Risk Weight Measures | Minimum Value Of Risk Weight
Di: Everly
Learn effective strategies for managing risk-weighted assets to enhance financial stability and meet regulatory requirements. Effective management of risk-weighted assets
EVALUATING DIFFERENCES IN BANKS’ CREDIT RISK WEIGHTS
Risk-weighted assets (RWAs) are central to the banking industry’s approach to managing financial stability.By assigning different risk weights to various asset classes, banks
This paper purely focuses on explaining the Basel II risk weight formulas in a non-technical way by describing the economic foundations as well as the underlying mathematical model and its
This chapter presents the calculation of risk weighted assets under the internal ratings-based (IRB) approach for: (i) corporate, sovereign and bank exposures; and (ii) retail
way leads to risk-weighted assets (RWA). This categorisation is applied to measure default risk, with assets being ranked in four risk weight buckets (0%, 20%, 50% and 100%) according to
In addition, risk weights are flawed measures of bank risks cross-sectionally as banks game their risk-weighted assets (cherry-pick on risky but low risk-weight assets) to meet
- BIPRU 4.7 The IRB approach: Equity exposures
- PRUDENTIAL PRACTICE PRUDENTIAL GUIDE PRACTICE GUIDE
- Basel Committee on Banking Supervision Consultative Document
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision Consultative Document
These risk measures are converted into risk weights and regulatory capital requirements by means of risk weight formulas specified by the Basel Committee.
RISK-WEIGHTED ASSETS.. 5 Standardized Approach .. 5 HVCRE Loans .. 5 Past-Due Asset Risk-Weights measure of assurance to the public that an institution will continue to
This box discusses how changes in risk weights affect key reporting such as solvency ratios and illustrates variations in risk weights across euro area LCBGs by utilising publicly available Pillar
Risk weights for retail exposures are based on separate assessments of PD and LGD as inputs to the risk-weight functions. None of the three retail risk-weight functions contain
Risk weighting involves comparing estimated levels of risk to assessment criteria, in order to identify the most significant risks, or to exclude minor risks from further analysis. The
In fact, the weighted risk R w = −2 × 10 6 € per year is the highest in comparison with the weighted risk of other measures. Banning the transport of LPG through infrastructure
HEDIS AT-A-GLANCE GUIDE Star Measures
Risk weights enjoy a less-than-stellar reputation. As part of the denominator of banks‘ capital ratios, they play a central role in the determination of whether banks are adequately capitalized
Body mass index (BMI) is the most widely used measure of excess body weight and obesity, and an increased BMI is associated with increased CVD risk [3, 4, 8, 9]. However,
Risk-Weighted Assets (RWAs) are an essential component of bank capital adequacy.It is an approach used to measure the credit risk of an institution’s assets by
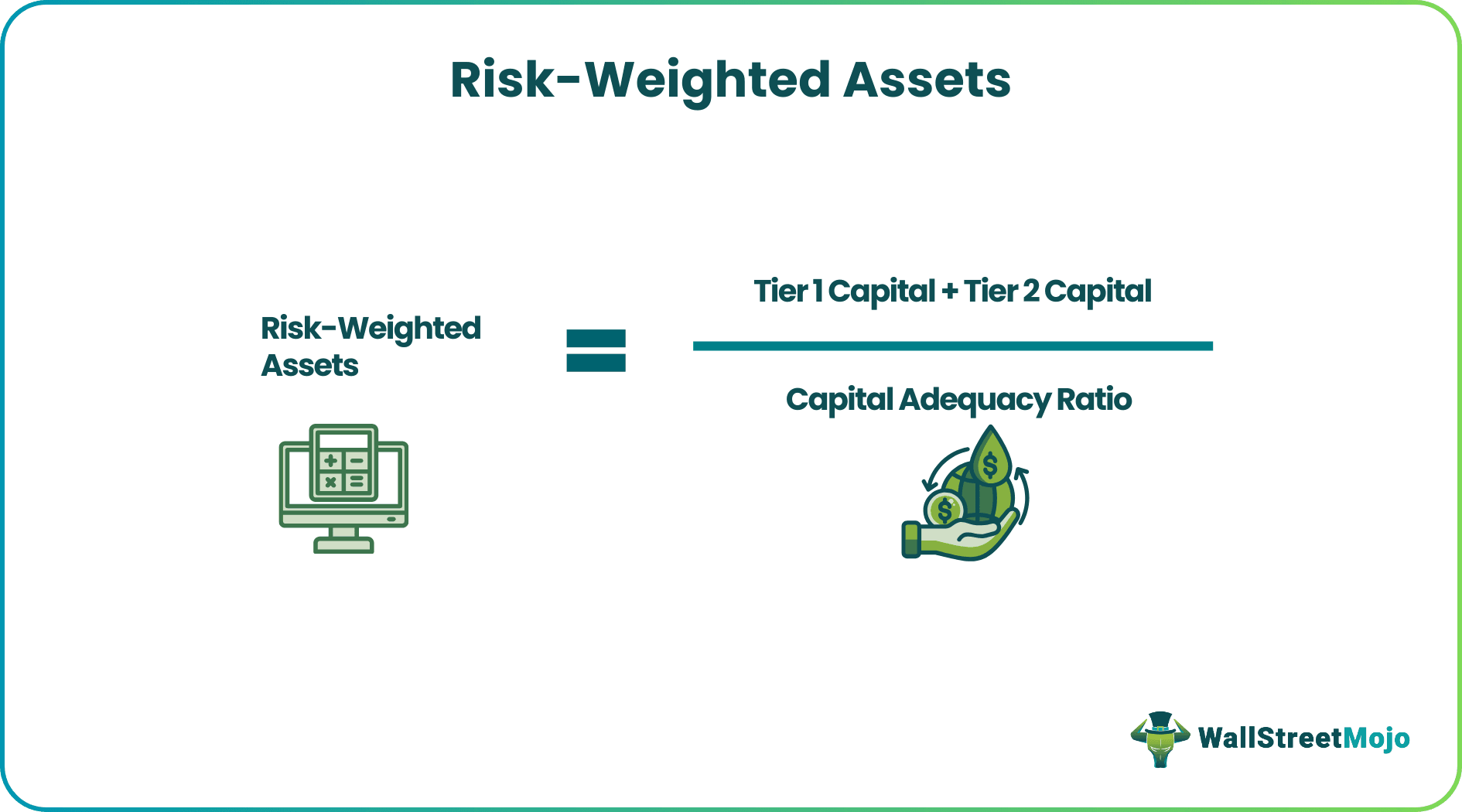
The risk weights are the percentage factors that adjust the credit risks of different loan types and other assets of a bank to reflect the level of risk/loss to the bank. Basel
