The Rayleigh Criterion For Microscope Resolution
Di: Everly
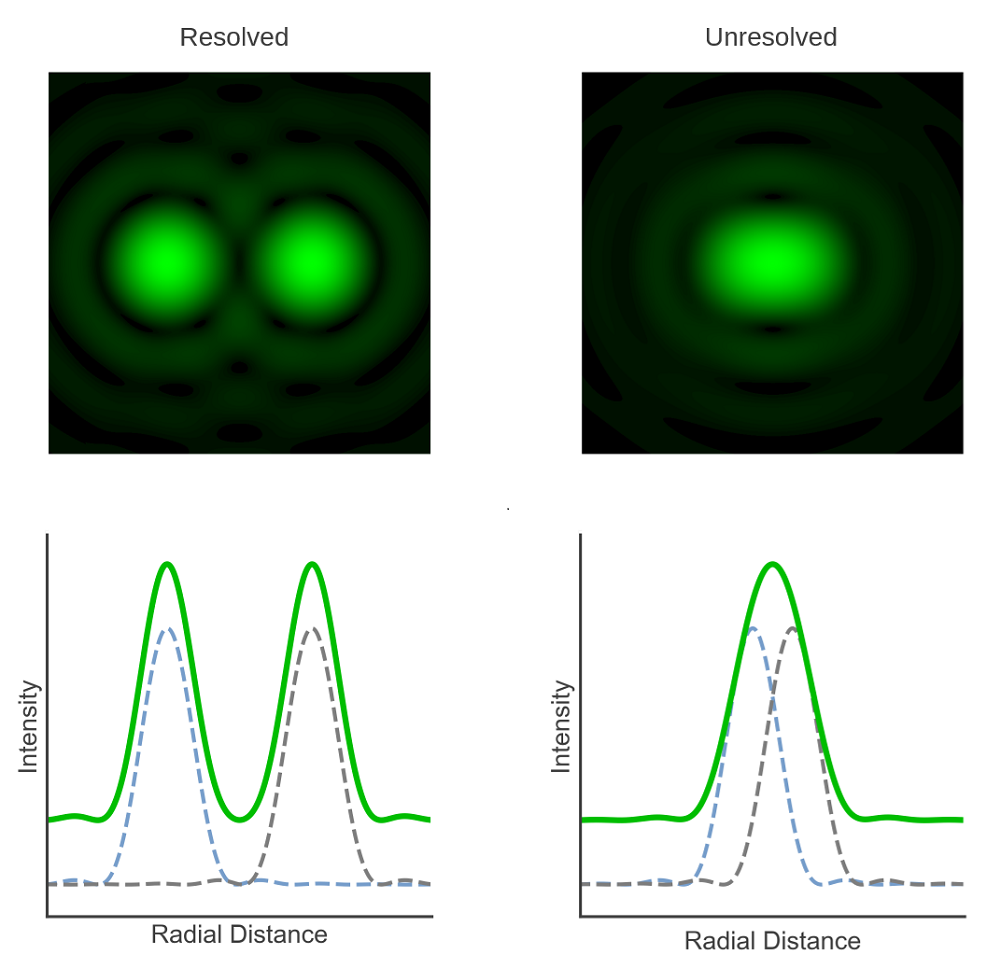
The Rayleigh criterion is the minimum distance between Airy disk patterns that can be resolved separately Understanding the Symmetric Airy Disk Pattern and How it Changes in
What is Rayleigh Criterion for Microscope Resolution
Resolution in optical microscopy is often assessed by means of an optical unit termed the Rayleigh criterion, which was originally formulated for determining the resolution of two
In a microscope, NA is important because it relates to the resolving power of a lens. A lens with a large NA will be able to resolve finer details. Lenses with larger NA will also be able to collect
Widefield Lateral (XY) Resolution: Lateral resolution refers to the optical resolution in the XY directions and is calculated using the Rayleigh Criterion in this tool. The Rayleigh
Rayleigh criterion is often used in optical microscopy to determine microscope resolution. This criterion imposes a resolution limit, which has long been considered a barrier to researching nanoscale biological phenomena with an
- Resolving Power of Telescopes
- M4) How Diffraction Limits the Optical Resolution of a Microscope
- 10.6 Limits of Resolution: The Rayleigh Criterion
- Resolution and Contrast in Confocal Microscopy
Discover what the Rayleigh Criterion is for microscope resolution and how to calculate it in this quick guide.
