
Ecosystem is the complex relationships between living things and their environment. Everything in nature is interconnected. Plants, animals and microorganisms are
Teaching Ecosystems at KS3. The ‘Ecosystem’ definition KS3 students are given: An ecosystem is typically defined as a community of living organisms (such as plants, animals, and
The ecosystem is the basic unit of our environment and comprises living organisms and non-living and how they interact with each other. In simple words, a geographical area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as
Ecosystems are dynamic systems where living organisms interact with each other and their environment. Understanding how resources influence species interactions is a critical
Ecosystem Definition in Biology. Biologists define an ecosystem as a community of living organisms and their physical environment, which includes both biotic and abiotic factors.
Because we are talking about interactions, ecosystems can be any size. A puddle on the ground can be as much of an ecosystem as a whole lake, forest, river or desert. Our native forests –
Grassland Ecosystem: Dominated by grasses, these ecosystems support herbivores and are found in temperate and tropical climates. Tundra Ecosystem: Cold and treeless, these
Ecosystems are the natural systems that work together to support a variety of organisms. The term can refer to different areas in the world, such as an ocean, a forest, or even your
Freshwater ecosystems represent the non-marine aquatic ecosystems, including rivers, ponds, lakes, springs, and wetlands. Abiotic factors affecting these ecosystems include
Ecosystems Ecosystems. An ecosystem is a community of animals, plants, micro-organisms, non-living things and their shared environment. Find out about energy transfer, niches and
An ecosystem is a unit of ecological studies that includes all the interactions between living organisms with their surrounding non-living environment. Learn about the biotic
An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form a bubble of life. Learn about the different types of ecosystems, how they are
- Timesheets, Timecards, And Payroll Templates For Excel
- Waggler Pose Shop | Waggler Posen Kaufen
- Virtuelle Maschine Von Virtualbox Nach Vmware Umziehen
- Squad Gameplay Review: Worth It In 2024?
- Who Is Squirrel Girl? With Milana Vayntrub
- Autoindustrie: Zulieferer Investieren Verstärkt In Mexiko
- Crash Bandicoot Native Fortress Walkthrough
- Jacques Auf Deutsch _ Jacques Französisch
- Kinoprogramm Für Leid Und Herrlichkeit Heute In Hamburg
- Dexcom G7 Sensor Setzen _ Dexcom G7 Sensor Anbringen