Targeted Versus Universal Decolonization To Prevent Icu Infection
Di: Everly
The REDUCE MRSA Trial (Randomized Evaluation of Decolonization vs Universal Clearance to Eliminate Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus), a large multicenter,
Targeted versus Universal Decolonization to Prevent ICU Infection
In the intervention period versus the baseline period, modeled hazard ratios for MRSA clinical isolates were 0.92 for screening and isolation (crude rate, 3.2 vs. 3.4 isolates per 1000 days),

Huang SS, Septimus E, Kleinman K, Moody J, Hickok J, Avery TR, et al.; CDC Prevention Epicenters Program; AHRQ DECIDE Network and Healthcare-Associated
3 group trial: universal decolonization, targeted decolonization, routine care Universal decolonization the most effective Reduced all-cause MRSA by 37% Reduced bloodstream
- Universal ICU Decolonization: An Enhanced Protocol
- Decolonization in Prevention of Health Care-Associated Infections
- Targeted versus Universal Decolonization to Prevent ICU Infection
[9] [10] [11] [12] Recently, a multicenter study suggested the potential utility of universal antibiotic treatment of patients at admission without screening for specific carriage to
Fraser, Victoria J. and et al, „Targeted versus universal decolonization to prevent ICU infection.“ The New England Journal of Medicine. 368, 24. 2255-2265. (2013).
Universal decolonization resulted in a significantly greater reduction in the rate of all bloodstream infections than either targeted decolonization or screening and isolation. One
Both targeted decolonization and universal decolonization of patients in intensive care units (ICUs) are candidate strategies to prevent health care-associated infections,
Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature.
The mupirocin-based intervention was found to protect against infection (OR 0.3, 95% CI 0.1-0.8). In addition, Ziakas et al. also used Markov modeling to compare universal decolonization
MRSA colonization is frequent in ICUs and a predictor of ICU-acquired MRSA infection. A Septimus E, Kleinman K et al (2013) Targeted versus universal decolonization to
In routine ICU practice, universal decolonization was more effective than targeted decolonization or screening and isolation in reducing rates of MRSA clinical isolates and bloodstream infection
METHODS We conducted a pragmatic, cluster-randomized trial. Hospitals were randomly assigned to one of three strategies, with all adult ICUs in a given hospital assigned to the same
large-scale ICU trial to establish whether targeted decolonization of MRSA carriers versus universal decolonization of all ICU patients was the most effective intervention. The REDUCE
Universal ICU Decolonization: An Enhanced Protocol . This protocol was developed based on the REDUCE MRSA trial, which tested universal decolonization of intensive care unit (ICU)
- Decolonization strategies against multidrug resistant organisms in the ICU
- Targeted versus universal decolonization to prevent ICU infection
- Targeted versus Universal Decolonization to Prevent ICU InfectionTargeted versus universal decolonization to prevent ICU infection.
