Types Of Transfection Dna – Types Of Transfections
Di: Everly
Types of Transfection. There is a wide range of transfection methods that include physical, chemical and biological techniques. These techniques generally involve the use of transient or
Types Of Transfection. Transfection is a key technique in molecular biology. It involves introducing nucleic acids into cells. This process helps scientists study gene function
Transfection types, methods and strategies: a technical review
With stable or permanent transfection, the transfected DNA is either integrated into the chromosomal DNA or maintained as an episome. Stable integration of plasmid DNA into the
Available transfection technologies are broadly classified into three groups: chemical, physical, and biological. No one transfection method can be applied to all cell types and experiments.
- Fundamental Techniques of Recombinant DNA Transfer
- Transfection-Principle, TYpes, Methods, Workflow, Applications
- What are the different types of transfection?
- Transfection: Methods, Applications and Protocols
The transfection efficiency can be influenced by many factors, including the type of transfection reagent, the size and type of the foreign DNA, the cell type, and the conditions of the transfection procedure.
Types of Transfection. There is a wide range of transfection methods that include physical, chemical and biological techniques. These techniques generally involve the use of transient or
Transfection is a modern and powerful method used to insert foreign nucleic acids into eukaryotic cells. The ability to modify host cells‘ genetic content enables the broad
ibidi Application Guide Transfection
The term transfection became generally accepted to mean the introduction of any sort of DNA— phage, plasmid, genomic or otherwise—into an animal cell, in the absence of a biological
Cells that have incorporated the foreign DNA are called transfectants. Stable transfectants: Cells that have integrated foreign DNA in their genome. Transient transfectants: Foreign DNA does
Physical methods like microinjection or electroporation simply punch through the membrane and introduce DNA directly into the cytoplasm. Each of these transfection technologies is discussed in the following sections. Figure 1.
Transfection is a method used to introduce foreign genetic material into eukaryotic cells in order to potentially change the genetic make-up of the host cell. There are two main
What is Transfection? Transfection is a technique for introducing foreign genetic material (nucleic acid) into eukaryotic cells, which has the potential to change the genetic make-up of host cell.
Transfection strategies can be classified into two general types; transient transfection and stable transfection.
Types of Transfection. There is a wide range of transfection methods that include physical, chemical and biological techniques. These techniques generally involve the use of transient or
Transfection: Methods, Applications and Protocols
- Introduction to Transfection
- Cell Culture Transfection Methods
- Transfection Protocols and Applications Guide
- Ähnliche Suchvorgänge für Types of transfection dna
Transfection is the forced introduction of small molecules such as DNA, RNA, or antibodies into eukaryotic cells. Just to make life confusing, “transfection” also refers to the
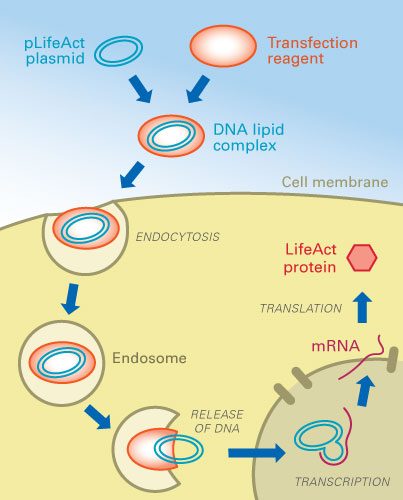
DNA-transfection procedure. 1987, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413 RELEASE OF DNA Protein TRANSLATION mRNA TRANSCRIPTION Plasmid DNA Transfection
In stable transfection, foreign DNA is either integrated into the cellular genome or maintained as an episomal plasmid. Unlike transient transfection, stable transfection allows the long-term
![Transfection types, methods and strategies: a technical review [PeerJ]](https://dfzljdn9uc3pi.cloudfront.net/2021/11165/1/fig-4-full.png)
Types of Transfection. There is a wide range of transfection methods that include physical, chemical and biological techniques. These techniques generally involve the use of transient or
Methods for DNA introduction into mammalian cells
Physical methods of transfection apply electrical, mechanical or thermal forces13 to facilitate nucleic acid entry into host cells. Some examples include microinjection, electroporation, biolistic transfection (gene gun),
Importantly, transfection can be divided into two types: stable transfection and transient transfection. The process of introducing genetic material into a cell in a way that it
Broadly defined, transfection is the process of artificially introducing nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) into cells, utilizing means other than viral infection. Such introductions of foreign nucleic acid
Transfection of DNA to host cell can be done by various methods in lab scale.Gene gun,electroporation,lipofection .These methods are used to transfer DNA to the host cell.
The optimal amount of DNA to use in the transfection will vary widely, depending on the type of DNA, transfection reagent, target cell line and number of cells. Optimization of Transfection Efficiency. You will need to optimize specific
B) Transfection: Plasmid DNA is diluted in 100 µL of commercially available, specialized transfection media or serum-free, antibiotic-free cell culture media. The amount of plasmid DNA used will depend on the size of the culture
The deliberate introduction of foreign DNA into cells is called transfection. For transferring of these DNA, several powerful techniques are employed. These techniques are
Optimize transfection conditions: First and foremost, it is important to choose a transfection reagent that is compatible with the nucleic acid and cell type of choice. Once
There are three common transfection methods: chemical, physical and viral. Physical transfection uses physical means such as biolistics, microinjection and lasers. Chemical transfection uses
Today, various transfection methods are available. These include viral vectors, polymer-based carriers, and nanoparticles. Each method has its advantages and limitations.
- Längen In Verschiedene Maßeinheiten Umrechnen
- Julianadorp Aan Zee Maps _ Julianadorp Aan Zee Sehenswürdigkeiten
- The 25 Best Cyberpunk-Themed Anime Of All Time (Movies
- Revlon Rvdr5318Ct One Step Volumizer Plus User Manual
- Digital Pathology – Digital Pathology Association
- Minijob, Jobs In Hameln | 520 Euro Job Hameln
- Buchtipp: Jim Knopf Und Lukas Der Lokomotivführer
- Skechers Razor Excess 2 Women
- Bernd Mäser Robinson Club – Robinson Club Geschäftsführer
- Günstige Flüge Von München Nach Frankreich From 67 €