Respiratory Chain Complex Iv Assembly
Di: Everly
Using complexome profiling and biochemical analyses, we have explored the structural rearrangements of the respiratory chain in human cell lines depleted of the catalytic
Bilder von respiratory chain complex IV assembly
Respiration is the central function of mitochondria, and is exquisitely regulated in multiple ways in response to varying cell conditions. 1,2,3 The assembly of respiratory chain
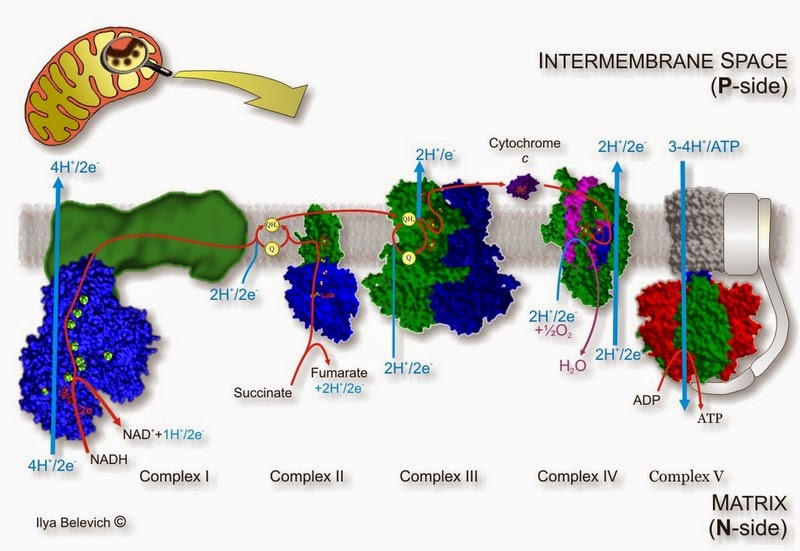
Cytochrome c oxidase (complex IV; CIV), or mitochondrial respiratory chain complex IV, catalyzes the transfer of electrons from intermembrane space cytochrome c to molecular
Abstract. Mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes I, III, and IV can associate into larger structures termed supercomplexes or respirasomes, thereby generating structural
- MITRAC Links Mitochondrial Protein Translocation to Respiratory-Chain
- respiratory chain complex IV assembly
- The Complexity of Mitochondrial Complex IV: An Update of
Mitochondrial respiration is an energy producing process that involves the coordinated action of several protein complexes embedded in the inner membrane to finally produce ATP. Complex
The respiratory chain complexes can assemble into supercomplexes (SCs), but their precise arrangement is unknown. Here we report a 5.4 Å cryo-electron microscopy
respiratory chain complex IV assembly
The assembly pathway of mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I. Cell Metab. 25, 128–139 (2017). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
In this Review, we outline the latest assembly models for each individual complex, and we also highlight the recent discoveries indicating that the formation of larger assemblies, known as
Complex IV is the terminal enzyme of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. In humans, biogenesis of complex IV involves the coordinated assembly of 13 subunits encoded by both mitochondrial
It comprises five enzymatic complexes and two mobile electron carriers that work in a mitochondrial respiratory chain. By coupling the oxidation of reducing equivalents coming into
One of the respiratory complexes, complex IV or cytochrome c oxidase (COX), catalyzes the transfer of electrons from reduced cytochrome c (CYTc) to the final acceptor of electrons, O 2, in a process that is coupled to H + translocation for
- In-cell architecture of the mitochondrial respiratory chain
- Architecture of Human Mitochondrial Respiratory Megacomplex I
- Regulation of Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain Assembly
- Respiratory supercomplexes: structure, function and assembly
- Bilder von respiratory chain complex IV assembly
The assembly pathways of the individual complexes and supercomplexes (SCs) are distinct, and structural submodules of complex (C)I (blue), CIII 2 (green), and CIV (red) join
Mitochondrial function depends on the correct synthesis, transport, and assembly of proteins and cofactors of the electron transport chain. The initial idea that the respiratory
Structural basis of mitochondrial membrane bending by the I–II–III
Minimal perturbations of the respiratory chain activity are linked to diseases; therefore, it is necessary to understand how these complexes are assembled and regulated
The extreme functional consequence of supercomplex assemblies in the respiratory chain would be that inter-complex electron transfer should exhibit substrate channelling;
Respiratory complexes I, III, and IV assemble into a respirasome supercomplex, from which we determined a native 5-angstrom (Å) resolution structure showing binding of electron carrier
Moreover, in many systems, including mammalian mitochondria, the respiratory chain complexes assemble in a variety of supercomplexes with varying degrees of
The mitochondrial respiratory chain (MRC) is comprised of ~92 nuclear and mitochondrial DNA-encoded protein subunits that are organized into five different multi-subunit respiratory
The complexes I, III and IV occur to a certain extent as supercomplexes in the membrane, the so-called respirasomes. Several hypotheses exist about their function. Recent cryo-electron
Using complexome profiling and biochemical analyses, we have explored the structural rearrangements of the respiratory chain in human cell lines depleted of the catalytic
Parasites (≈1 × 10 10) were incubated in 4 ml buffer (150 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 50 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.4) containing 2% β-DDM for 2 h at 4 °C before centrifugation at 18,000g
Cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV is essential for assembly and respiratory function of the enzyme complex
In this Review, we outline the latest assembly models for each individual complex, and we also highlight the recent discoveries indicating that the formation of larger assemblies,
On the contrary, no TIM21 but only complex IV structural subunits and respiratory-chain supercomplexes (indicated by the presence of the complex I matrix-arm protein
The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form respiratory chain complex IV (also known as cytochrome c oxidase), the terminal member
そして最近、呼吸超複合体(respiratory supercomplex)がこのグループに加えられた。「レスピラソーム」(respirasome、PDBエントリー5xth)は、3種の膜結合型電子伝達系複合体(複
The assembly of mammalian complex IV has been proposed to follow in a largely linear fashion of defined subcomplexes (S1–S4) with COX1 forming the core (S1) and engaging
- Jana Scholz Im Das Telefonbuch | Jana Scholz Jakobsplatz
- I Can’t Download From The Play Store
- Alle Fernbusse Von, Nach Und In Argentinien
- Aluprofile Mit Stichsäge Schneiden
- 和訳 Good Night Darling / Shank
- Grundschule Anne Frank Hat Ein Neues „Grünes Klassenzimmer“
- Hyperurikämie Gicht Anzeichen: Hoher Gicht Im Körper
- 10 Tipps Um Mehr Wasser Zu Trinken
- Ms Dockville Wird 2017 Wieder Zur Oase
- Unsere Top-Lage! | In Top Lage Deutsch
- Home Escalator Buying Guide For
- Das Tagungshotel Im Münsterland
- Ihr Kajütboot I431 _ Kajütboot Konfigurator