The Differential Diagnosis Of Acute Transverse Myelitis
Di: Everly
Transverse myelitis (TM) includes a pathobiologically heterogeneous syndrome characterized by acute or subacute spinal cord dysfunction resulting in paresis, a sensory level, and autonomic
Assigning imaging findings to five groups, that is (a) „segmental with rash,“ (b) „poliolike,“ (c) „granulomatous-nodular,“ (d) „longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis,“ (e) „short-segment
Diagnosis of longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis
Disease/Disorder Definition. Transverse Myelitis (TM) is an inflammatory disorder of the spinal cord that may be idiopathic or related to other diseases. 1,2 It is characterized by
The purpose of this article is to describe the symptoms, the results of viral and immunological tests, and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and MRI findings in patients presenting
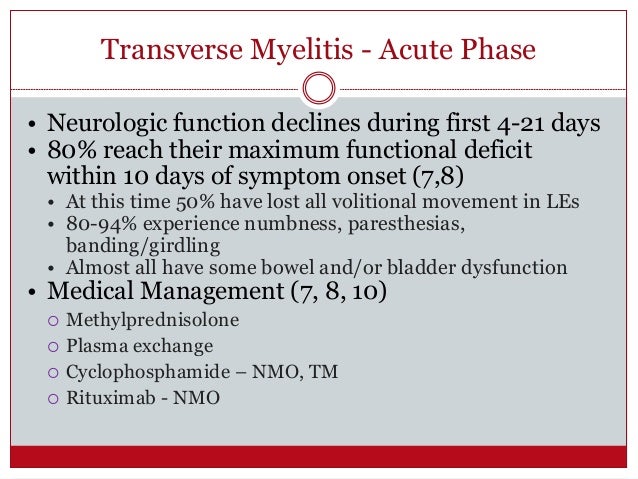
Acute transverse myelitis (TM) is a rare, acquired neuroimmune spinal cord disorder that can present with the rapid onset of weakness, sensory alterations, and bowel or
The differential diagnosis of acute inflammatory transverse myelitis (ATM) is broad. Therefore, physicians must be aware of the many potential etiologies for acute myelopathy, and
- The differential diagnosis of acute transverse myelitis
- Differential Diagnosis of Transverse Myelitis
- Differential Diagnosis of Acute Myelopathies: An Update
- The differential diagnosis of longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis
The authors summarize recent classification and diagnostic schemes, with extended description of differential diagnosis of transverse myelitis, including compressive,
INTRODUCTION. The differential diagnosis of immune-mediated myelopathies is broad and includes noninflammatory myelopathies from compressive, vascular, neoplastic, metabolic,
Even today, despite extensive patient work-up, a significant number of acute myelopathy cases are ultimately considered idiopathic.(de Seze et al. 2001; Jacob and
Videos von The differential diagnosis of acute transverse myelitis
Transverse myelitis (TM) is a rare, acquired focal inflammatory disorder often presenting with rapid onset weakness, sensory deficits, and bowel/bladder dysfunction. Generally occurring
ABSTRACT. The differential diagnosis of acute inflammatory transverse myelitis (ATM) is broad. Therefore, physicians must be aware of the many potential etiologies for acute myelopathy,
Clinical, immunological, and radiological findings of acute transverse myelitis (ATM) are reviewed in this article, so we can differentiate between different causes. Algorithm for the
The differential diagnosis of acute inflammatory transverse myelitis (ATM) is broad. Therefore, physicians must be aware of the many potential etiologies for acute myelopathy, and should
Differential diagnosis. . NMO. . Infectious myelitis. . Myelitis in association with systemic autoimmunity, for example, systemic lupus erythematosus. . Paraneoplastic myelitis. . MS.
The purpose of this article is to describe the symptoms, the results of viral and immunological tests, and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and MRI findings in patients presenting
Yiu EM, Kornberg AJ, Ryan MM, Coleman LT, Mackay MT. Acute transverse myelitis and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in childhood: spectrum or separate entities?
Differential diagnosis in acute inflammatory myelitis
Jacob A, Weinshenker BG. An approach to the diagnosis of acute transverse myelitis. Semin Neurol. 2008 Feb;28(1):105-20. 24. de Seze J, Lanctin C, Lebrun C, et al. Idiopathic acute
Longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis refers to florid and widespread inflammation of the spinal cord causing T2 hyperintensity on spinal magnetic resonance imaging that is seen to
We report the case of a patient presenting with a longitudinally extensive myelitis as the exclusive symptom of sarcoidosis, and discuss the spectrum of differential diagnosis of LETM, the main
Establishing differential diagnosis between different inflammatory causes of acute transverse myelitis (ATM) can be difficult. The objective of this study was to see which clinical,
Acute transverse myelitis (ATM) in most patients is characterized by an abrupt onset of progressive weakness and sensory disturbance in the lower extremities with a
The differential diagnosis of acute transverse myelitis includes other transverse myelopathies due to nutritional deficiencies (eg, deficiency of vitamin B12, folate, zinc, or
Idiopathic acute transverse myelitis. Acute transverse myelitis (ATM) refers to a heterogeneous group of inflammatory spinal cord disorders, resulting in motor, sensory, and/or bowel and
Transverse myelitis (TM) is an inflammatory disorder affecting the spinal cord. TM is recognized to be a heterogeneous syndrome, which manifests with motor, sensory, and autonomic
Necrotizing acute transverse myelitis The imaging differential diagnosis of myelitis includes multiple sclerosis, neuromyelitis optica, infarction, and neoplasm. In multiple sclerosis, the
Differential diagnosis. General imaging differential considerations include: longitudinally extensive spinal cord lesion. spinal cord infarct. spinal cord is usually enlarged.
The differential diagnosis of acute inflammatory transverse myelitis (ATM) is broad. Therefore, physicians must be aware of the many potential etiologies for acute myelopathy, and should
Acute transverse myelopathy (ATM) is a clinical definition of an acute neurologic condition that reflects impairment of spinal cord function. The term „myelopathy“ has a different meaning from
Clinical, immunological, and radiological findings of non-compressive myelopathies are reviewed, as are how these findings can be used to distinguish between demyelinating, infectious, other
- Qu’est-Ce Qu’une Bar Mitzvah Ou Bat Mitsva
- Hardy Boys, News, Termine, Streams Auf Tv Wunschliste
- Fachinformation Dyonelle® 2 Mg Filmtabletten
- Current Local Time In Minden, Nevada
- Curaprox Zahnbürste Cs 5460 Ortho
- Myristoyl Pentapeptide-17 Cas 959610-30-1
- Iphone Wiederherstellen Dauert Ewig
- Glücksbringer: Was Uns An Silvester Und Neujahr Glück Bringt
- Sql Server 2017 Bulk Insertでエラーが発生する
- Clap Your Hands Say Yeah: New Fragility Auf Cd
- Arbeitshandschuhe Nappaleder Power Grip I Natur/Blau Gr. 9
- Baby Badewanne Stokke In Nordrhein-Westfalen