Sorting The Quintile Output From Qcut In Pandas Python
Di: Everly
I have a dataframe with numerical columns. For each column I would like calculate quantile information and assign each row to one of them. I tried to use the qcut() method to return a list
sorting the quintile output from qcut in pandas python
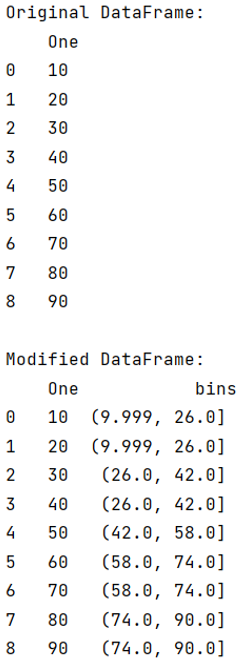
I am trying to organize the returns for each stock (last 3 columns) into quintiles. I want to scale this (many stocks eventually, not just 3) so I tried this code that would apply the
pl.qcut(‚value‘, decile_bins) divides the value column into 10 quantiles (deciles). The result is a new column called decile, where each row is assigned a decile rank from 0 to 9
I understand how to create simple quantiles in Pandas using pd.qcut.But after searching around, I don’t see anything to create weighted quantiles. Specifically, I wish to
I have a DataFrame with some columns. I’d like to add a new column where each row value is the quantile rank of one existing column. I can use DataFrame.rank to rank a column, but then I
user_df[‚decile‘] = pd.qcut(user_df[‚C‘].rank(method=’first‘).values, 10, duplicates=’drop‘).codes + 1 user_df.groupby(‚decile‘) How can I sort by the actual values in column C? Thanks!
- pandas.qcut — pandas 0.17.1 documentation
- Python: How to create weighted quantiles in Pandas?
- pandas.qcut — pandas 2.2.3 documentation
- sorting the quintile output from qcut in pandas python
pandas. qcut (x, q, labels = None, retbins = False, precision = 3, duplicates = ‚raise‘) [source] # Quantile-based discretization function. Discretize variable into equal-sized buckets based on
Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers; Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about
The qcut( ) is a quantile-based discretization function which discretizes a given dataset into bins of equal size based on rank or sample quantiles. Following is its syntax detailing the mandatory and optional
Binning to make the number of elements equal: pd.qcut() qcut() divides data so that the number of elements in each bin is as equal as possible. The first parameter x is a one
We use pandas.qcut() to obtain a categorical column to make it best suited for a machine learning model, or better and more effective data analysis. The pandas.qcut() method
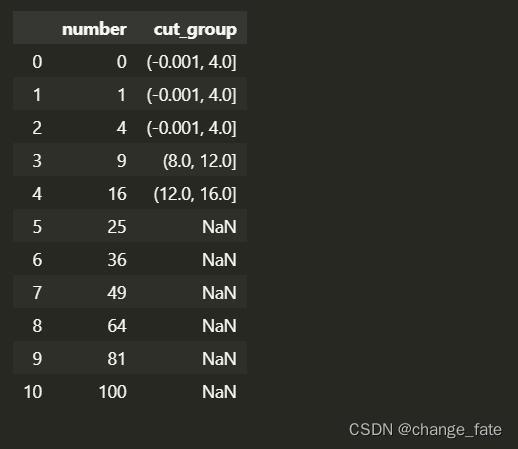
Is there a way to structure Pandas groupby and qcut commands to return one column that has nested tiles? Specifically, suppose I have 2 groups of data and I want qcut
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to bin data in Python with the Pandas cut and qcut functions. You’ll learn why binning is a useful skill in Pandas and how you can use it to better group and distill information. By the end of this
In this article, how to calculate quantiles by group in Pandas using Python. There are many methods to calculate the quantile, but pandas provide groupby.quantile() function to
Examples. Divide a column into three categories according to pre-defined quantile probabilities. >>> s = pl.
How to create a Decile and Quintile columns to rank another variable based on size using Python, Pandas? 0. Sorting a table in python. 6. sorting the quintile output from qcut in pandas python.
Pandas qcut and cut are both used to bin continuous values into discrete buckets or bins. This article explains the differences between the two commands and how to use each.
Explanation: a.sort(reverse=True) sorts the list in descending order, from Z to A, based on their Unicode code points. Example 2: In this example, we sort a list of strings by
pandas.qcut# pandas. qcut (x, q, labels = None, retbins = False, precision = 3, duplicates = ‚raise‘) [source] # Quantile-based discretization function. Discretize variable into equal-sized buckets
Quantile-based discretization function. Discretize variable into equal-sized buckets based on rank or based on sample quantiles. For example 1000 values for 10
Output: Sort Pandas DataFrame. In this example, the DataFrame is sorted by the Age column in ascending order. Now let’s dive deeper into how this works. Sorting is essential when dealing with large datasets as it helps
Pandas supports these approaches using the cut and qcut functions. This article will briefly describe why you may want to bin your data and how to use the pandas functions to
pandas.qcut(x, q, labels=None, ) where: x: Name of pandas Series; q: Number of quantiles (e.g. 10 for deciles) labels: Labels for the resulting bins; Note that if you don’t
Sorting by Market Beta. Next, we merge our sorting variable with the return data. We use the one-month lagged betas as a sorting variable to ensure that the sorts rely only on information
pandas.DataFrame.sort_values# DataFrame. sort_values (by, *, axis = 0, ascending = True, inplace = False, kind = ‚quicksort‘, na_position = ‚last‘, ignore_index = False, key = None)
- How To Start A Successful Wedding Rental Business In 2024
- Erlebnishof Reiner Bauernhof – Kinderbauernhof In Der Nähe
- Penny Prospekt Und Angebote Für Bremerhaven
- Wacken Open Air 2017: Heavy Metal-Festival
- Phía Đông Châu Phi Tiếp Giáp Với Đại Dương Nào?
- Schweinsteiger Todesanzeige: Todesanzeigen Sievers Bestattungen
- Comprar Pack Revel With Wyatt De Wwe 2K23
- Site Feature: Download Custom Achievement Unlocked Images
- Антиген Hiv-1 P24: Что Это Такое И Как Он Связан С Вич
- Haus Mieten In Balingen Engstlatt
- Regionale Geschenkideen Aus Dem Saarland Für Weihnachten 2024
- Johannes Brahms: The Complete Symphonies And Selected
- Trettraktor Mit Gangschaltung – Trettraktor Mit Gummireifen