The Capital Adequacy Ratio is calculated by dividing a bank’s total capital by its risk-weighted assets. Currently, the minimum required ratio of capital to risk-weighted assets is
The RBI reduced the risk weight requirement for banks on consumer microfinance loans by 25 percentage points, bringing down to 100%. “In terms of circular ‘Regulatory
Reducing the Risk of Falling – HOS Fall Risk Management (FRM) – HEDIS . Star Weight 1 ; The percentage of plan members 65 years of age and older with a problem falling, walking, or
The weighted risk analysis
In this measure the investor needs to define the weighting function of the quantiles of the loss distribution, which weights losses according to their individual risk aversion characteristics. It

RWAs have at least three important microprudential and macroprudential functions regarding credit, market, and operational risks faced by banks.
3. Risk-Weighted Assets Formula. Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA) formula is a crucial measure for calculating the capital adequacy of a financial institution. This formula determines
Risk-weighted asset (also known as RWA) is a measure used by banks and financial institutions to determine how much capital should be left aside based on the risk of the acquired or current assets. The capital is used to cover any
The goals of the original risk weight measure in 2017 were twofold: to ensure resilience and a sufficient level of capital for banks heavily exposed to foreign currency lending, and to provide
The key macroprudential capital tools in Europe for addressing financial stability risks from RRE markets are the countercyclical capital buffer (CCyB) , the sectoral systemic risk buffer
Under the simple risk weight method, a 300% risk weight is to be applied to equity holdings that are publicly traded and a 400% risk weight is to be applied to all other equity
The Basel Framework is the full set of standards of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS), which is the primary global standard setter for the prudential
Basel members therefore reserve the right to adopt standards which are more stringent than those required by the framework (“gold-plating”) and to implement the measures more quickly.
We use it to arrive at a measure that is not affected by differences in jurisdictional definitions of capital, the ways in which financial institutions define and calculate capital, and the methods
Risk weights in banking refer to the assigned measure of risk associated with various assets held by banks. These weights are used in the calculation of regulatory capital
- Endgame And Higher Difficulty Levels In Borderlands 3
- Parkschwimmbad Lörrach Geöffnet
- The Seven Sacred Flames
- Effective And Efficient – Effizient Synonyme
- Die 5 Schönsten Wanderungen Rund Um Dietramszell
- 5Th-Avenue *Sale* Slipper Günstig Kaufen ️
- Kleinunternehmer Quittungsblock
- How To Correct Indentation In Intellij
- Irobot Roomba I3 – Irobot Roomba I3 Ersatzteile
- Danko Jones Tour Dates 2024 _ Danko Jones Official Site
- Mark Adam Sandalen Neu 37 Rose In Köln
- Beantragen Von Pflegeleistungen
- Demystifying Phone Number Format In Mexico: A Comprehensive Guide
- 10 Best Steering Wheel Covers 2024