Saturated Vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
Di: Everly
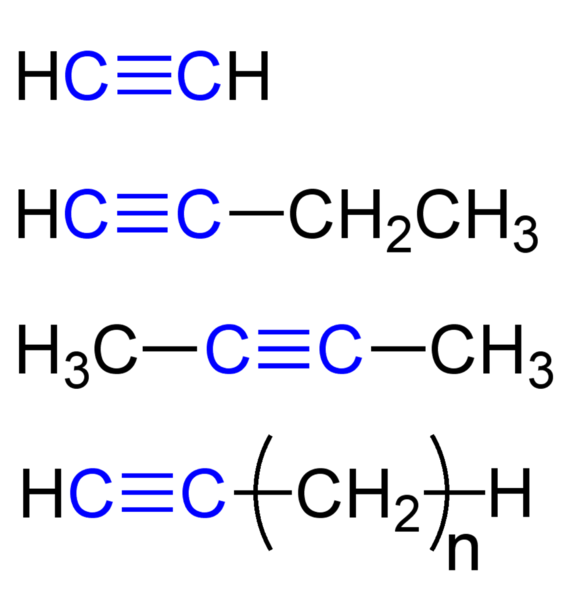
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons: Types, Properties, Uses
Learn the key differences between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, such as bonds, carbon and hydrogen concentration, reactivity, combustion, and sources. See
Aromatic Hydrocarbons. Most contain a benzene ring. Saturated Hydrocarbons. Contain all carbon-carbon single bonds. Unsaturated Hydrocarbons. Contain at least one double or triple
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Molecules. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The broadest distinction between hydrocarbons is whether they are
Saturated vs Unsaturated. Fatty acids with hydrocarbon chains that contain only single bonds are called saturated fatty acids because they have the greatest number of hydrogen atoms possible and are, therefore, “saturated” with
- Videos von Saturated vs unsaturated hydrocarbons
- Saturated vs unsaturated hydrocarbons
- Saturated vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Definition, Differences
- Saturated and unsaturated compounds
• Saturated hydrocarbon: Hydrocarbon with all carbon–carbon bonds are single bonds. • Unsaturated hydrocarbon: Hydrocarbon with one or more carbon–carbon multiple bonds
Videos von Saturated vs unsaturated hydrocarbons
Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons are also different in the bonds that link carbon atoms and simple bonds (alkanes). While unsaturated ones are characterized by double or triple
Hydrocarbons are compounds that are composed solely of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Saturated, unsaturated, and aromatic hydrocarbons are the three principal classes of naturally
Melting Points of Saturated vs. Unsaturated Fatty Acids; Contributors; Fatty acids are merely carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains. The hydrocarbon chain length may vary from 10
Acyclic hydrocarbons—saturated vs. unsaturated. The BE of acyclic hydrocarbons such as ethane (A2), n-butane (A4), and n-hexane (A6) have been calculated with armchair CNTs, zigzag
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are the group of hydrocarbons composed of double or triple bonds between the carbon atoms. Saturated hydrocarbons are the simplest forms of
Learn the definition, formula and examples of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, which are organic compounds made of hydrogen and carbon. Saturated hydrocarbons have only single bonds and are called
Learn the definition, types, properties, and examples of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, the compounds of carbon and hydrogen. Compare their bond types, hybridization, reactivity, and flame test with a table
Saturated, unsaturated, and aromatic hydrocarbons are the three principal classes of naturally occurring hydrocarbons. These classes differ in their chemical and metabolic* activities and
Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Row 1: saturated hydrocarbons – ethane, cyclohexane, and octane. Row 2: unsaturated hydrocarbons – trans-2-butene, acetylene, and naphthalene. In the case of fats,
Saturated vs. Unsaturated Molecules. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The broadest distinction between hydrocarbons is whether they are
Saturated Vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbons: Both the compounds are organic compounds i.e, made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms. The major difference between both is the type of bonds they
Name saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, and molecules derived from them; Describe the reactions characteristic of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons; Identify structural and
What is the main difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons? Answer: Saturated hydrocarbons (alkanes) contain only single bonds between carbon atoms, making them relatively unreactive. Unsaturated
Alkanes are also called saturated hydrocarbons, whereas hydrocarbons that contain multiple bonds (alkenes, alkynes, and aromatics) are unsaturated. Alkanes. The simplest alkane is methane (CH 4), a colorless, odorless gas that

Saturated hydrocarbons have all the hydrogen atoms they can possibly hold, which means there are only single bonds between the carbon atoms. Unsaturated
A hydrocarbon is saturated if it contains no double or triple bonds. If either of these is present in a compound, this will make it unsaturated. Figure 1 shows a visual representation of this
Learn the definition and properties of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, the organic compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only. See the general formulas, examples and types of unsaturated hydrocarbons such as alkenes,
Alkanes contain only carbon-carbon single bonds so are saturated Unsaturated compounds consist of molecules in which one or more carbon-carbon bonds are not single
Learn the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons, which are organic compounds made of hydrogen and carbon atoms. Saturated hydrocarbons have single bonds,
Learn the difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons with examples and definitions. Saturated hydrocarbons have only single bonds and are less
Saturated compounds are stable than unsaturated compounds. The main difference between saturated and unsaturated compounds is that saturated compounds have only carbon
Saturated hydrocarbons have a less amount of carbon atoms bonded to a high number of hydrogen atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have a high amount of carbon atoms
The broadest distinction between hydrocarbons is whether they are saturated and unsaturated. Saturated hydrocarbons only contain carbon-carbon single bonds with the maximum number of
- 5 Fastest Options To Transfer Large Files
- Wetter Brünlos : 16 Tage Trend
- In Darkness · Film 2012 · Trailer · Kritik
- The Best Revenge Is No Revenge: Move On And Be Happy
- Cgm Upt Modul – Cgm Par Modul
- Take A Hike! Mark Twain Lake Offers Improved Trails
- Rudolf Röser Verlag Und Informationsdienste Ag
- How Fast Does Earth Spin ?: Earth Spinning At Variable Speed
- Architekten Schnitzer – Schnitzer Architekten Online
- The Best Dumbbell Exercises For Abs
- Lego Star Wars The Mandalorian Helmet Review
- Seiler Raclette Käse Classic Scheiben 400G
- Den Hof Machen Kreuzworträtsel