The Full Model Of The Pmhc-Tcr-Cd3 Complex: A
Di: Everly
Understanding the structural dynamics of TCR-pMHC interactions
This issue prompted us to reevaluate the extent of TCR cell surface stability, internalization, and recycling. Some early studies suggested that the TCR:CD3 complex
The T cell receptor (TCR) is one of the most complicated receptors in mammalian cells, and its triggering mechanism remains mysterious. As an octamer complex, TCR
(2022) Alba, D’abramo. Cells. The machinery involved in cytotoxic T-cell activation requires three main characters: the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) bound to the peptide (p),
In this study, we present an allosteric mechanism for T cell receptor (TCR) triggering upon binding a peptide-MHC complex (pMHC), in which a conformational change in
- Structure of a fully assembled tumor-specific T cell
- In situ cell-surface conformation of the TCR-CD3 signaling complex
- TCR Triggering by the pMHC Complex: Valency, Affinity, and
Very recently, the determination of the TCR:CD3 complex structure by means of Cryo-EM technique has given a chance to build the entire system essential in the activation of T-cells, a
RMSDs and root-mean-square fluctuations of the complex subunits revealed that the subdomains of the GPa3b17 and WT TCR complexes were stable throughout the simulations , with two local exceptions: one of the
Supporting: 1, Mentioning: 4 – The machinery involved in cytotoxic T-cell activation requires three main characters such as: the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) bound to the
TCR Triggering by the pMHC Complex: Valency, Affinity, and
First, the receptor and CD3 signaling modules assemble into complexes that possess a full complement of 10 ITAMs and other key motifs that mediate or regulate signaling through the
The T cell receptor (TCR)-CD3 complex recognizes antigens and transmits signal into the T cell to initiate the adaptive immune response. Natarajan et al. examine the TCR-CD3
The machinery involved in cytotoxic T-cell activation requires three main characters: the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) bound to the peptide (p), the T-cell receptor (TCR),
Mechanisms of TCR activation. A, in the aggregation model, pMHC binding induces oligomerization of TCR–CD3 complexes.This clustering could increase the proximity of
- Understanding the structural dynamics of TCR-pMHC interactions
- The full model of the pMHC-TCR-CD3 complex: a structural and
- Mechanisms for T cell receptor triggering
- The TCR/CD3 complex in leukemogenesis and as a
To generate a 3D model of the TCR-CD3 complex using cross-linking Full atom, 3D models of the two CD3 hetero-oligomers were docked to a grid potential representation of
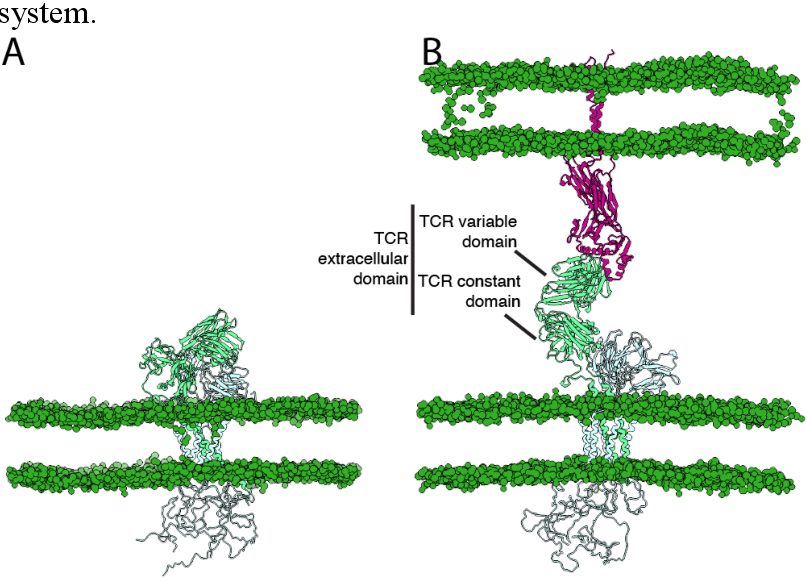
Here, we present the first complete model of the pMHC interacting with the TCR:CD3 complex, built in a lipid environment.
T cells are critical for protective immune responses to pathogens and tumors. The T-cell receptor (TCR)–CD3 complex is composed of a diverse αβ TCR heterodimer noncovalently associated
The TCR regulates T cell activation through the linkage of peptide-MHC complex (pMHC) and co The CD3δ chain is loosely bound to the pre-TCR-CD3 complex and the γδ
The cryoEM structure of a fully-assembled TCR–CD3 complex has provided a wealth of new information on its overall molecular architecture and the exact interactions
Starting from the available experimental data on the complex between SEB, the TCR and MHC class II (19), we initially rebuilt a tentative model of the whole SEB-MHCII-TCR-CD3gϵ-CD3dϵ
AMA Style. Alba J, D’Abramo M. The Full Model of the pMHC-TCR-CD3 Complex: A Structural and Dynamical Characterization of Bound and Unbound States.
Here, we present the first complete model of the pMHC interacting with the TCR:CD3 complex, built in a lipid environment. To describe the conformational behavior
Alba, J., & D’Abramo, M. (2022). The Full Model of the pMHC-TCR-CD3 Complex: A Structural and Dynamical Characterization of Bound and Unbound States. Cells, 11(4), 668.
The machinery involved in cytotoxic T-cell activation requires three main characters: the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) bound to the peptide (p), the T-cell receptor (TCR),
those of the TCR-CD3 complex cryo-EM structure: with TCRα in cyan, TCRβ in dark green, CD3ε in pale green, CD3γ in royal blue, CD3δ in orange, and CD3ζ in red orange.
In this study, we demonstrate that upon dissociation of a CD3-TCR or CD4-CD3-TCR complex from a cognate pMHC, there are increased energetic and structural fluctuations
The machinery involved in cytotoxic T-cell activation requires three main characters: the major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC I) bound to the peptide (p), the T-cell receptor (TCR),
Interaction of the T cell receptor (TCR) with an MHC-antigenic peptide complex results in changes at the molecular and cellular levels in T cells. The outside environmental
A consensus regarding how the TCR-CD3 complex relays pMHC-specific information from the T cell:APC interface to the CD3 ITAMs has been elusive (Brazin et al.,
- Dipl.-Med. Ute Czerwinski Fachärztin Für Innere Medizin Calbe
- Oberbett Aus Schurwolle _ Schafwolle Unterlage Bett
- Userbenchmark: Intel Core I7-4770K Vs Xeon E3-1270 V3
- Linkedin Ireland Unlimited Company In Dublin
- Brandschutz Rei 30 – Ei 30 Erklärung
- Bäckerei Schmidt Zieht In Der Eschstraße Um
- Lean Orthodontics® – Lean Orthodontics Kurse
- Feeding Young Dairy Calves | Dairy Calves For Sale
- Utah Commercial Real Estate Map Search
- How To Descale Your Nespresso Delonghi Coffee Machine
- Parceiras Aereas
- Besoffen Ausziehen | Gofeminin Total Besoffen
- Spruce Trapdoor Minecraft Crafting
- Pension Restaurant Nika
- Tips For Becoming A Self-Taught Singer