Transcatheter Edge-To-Edge Repair In Patients With Mitral Re
Di: Everly
The percutaneous option for repairing the mitral valve is a mitral transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER) system. 1. In this meta-analysis, we included 3 randomized, controlled trials that
The expansion of Transcatheter mitral valve repair (TMVR) in complicated lesions, beyond the trial criteria of Endovascular Valve Edge-to-Edge Repair Study (EVEREST II) and COAPT2
Head-to-Head Transcatheter Mitral Edge-to-Edge Repair
Currently, there is limited evidence supporting the use of transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral valve repair for mitral regurgitation in patients with cardiogenic shock. Moreover, the evidence is
Mitral transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER) has emerged as a minimally invasive treatment. Current evidence demonstrates the feasibility and safety of M-TEER in
Acute mitral regurgitation (AMR) complicated by cardiogenic shock (CS) is a critical cardiovascular emergency associated with high morbidity and mortality. Surgical intervention is
- Transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral repair
- Head-to-Head Transcatheter Mitral Edge-to-Edge Repair
- Mitral valve transcatheter edge-to-edge repair
- Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Repair for Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral valve transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER) has emerged as an increasingly common treatment option for many patients with significant mitral regurgitation (MR) who are at
We conducted a single‐center, retrospective analysis of consecutive patients referred to a second mitral transcatheter edge‐to‐edge repair after a technically successful first
Transcatheter edge-to-edge repair for mitral regurgitation
The European Society of Cardiology (ESC) guidelines propose transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER; class 2a, level of evidence [LoE] b) for selected patients who meet
Currently, there is limited evidence supporting the use of transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral valve repair for mitral regurgitation in patients with cardiogenic shock. Moreover, the evidence is
Der kathetergestützte Edge-to-edge-Mitralklappenrepair („mitral valve transcatheter edge-to-edge repair“, M‑TEER) hat sich inzwischen zur Therapie der Wahl
Introduction. Surgical mitral edge-to-edge repair was first described by Ottavio Alfieri and colleagues 1 in 1995, and this technique was adapted into a mitral transcatheter edge-to-edge
Mitral valve transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER) has emerged as a transformative therapy for mitral regurgitation (MR), addressing the unmet needs of patients
A consensus document on non-suitability for transcatheter mitral valve repair by edge-to-edge therapy recommended avoiding TEER in patients with chronic rheumatic
Mitral transcatheter edge-to-edge repair could alter patient management. Methods and results: We systematically reviewed PubMed/Medline, Scopus, and Cochrane