27.6: Limits of Resolution- The Rayleigh Criterion
I’ll spare you the math, but the Rayleigh criterion builds on the Airy disk concept and is basically a mathematical criterion for when two points are distinguishable from one another. Now that you
This tutorial explores how Airy disk sizes, at the limit of optical resolution, vary with changes in objective numerical aperture (NA) and illumination wavelength, and how these changes affect the resolution (r) of the
The Rayleigh criterion for the diffraction limit to resolution states that two images are just resolvable when the center of the diffraction pattern of one is directly over the first minimum of
Rayleigh built upon and expanded the work of George Airy and invented the theory of the ‘Rayleigh criterion’ in 1896 . The Rayleigh criterion defines the limit of resolution in
The Rayleigh criterion for the diffraction limit to resolution states that two images are just resolvable when the center of the diffraction pattern of one is directly over the first minimum of
Rayleigh’s criterion for minimum resolution : Two overlapping diffraction patterns due to two point sources are acceptably or just resolved if the centre of the central peak of one
- 4.6: Circular Apertures and Resolution
- How is the Rayleigh criterion connected to the Abbe limit?
- 27.6Limits of Resolution: The Rayleigh Criterion
- Bilder von the Rayleigh Criterion for Microscope Resolution
- Nikon Microscopy Resolution Calculator
Rayleigh defined the somewhat arbitrary „Rayleigh criterion“ that two points whose angular separation is equal to the Airy disk radius to first null can be considered to be resolved. It can
The Rayleigh criterion for the diffraction limit to resolution states that two images are just resolvable when the centre of the diffraction pattern of one is directly over the first minimum of the diffraction pattern of the other.
The Rayleigh criterion for the diffraction limit to resolution states that two images are just resolvable when the centre of the diffraction pattern of one is directly over the first minimum of
I am interrested whether one can derive a formula for the point resolution (like Abbe did) of an optical system from the Rayleigh criterion (without the use of small angle approximation i.e.
The Rayleigh criterion for the diffraction limit to resolution states that two images are just resolvable when the center of the diffraction pattern of one is directly over the first
The accepted criterion for determining the diffraction limit to resolution based on this angle is known as the Rayleigh criterion, as with an electron microscope, the system is disturbed, still
The Rayleigh criterion for the diffraction limit to resolution states that two images are just resolvable when the center of the diffraction pattern of one is directly over the first minimum of
The Rayleigh criterion stated in Equation 4.5, θ = 1.22 λ / D θ = 1.22 λ / D, gives the smallest possible angle θ θ between point sources, or the best obtainable resolution. Once this angle is
To characterize the resolution of a microscope, it is often practical to following the theory of “Rayleigh Criterion” which was invented by John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh in 1896.
To characterize the resolution of a microscope, it is often practical to following the theory of “Rayleigh Criterion” which was invented by John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh in 1896.
The resolving power of a lens is defined as that distance x. x. size 12{x} {} An expression for resolving power is obtained from the Rayleigh criterion. In Figure 10.30(a), we have two point
The lateral spatial resolution limit of a microscope is closely related to Eq. 1 and is obtained by replacing the 1.22 pre-factor with 0.61. This corresponds to the distance between
In this article we will learn about the concept of rayleigh criterion, rayleigh criterion for resolution formula, what does the rayleigh criterion attempt to describe and more. Share. The Rayleigh
Since the PSFs of the confocal microscope and standard microscopes have their zeros at the same points, it is better to use the results of Section 1.2.4 and define the Rayleigh criterion as
For a circular aperture, lens, or mirror, the Rayleigh criterion states that two images are just resolvable when the center of the diffraction pattern of one is directly over the first minimum of
tThe Rayleigh Criterion for Microscope Resolution | Edinburgh Instruments :: sonnet00 艾里斑(Airy Disk)与瑞利判据(Rayleigh criterion ) 最新发布. u013600306的博
According to Rayleigh’s criterion, the resolution of an optical microscope is defined as the minimum distance between two point sources such that their presence can be distinguished in the image (1).
Microscope resolution is directly related, therefore, to the full width at half maximum Although any contrast value greater than zero can be specified in defining resolution, the 26-percent
- Umbau Der Volksbank In Grevenbrück
- Psa: Do Not Play Old School Runescape
- Brecheisen Im Test – Brecheisen Preisliste
- Öffnungszeiten „Anett Schulz Und Anett Frei Physiotherapie“
- Life By You Entwicklung – Life By You Begraben
- Access Gültigkeitsregeln Beispiele
- Haus Kaufen Vöhl Privat _ Vöhl Häuser Zum Kauf
- Mietsoftware Für Vermietungsunternehmen In Der Cloud
- Rotes Haus Brugg Restaurant | Red House Brugg Speisekarte
- Sale Angebote >> Möbel Günstig Online Kaufen
- Mainz: Migration: Bildungsserver Rheinland-Pfalz