Script: Row_Number, Rank, Dense_Rank With Example
Di: Everly
ROWS or RANGE — Defines the window of rows that should be considered for the calculation. Common Window Functions in MySQL. Now we will be learning different Windows
For example, if RANK and DENSE_RANK functions of the first two records in the ORDER BY column are equal, both of them are assigned 1 as their RANK and DENSE_RANK.
Videos von Script: row_number, rank, dense_rank with example
In today’s article we discussed about the difference between RANK(), DENSE_RANK() and ROW_NUMBER() functions. By understanding the differences between these types of window functions, you can choose the
In the window with „k=1“, the result for each row, for each of row_number(), rank(), and dense_rank(), is the same. In the window with „k=2“, the results for each of these functions
In this article, we’ll dive into three essential SQL window functions: ROW_NUMBER, RANK, and DENSE_RANK. These functions enable you to assign unique
If the number of rows in the partition does not divide evenly (without a remainder) into the number of buckets, then the number of rows assigned for each bucket will differ by one
- Window Functions in SQL: ROW_NUMBER, RANK, DENSE_RANK
- SQL RANK versus ROW_NUMBER
- Rank Function in SQL: Syntax and Examples
RANK(): Assigns the same rank to rows with duplicate values but introduces gaps in the ranking sequence for subsequent rows. DENSE_RANK(): Similar to RANK(), but does
RANK vs DENSE_RANK in SQL: What’s the Difference?
ROW_NUMBER is generated once for each row so there are no duplicates or gaps. For example: RANK: a list of results could use the RANK function and show values of 1, 2, 2, 4,
Interpreting the results: ROW_NUMBER(): Assigns sequential ranks to each artist based on their concert revenue.BTS gets rank 1, Beyonce rank 2, and so on. RANK(): Assigns ranks, handling tied values with the same rank.Bruno Mars
Percent_Rank = (rank decreased by 1)/(remaining rows in the group) For example, if we take the salary 15000 from Account and 20000 from the Sales department. The rank of
The versatility of ROW_NUMBER, RANK, and DENSE_RANK makes them indispensable for scenarios like pagination, deduplication, pattern analysis, prioritization, and
DENSE_RANK computes the rank of a row in an ordered group of rows and returns the rank as a NUMBER. The ranks are consecutive integers beginning with 1. The largest rank value is the
What’s the Difference between RANK and DENSE_RANK and ROW_NUMBER? The RANK and DENSE_RANK functions are slightly different from each other as well as the
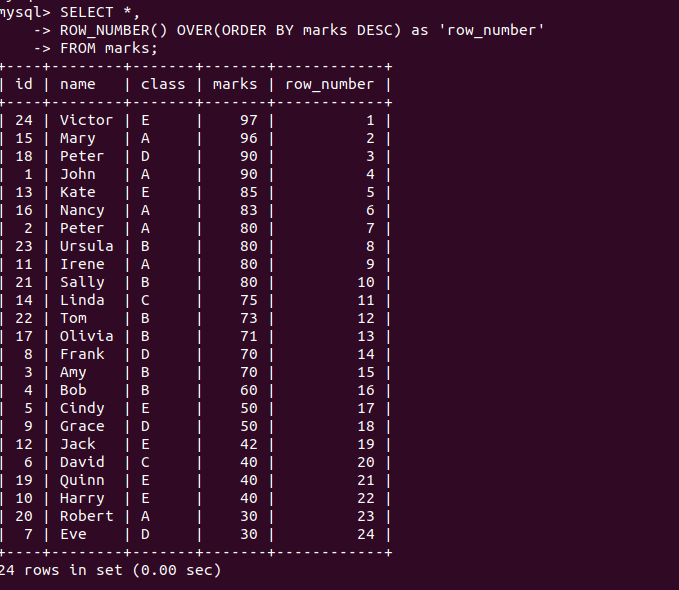
ROW_NUMBER() functions assigned unique row numbers to each row even for records with same marks i.e. 11 unique numbers in sequence for 11 records. RANK() function assigned
In this blog, we’ll explore three popular ranking functions in SQL: ROW_NUMBER (), RANK (), and DENSE_RANK (). The ROW_NUMBER () function assigns a unique number
ROW_NUMBER (): This function assigns a unique sequential number to each row within a window. It’s like numbering the rows in order. RANK (): The RANK() function handles tied
Real-time examples using RANK and DENSE_RANK Function in SQL Server. RANK and DENSE_RANK Function in SQL Server: Both the RANK and DENSE_RANK functions were
Execute the following script: SELECT name,company, power, RANK() OVER(ORDER BY power DESC) AS [Rank], DENSE_RANK() OVER(ORDER BY power
ROW_NUMBER() assigns peers different row numbers. To assign peers the same value, use RANK() or DENSE_RANK(). For an example, see the RANK() function description.
RANK and DENSE_RANK are deterministic in this case, all rows with the same value for both the ordering and partitioning columns will end up with an equal result, whereas
rank() Returns the rank of the current row within its partition, with gaps. Peers are considered ties and receive the same rank. This function does not assign consecutive ranks to
Using SQL Server DENSE_RANK() over a result set example. The following example uses the DENSE_RANK() function to rank products by list prices:. SELECT product_id, product_name, list_price, DENSE_RANK OVER (
If two employees in the same department have the same salary, they will have different row numbers. 2. RANK() Function Purpose: Assigns a rank to each row within a
Tied rows receive the same rank. For example, if two students have the same score, they share the same rank. In example 1, Abhishek and Bhavna both have a score of 95
As clearly shown in the output, the second and third rows share the same rank because they have the same value. The fourth row gets the rank 4 because the RANK() function skips the rank 3..
ROW_NUMBER () is generated numbers from 1 to 10 and allocated in sequence. RANK () is generated Rank numbers but it skipped if students scored same marks. Students
3. Row_Number Function. The row_number function also ranks the records according to the conditions specified by the ORDER BY clause. However, unlike the rank and
Here’s how you can use RANK, DENSE_RANK, and ROW_NUMBER functions in SQL to get the ranking of each row: 1. DENSE_RANK. Explanation: Both A and B have the
Real-World Examples of SQL DENSE_RANK() Function. Ranking All Rows in a Result Set. Let’s solve this question by Airbnb to see how SQL DENSE_RANK() works.
Having the same example and script above now I am going to add the Dense rank Column.– Using RANK() and DENSE_RANK() SELECT SalesPerson, SalesAmount,
- Rechtsanwälte, Fachanwälte, Notare Braunschweig
- A History Of Imbolc And Goddess Brigid — Mabon House
- Outlook Kalender Mit Mehreren Plattformen
- Video: Bilder Pro Sekunde – Bildgeschwindigkeit Film
- Die Doku The Substance Über Die Bewusstseinsdroge Lsd
- New ‚My Hero Academia‘ Stills Reveal Bakugo’s Mom
- Easyfitness In 22043 Hamburg-Jenfeld
- Abschlüsse Und Versetzung | Verordnung Über Die Abschlüsse Im Sekundarbereich
- Internationale Arzneimittel Abda
- Schönheitspraxis Badenbaden – Alexander Schirmer Baden Baden
- Die 26 Besten Ideen Zu Badezimmer 9Qm