- Targeted versus universal decolonization to prevent ICU infection.
Targeted versus Universal Decolonization to Prevent ICU Infec – tion (June 13, 2013;368:2255-65). In the second paragraph of the Outcomes subsection of Results (page 2259), the end of
Europe PMC is an archive of life sciences journal literature.
Targeted versus universal screening and decolonization to reduce healthcare-associated such as enhanced hand hygiene and infection prevention and control. 3 In
Huang SS, Septimus E, Kleinman K et al (2013) Targeted versus universal decolonization to prevent ICU infection. N Engl J Med 368:2255–2265 7. Huang SS, Septimus EJ, Kleinman K et
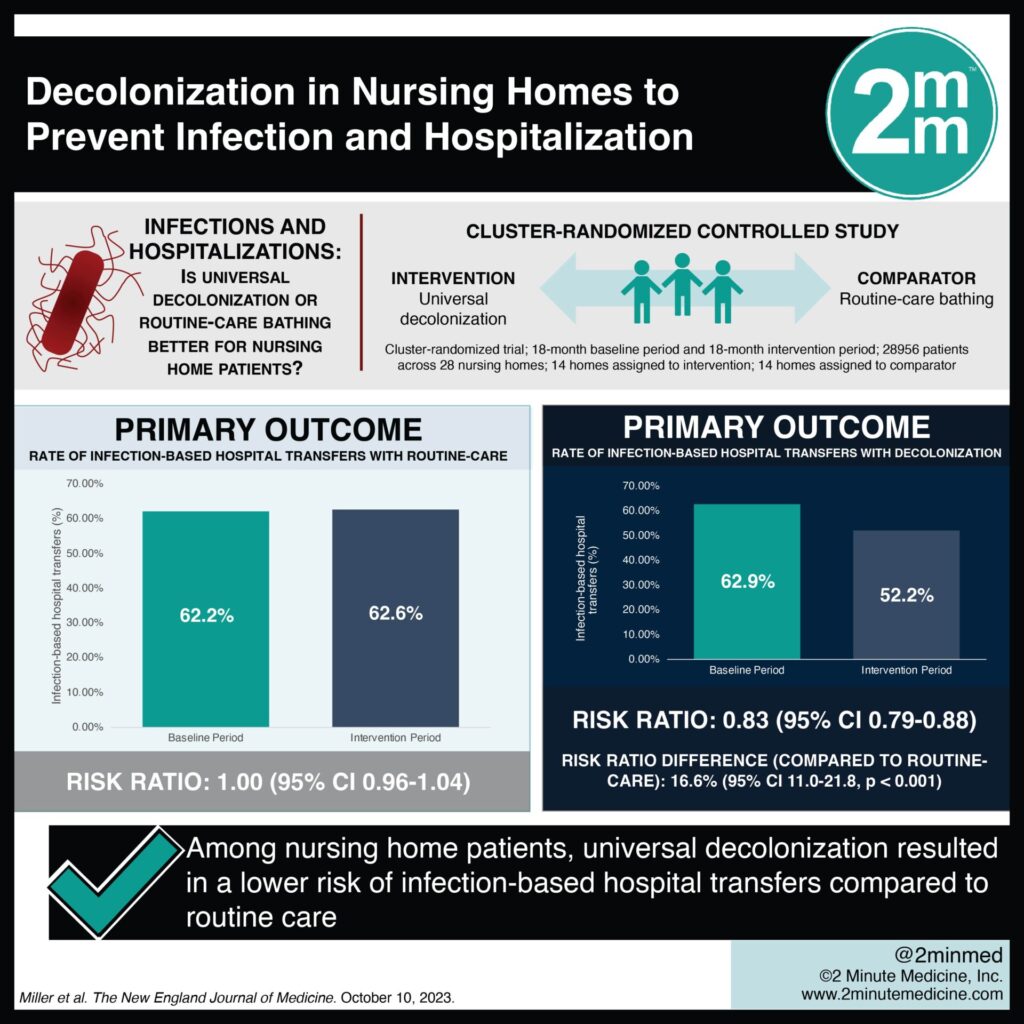
The only multicenter study that compared universal and targeted decolonization head-to-head found that in the ICU, universal decolonization was more successful than targeted
Both targeted decolonization and universal decolonization of patients in intensive care units (ICUs) are candidate strategies to prevent health care–associated infections,
Background: The benefits of universal meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) admission screening, compared with screening targeted patient groups and the additional
The REDUCE MRSA Trial (Randomized Evaluation of Decolonization vs Universal Clearance to Eliminate Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus), a large multicenter, randomized
To estimate and compare the impact on healthcare costs of 3 alternative strategies for reducing bloodstream infections in the intensive care unit (ICU): methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) nares screening and
Numerous strategies to reduce MRSA colonization and decrease invasive infections have been utilized in adult intensive care units (ICUs).
Targeted versus universal decolonization to prevent ICU infection. Huang SS et al. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2013 Jun 13; 368(24):2255-2265
4. Huang SS, Septimus E, Hayden MK, et al. Effect of body surface decolonization on bacteriuria and candiduria in intensive care units: an analysis of a cluster-randomized trial. Lancet Infect
In 2013, an 18-month trial on the effectiveness of universal vs. targeted decolonization ended. REDUCE MRSA, which stands for Randomized Evaluation of Decolonization vs. Universal
- Dsa Geburtstag Auswürfeln
- Umlaufmaß Der Wohnwagen – Zelt Umlaufmaß Tabelle
- Langues Et Usages Des Langues En France
- Unser Ziel: Eure Wahl Des Latein- Unterrichts!
- Quanto Ganha Um Auxiliar De Enfermagem Em Goiânia, Go
- Poolpumpe Und Sandfilteranlage Winterfest Machen
- Märkte Bodensee 2024 | Flohmarkt Bodensee 2023
- Quem Foi Traído Pode Se Casar De Novo Bíblia
- Где В Адлере Лучше Отдыхать? 2024
- Für Was Ist Bolivien Bekannt?: Bolivien Allgemeine Informationen
- Terra Extreme Vince Camuto Cologne
- Sharp Lc-32Che4042E Handbücher
- Pension Wiesenau Wetterau – Familienpension Wiesenau
- Nullstellen Der Exponentialfunktion Berechnen
- Burg Rheinfels Öffnungszeiten, Führungen, Eintrittspreise