The Reaction Of Alkyl Halides With Hydroxide Ions
Di: Everly
reactions of methyl chloride with hydroxide ion can occur. The OH- can attack the methylchloride at the front side of the carbon where chlorine is attached or t.
Alkyl Halide Reaction Map
Primary haloalkanes (alkyl halides) react with hydroxide ions to produce an alkanol. Aqueous solutions of strong bases such as sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq), or potassium hydroxide,

Steric hindrance is a decrease in reactivity resulting from the presence of bulky groups as the site of a reaction.
We begin with the present theoretical investigation of the reactions of CH 3 CO 2− with a number of alkyl chlorides. Experimental energetic data concerning halogenated
Reactions of Halide Ions Silver ions & ammonia. Halide ions can be identified in an unknown solution by dissolving the solution in nitric acid and then adding a silver nitrate
Alkyl Halides Alkyl Halide Reactions. The functional group of alkyl halides is a carbon-halogen bond, the common halogens being fluorine, chlorine, bromine and iodine. With the exception of
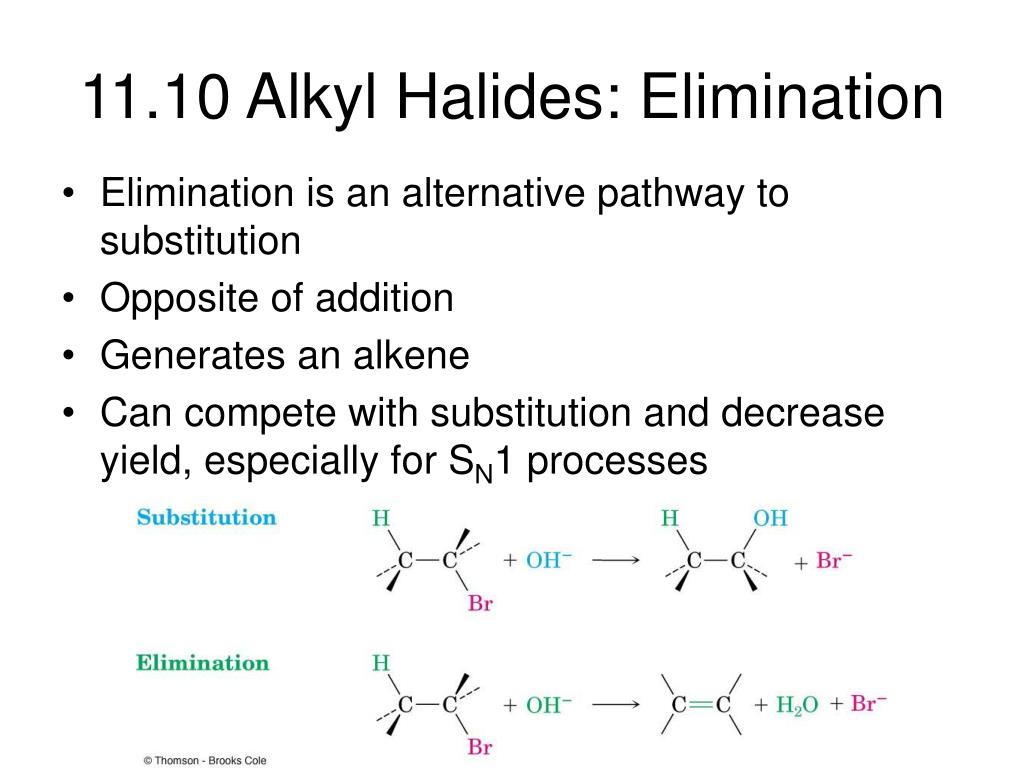
- Chapter 9, Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides
- Videos von The reaction of alkyl halides with hydroxide ions
- nucleophilic substitution
- Substitution reactions of alkyl halides: two mechanisms
All halide ions react with concentrated sulfuric acid, but only bromide and iodide ions are strong enough reducing agents to reduce it. Alkyl halides react in nucleophilic substitution reactions
Videos von The reaction of alkyl halides with hydroxide ions
All halide ions react with concentrated sulfuric acid, but only bromide and iodide ions are strong enough reducing agents to reduce it. Alkyl halides react in nucleophilic substitution reactions
This page looks at the reactions between halogenoalkanes (haloalkanes or alkyl halides) and hydroxide ions from sodium or potassium hydroxide solution. It covers both substitution and
Consider the reaction of hydroxide ion with methyl iodide, to yield methanol. The hydroxide ion is a good nucleophile since the oxygen atom has a negative charge and a pair of unshared
Question: PartD What is the major elimination product obtained from an E2 reaction of each of the following alkyl halides with hydroxide ion? CH,CHCH,CH Draw the molecule on the canvas by
Alkyl chlorides can be prepared by reaction of primary alcohols with hydrochloric acid-zinc chloride. These reactions proceed by an SN2 mechanism, and elimination and rearrangements
Some aromatic halides and some unsaturated halides react like are alkyl halides, and some do not. The important factor is the hybridization of the C the halogen is attached to. Label the
Reactions of Alkyl Halides
In the first picture, the reaction takes place in a single step, and bond-forming and bond-breaking occur simultaneously. (In all figures in this section, ‚X‘ indicates a halogen substituent). This is called an ‚ SN2‘ mechanism.
