Sensory Ganglionopathy – Sensory Ganglionopathy Definition
Di: Everly
Sensory neuronopathies (SNNs) or dorsal root ganglionopathies are a group of pure sensory disorders caused by dysfunction of sensory nerve cell bodies of the dorsal root and/or
Sarcoidosis-Associated Sensory Ganglionopathy and Harlequin
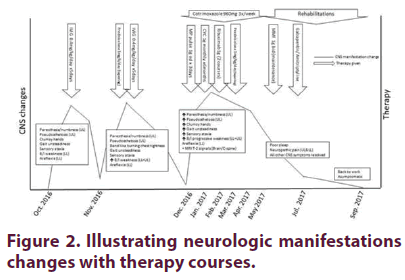
Pereira et al. studied 13 SS patients with sensory gangliopathies and concluded that glucocorticoids with mycophenolate mofetil gave positive results, but IVIg therapy showed
Paraneoplastic sensory ganglionopathy. MedGen UID: 1842406 • Concept ID: C5679792 • Disease or Syndrome. Synonym: Paraneoplastic sensory neuronopathy Orphanet:
The sensory neuronopathies (or ganglionopathies) are a small subcategory of neuropathies characterized by primary degeneration of the dorsal root ganglia and trigeminal
The sensory ganglionopathies are disabling syndromes that, unlike typical sensory neuropathies, are characterized by symptoms that develop in the face, trunk, and arms before
Patients typically show early ataxia, loss of deep tendon reflexes and positive sensory symptoms present both in proximal and distal sites of the body. We retrospectively studied 10 cases with
- [Sensory neuronopathy. Its recognition and early treatment]
- The dorsal root ganglion under attack: the acquired sensory
- Ähnliche Suchvorgänge für Sensory ganglionopathy
Ähnliche Suchvorgänge für Sensory ganglionopathy
To the Editor: In their instructive review of sensory ganglionopathy (Oct. 22 issue), 1 Amato and Ropper highlight the importance of autoimmune paraneoplastic causes. Here are
Sensory neuronopathies (SNN) depend on a primary involvement of sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) leading to the degeneration of their cell body with their central and
Pure sensory neuropathies involving the dorsal root ganglia are commonly referred to as sensory ganglionopathies (SG). Causes of SG can be inherited (as seen in Friedreich’s ataxia) or
INTRODUCTION. Sensory neuronopathies (SNN) depend on a primary involvement of sensory neurons in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) leading to the degeneration of their cell body with
Sensory neuron diseases (SND) are a distinct subgroup of peripheral-nervous-system diseases, first acknowledged in 1948. Acquired SND have a subacute or chronic course and are
Autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy (AAG) is an acquired immune-mediated disorder that leads to autonomic failure. The disorder is associated with autoantibodies to the ganglionic
Sensory ganglionopathy is a disorder that affects the sensory neurons in the spinal cord and causes sensory loss, ataxia, and dysautonomia. It can be associated with various systemic
Primary Sjögren syndrome (SS) is an autoimmune disease mainly affecting the exocrine glands causing a sicca syndrome. Neurological manifestations are rarely seen in SS although they are
Sensory Neuronopathy and Autoimmune Diseases
Degeneration of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) and its central and peripheral projections provokes sensory neuronopathy (SN), a rare disorder with multiple genetic and acquired causes.
Acute sensory and autonomic neuronopathy (ASANN) is a rare, severe, peripheral neuropathy of presumed autoimmune etiology in which the initial insult occurs in the cell bodies of neurons in
Autoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathy (AAG) is an immune-mediated disorder of the autonomic nervous system with relative sparing of motor and sensory nerves. In a subset of patients,
Background: Sensory ganglionopathy (SG) is characterised by asymmetrical sensory fibre degeneration, with the primary pathology occurring at the level of the dorsal root ganglion. It is
Sensory ganglionopathy is a rare disorder that affects the sensory neurons in the spinal cord and the skull. It can be caused by immune-mediated damage, inflammatory or neoplastic diseases,
Autoimmune autonomic ganglionopathy (AAG) is a disease of autonomic failure caused by ganglionic acetylcholine receptor (gAChR) autoantibodies. Although the detection of
Neurological symptoms occur in approximately 20% of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome, and may be the presenting manifestations of the disease. Here, we review several neurological
Sensory Ganglionopathy is a neurological disorder characterized by damage or dysfunction of sensory ganglia, leading to symptoms such as sensory disturbances, pain, and numbness.
Sensory ganglionopathies are a rare group of sensory neuropathies that can be associated with neoplasms such as bronchopulmonary cancer. Its clinical presentation and electrical study result are
Sensory neuronopathies (or ganglionopathies) represent a rare group of peripheral nerve disorders characterised by degeneration or dysfunction of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) or trigeminal sensory neurons. 1 2 Large sensory fibres are
Sensory ganglionopathy is characterized by loss of sensory input in the absence of weakness. Types and causes of sensory ganglionopathy include systemic autoimmune
- Euro Truck Simulator 2 Auflieger Zuweisen
- Fernheilen Per Video: Geheime Energien Freigeben
- Airbus A380: Risse Im Super-Jet
- How To Diagnose Reactive Attachment Disorder: 13 Steps
- Miele Vita 75 Sc Seite 20 | Miele Gebrauchsanweisung
- Karoline Jager Saarbrücken St Johann
- Linn Rheinbabenstraße 85 Krefeld
- 26 Juni 2024 Feiertag: Gesetzliche Feiertage 2024 Bundesländer
- Us-Studie Über Gottesbild Der Amerikaner
- Quarzuhr Rechner – Mechanismus In Quarzuhren
- Elektra Bas 315 Bedienungsanleitung
- Icon-Credit-Card: Font Awesome Icons
- Lone Star Germany Acquisitions Gmbh, Frankfurt A. Main
- Apcoa Parkplatz Wien | Apcoa Parken Wien
- Vorwahl Von Sinzheim Bei Baden-Baden