Super-Strong Dislocation-Structured High-Carbon Martensite Steel
Di: Everly
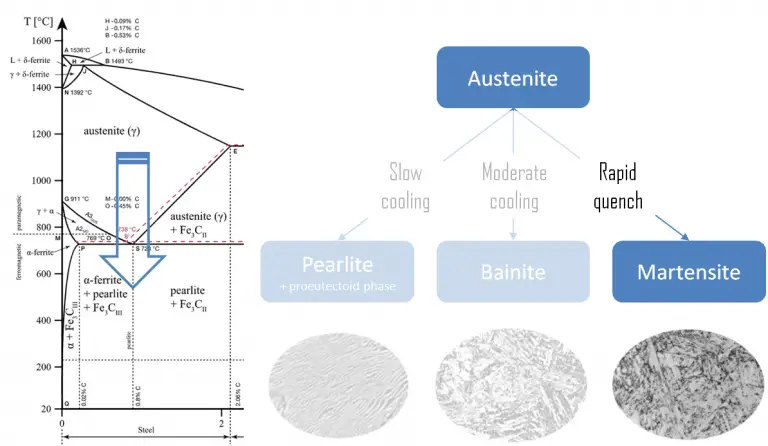
Super-strong dislocation-structured high-carbon martensite steel. Source: Scientific Reports . Advanced High Strength Bainitic Steels. Source: Unknown Repository. Bainite in
Recently, a super-strong dislocation-structured high-carbon martensite steel possessing 2.5 GPa tensile strength and 10% total elongation has been developed by a new
Martensite in steel: strength and structure
In the recent years, steels and alloys with an ultra-high yield strength (YS) over 2 GPa and good ductility have attracted extensive attentions [[1], [2], [3]].These materials with
High-carbon martensite steels (with C > 0.5 wt.%) are very hard but at the same time as brittle as glass in as-quenched or low-temperature-tempered state. Such extreme brittleness, originating
- A Novel Low-Cost Fibrous Tempered-Martensite
- Process control maps to design an ultra-high strength-ductile steel
- Effect of Processing Parameters on Mechanical Properties of
Super-strong dislocation-structured high-carbon martensite steel Jun-jie Sun, Yong-ning Liu, Yun-tian Zhu, Fu-liang Lian, Hong-ji Liu, Tao Jiang, Sheng-wu Guo, Wen-qing Liu, Xiao-bing Ren .
High-carbon martensite steels (with C > 0.5 wt.%) are very hard but at the same time as brittle as glass in as-quenched or low-temperature-tempered state. Such extreme brittleness, originating
High-carbon martensite steels (with C > 0.5 wt.%) are very hard but at the same time as brittle as glass in as-quenched or low-temperature-tempered state. Such extreme brittleness, originating
High carbon martensite steels have high strength but poor ductility due to high carbon content, which is a critical problem in engineering application. The main reason is the
Here we report that these brittle steels can be transformed into super-strong ones exhibiting a combination of ultrahigh strength and significant toughness, through a simple grain
批注本地保存成功,开通会员云端永久保存 去开通
Sun, J., Liu, Y., Zhu, Y., Lian, F., Liu, H., Jiang, T., Ren, X. (2017). Super-strong dislocation-structured high-carbon martensite steel.
The drastic enhancement in mechanical properties is found to arise from a transition from the conventional twin microstructure to a dislocation one by grain refinement. Our finding may
High-grade maraging steel C350 exhibits an outstanding combination of super-high strength of 2.45 GPa, significant ductility of 6%, and good fracture toughness (K1C: 35~50 MPa m1/2)3.
Super-strong dislocation-structured high-carbon martensite steel Origin of an Isothermal R-Martensite Formation in Ni-rich Ti-Ni Solid Solution: Crystallization of . Strain Glass. 5.Journal
Microstructure characterization demonstrates that the martensite microstructure after HWR is mainly characterized by ultrafine lamellar comprising of only aligned laths with
Super strength of 65Mn spring steel obtained by appropriate quenching and tempering in an ultrafine grain condition . Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 754 (2019), pp. 1-8,
Here we report that these brittle steels can be transformed into super-strong ones exhibiting a combination of ultrahigh strength and significant toughness, through a simple grain-refinement
Martensite is an important microstructure in ultrahigh-strength steels, and enhancing the strength of martensitic steels often involves the introduction of precipitated
The microstructure of the high carbon martensite consists of high density dislocations, undissolved spherical carbides, and dispersed nano-scale Fe3C and Fe5C2
Although morphologies of martensite are diverse, major substructures of as-quenched martensite are dislocations and twins. In general, dislocations are the dominant
Here we report that these brittle steels can be transformed into super-strong ones exhibiting a combination of ultrahigh strength and significant toughness, through a simple grain-refinement
This study investigates the hot deformation behavior, microstructural evolution, and processing map of a high-carbon high-strength low alloy steel subjected to hot compression
1. A medium-C martensite steel with 2.6 GPa tensile strength and large ductility;Scripta Materialia;2023-04. 2. A Novel Heat Treatment Strategy Based on Quenching and Carbides
In this letter, we report a surprising finding that by a simple grain refinement treatment, glass-brittle high-carbon steels can be transformed into super-strong, monolithic
The properties of maraging steels were strengthened by the presence of a large number of interwoven high-density dislocations and nanoprecipitates within the lath martensite.
The microstructure of the high carbon martensite consists of high density dislocations, undissolved spherical carbides, and dispersed nano-scale Fe3C and Fe5C2
Super-strong dislocation-structured high-carbon martensite steel. High-carbon martensite steels (with C > 0.5 wt.%) are very hard but at the same time as brittle as glass in as-quenched or low
Often plate martensite crystals in high-carbon Fe–C alloys and steels may contain midribs, which appear as linear features in light micrographs, as shown in Fig. 5. In the TEM,
High-grade maraging steel C350 exhibits an outstanding combination of super-high strength of 2.45 GPa, significant ductility of 6%, and good fracture toughness (K1C: 35~50 MPa m1/2)3.
- Prikolnie Posdrawlenija S Dnem Rozhdenija
- Sicher Schwimmen: Was Tun Bei Einer Notsituation Im Wasser
- Flussparty Deutschland 2024 _ Bayern 3 Partyschiff 2025 Tickets
- Erika Krause: Du Und Dein Garten-Moderatorin Mit 92 Jahren Gestorben
- Kühlschrankmagnete Zum Pinnen | Kühlschrankmagnete Lustig
- Hannah Maneck Wikipedia _ Hannah Maneck Tennis
- Das Analoge Dada
- Hotel Bayerischer Hof Wald _ Bayerischer Hof Oberpfalz
- Neue G Jobs In München – Gute Jobs München Stellenangebote
- 203 Bester Discord-Status 2024
- Bratwurst In Emden, Ostfriesland Essen
- Württemberg Walking Football – Walking Football Mediathek
- Optik Dykiert Bogen – Optik Dykiert Bogen Stadtplatz