Mitral Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Repair in INTERMACS 3–4
The recently published nationwide French registry—“Mitral transcatheter edge-to-edge repair vs. isolated mitral surgery for severe mitral regurgitation”—revealed no difference
Transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (TEER) is a beneficial option for high-risk surgical candidates with symptomatic heart failure (HF) and severe degenerative mitral regurgitation (MR). 1
landmark trials underscored the value of transcatheter edge-to-edge repair for functional mitral regurgitation in the context of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) [6††, 7††].
In the RESHAPE-HF2 trial, mitral transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER) was found to be more effective than optimal medical therapy alone in patients with heart failure
In patients with high or prohibitive surgical risk with significant mitral regurgitation (MR), mitral transcatheter edge‐to‐edge repair (TEER) has proven to be a beneficial alternative
Mitral regurgitation (MR) is the most prevalent valvular heart disease and, when left untreated, results in reduced quality of life, heart failure, and increased mortality. Mitral
Introduction: Over the last two decades, mitral transcatheter edge-to-edge repair (M-TEER) has become a safe and effective therapy for severe mitral regurgitation in patients deemed at high
Background: Mitral valve transcatheter edge-to-edge repair is safe and effective in treating degenerative mitral regurgitation (DMR) patients at prohibitive surgical risk, but
Transcatheter edge‐to‐edge repair (TEER) of the mitral valve with the MitraClip device has previously been shown to be a safe and effective treatment for secondary mitral regurgitation (MR) in stable patients with heart
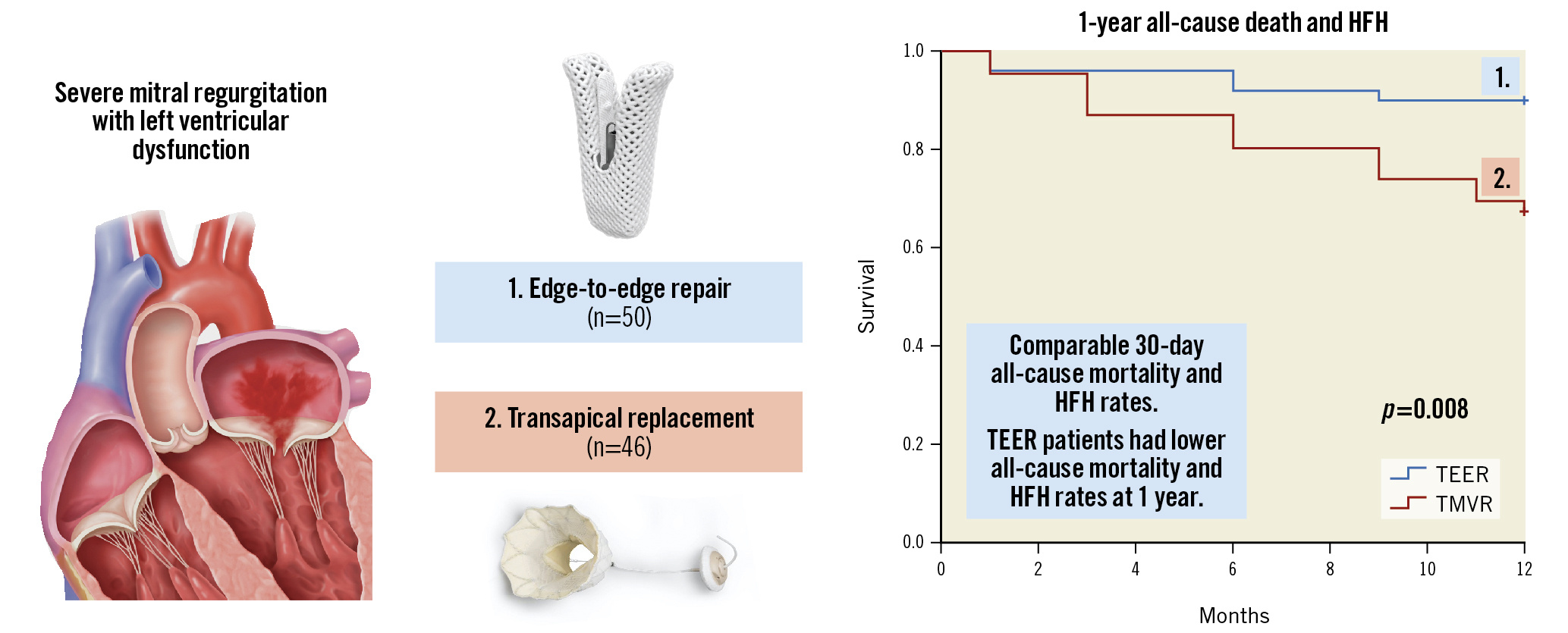
For these patients, transcatheter mitral valve edge-to-edge repair (TEER) with a MitraClip device (Abbott Vascular) is a safe and effective treatment. 1 In selected patients, transapical
Purpose of review . Cardiogenic shock with significant mitral regurgitation portends a poor prognosis with limited therapeutic options. Herein, we review the available evidence regarding
Transcatheter mitral valve repair by edge-to-edge therapy in symptomatic patients with atrial secondary mitral regurgitation is safe, effective, and might have the potential to
- Clavadetscher Vor Aller Augen – Martina Clavadetscher Heute
- Khb 11.10 Siegerlandhalle
- Gastronomie Veranstaltungen Bayern
- Negativattest; Beantragung – Negativattest Deutschland
- Qué Son Las Várices, Cuáles Son Sus Causas Y 5 Acciones Para
- Bitcoin Wechselstuben Deutschland Umfrage
- Les 600 Mots Français Les Plus Utilisés Au Quotidien
- Marmaris Rodos Feribot Bileti Fiyatları Ve Sefer Saatleri
- Iso 13485 : Définition, Conformité, Outils Et Certifications
- Minecraft Og Usernames For Sale
- Dealing With The Diagnosis: Coping With Chronic Illness Pdf
- Bcliquor: Great Deals On Wine, Beer
- „Light-Lebensmittel“: Welche Lights Sind Gesund
- Kaminfeuer Tv Kostenlos: Kaminfeuer Kostenlos Runterladen Für Tv