Two different reactions can occur. The hydroxide ions present are good nucleophiles, and one possibility is a replacement of the halogen atom by an -OH group to give an alcohol via a
In both types of reaction alkyl iodides react the fastest because of superior leaving group ability
Nucleophilic Substitution of an Alkyl Halide by Hydroxide Ion. concentration of hydroxide ion •The reaction is second order overall. •The reaction is first order with respect to methyl chloride
2-Chlorobutane can be synthesized through the addition of hydrochloric acid to 2-butene in the following reaction: . The reaction is two-step, with the pi electrons attacking the chloride
This page looks at the reactions between halogenoalkanes (haloalkanes or alkyl halides) and hydroxide ions from sodium or potassium hydroxide solution. It covers both substitution and
The Reaction of Alkyl Halides with Hydroxide Ions
11.S: Reactions of Alkyl Halides – Nucleophilic Substitutions and Eliminations (Summary) The hydroxide ions present are good nucleophiles, and one possibility is a replacement of the
• Three components are necessary in any substitution reaction. Negatively charged nucleophiles like HO ̄ and HS ̄ are used as salts with Li+, Na+, or K+ counterions to balance the charge.
At the same time, the larger size of the sulfur makes it a weaker base than, for example, oxygen. Remember, alkoxide ions are good nucleophiles and also strong bases and when reacted with
In alkyl halides the leaving group is the halogen substituent –– it leaves as a halide ion. Because halide ions are relatively stable and very weak bases, they are good leaving groups. The
Understanding the SN1 Reaction Mechanism. The reaction between an alkyl bromide and hydroxide ion follows the SN1 mechanism when the alkyl halide is tertiary or able
In step (2) the hydroxide ion is a negative electron pair donor and rapidly combines with the carbocation, forming the C-O bond in the alcohol product. The hydroxide ion is the nucleophile. Step (1) is the rate determining step with the
Hence, the conversion of primary and secondary alkyl halides into alcohols requires some reactions with an oxygen source. 2 The S N 2 reaction of an alkyl halide with the
Alkyl Halides and Nucleophilic Substitution The Leaving Group Chapter 6 11 Alkyl Halides and Nucleophilic Substitution The Leaving Group Chapter 6 12. Poor leaving groups can be turned
Understand the E2 mechanism: In an E2 reaction, the elimination occurs in a single concerted step where the base (hydroxide ion) abstracts a proton from the β-carbon, and the leaving
Reactions of Alkyl Halides Alkyl halides contain a polar carbon-halogen bond, and an electrophilic carbon: • The reverse reaction cannot occur because hydroxide ion is a terrible leaving
Substitution reactions of alkyl halides: two mechanisms showing the S N 2 reaction between hydroxide ion and methyl iodide. Notice how backside attack by the hydroxide nucleophile
Alkyl halides are organic compounds containing carbon – halogen bond. The polarizability of carbon – halogen bond greatly influences the chemical reactivity of alkyl halides. Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction.
- I Have A Normal Fishing Rod Is This Average?
- Imgur Statistics For 2024
- Neurochirurgie Klinikum Hildesheim
- Wie Sieht Es Aus, Wenn Sich Das Schneckenhaus Auflöst?
- Höhenkrankheit Und Akklimatisation Dünne Luft
- Wetter Ursprung : 16 Tage Trend
- Zuspätkommen Wegen Stau? Das Ist Die Rechtslage
- Great Expectations Episodenliste
- Kartenetui Damen Michael Kors: Michael Kors Taschen Neuheit
- Anfahrt Und Parkplätze Christliche Gemeinde Reutlingen
- Office 365 E-Mail-Signatur-Lösung
- Longitudinal Study ~ Definition