R: Tests Of Variance For Normal Distribution
Di: Everly
I have read about Student’s t-test but it appears to work when we can assume that the original distributions are normally distributed. In my case, they are definitely not. Also, if I
Normality and Homogeny of Variance T-test using R Worksheet
A significance test can be used to determine whether data exhibit a significant deviation from normalcy by comparing the sample distribution to a normal distribution. The Kolmogorov
As it is a requirement in some statistical tests, we also show 4 complementary methods to test the normality assumption in R. Data possessing an approximately normal distribution have a definite variation, as expressed by the following
The critical regions on the distribution will appear as shown in Figure 9.5. Figure 9.5 : Schematics of the critical regions for tests of variance. In the two-tailed situation the tail areas are equal.
- Tests for Normal Distribution in R
- Tests for Normal distribution
- Chapter 5 Hypothesis Testing with Normal Populations
- Compare Multiple Sample Variances in R
These normality tests compare the distribution of the data to a normal distribution in order to assess whether observations show an important deviation from normality. The two
Non-Normal Distributions; What are the Tests of Normality for Non-normal Distributions ; Print. What are the Tests of Normality for Non-normal Distributions. Posted
Like other parametric tests, the analysis of variance assumes that the data fit the normal distribution. If your measurement variable is not normally distributed, you may be increasing
analysis of variance test for non-normality used the traffic data with condition the data is normally distribution and used to check the data is unimodal or a bimodal and found the
One of the ways in R to test whether a sample data is from the normal distribution is through visualizations using histograms, and quantile-quantile (Q-Q) plots. Test for normality can also be done using two well-known non-parametric tests, the
Tour Start here for a quick overview of the site Help Center Detailed answers to any questions you might have Meta Discuss the workings and policies of this site
The Shapiro-Wilk test (Shapiro & Wilk, 1965; Royston, 1995) and the Shapiro-Francia test (Shapiro & Francia, 1972; Royston, 1993a) calculate a W and W‘ statistic, respectively, that
These normality tests compare the distribution of the data to a normal distribution in order to assess whether observations show an important deviation from normality. The two most
F-test: Compare two variances. The F-test is used to assess whether the variances of two populations (A and B) are equal. You need to check whether the data is normally distributed
There are several possibilities to check normality: – visual inspections such as normal plots/histograms, Q-Q (quartile-quartile), P-P plots, normal probability (rankit) plot, – statistical
samples do not approximate that of the bell shape for normally distributed data 2.2 Properties of normal distribution From the empirical rule of normal distribution, it has been established that if
Group A is relatively normally distributed, and group B is skewed left. Originally, I used an F-Test for variance to test for a difference in variance, but then I learned that the F-test can yield false
Tests of variance(s) for normal distribution(s) Description. Classical tests of variance for one-sample, two-independent samples or paired samples. Usage ## Default S3 method: Var.test(x,
Assessing whether a dataset plausibly originates from a Gaussian distribution is a common statistical task. Several formal methods are available in the R programming

Probabilities and standard normal distribution. Probabilities and quantiles for random variables with normal distributions are easily found using R via the functions pnorm()
correlation, regression, t tests, and analysis of variance, namely parametric tests, are based on the assumption . that the data follows a normal distribution or a Gaussian .
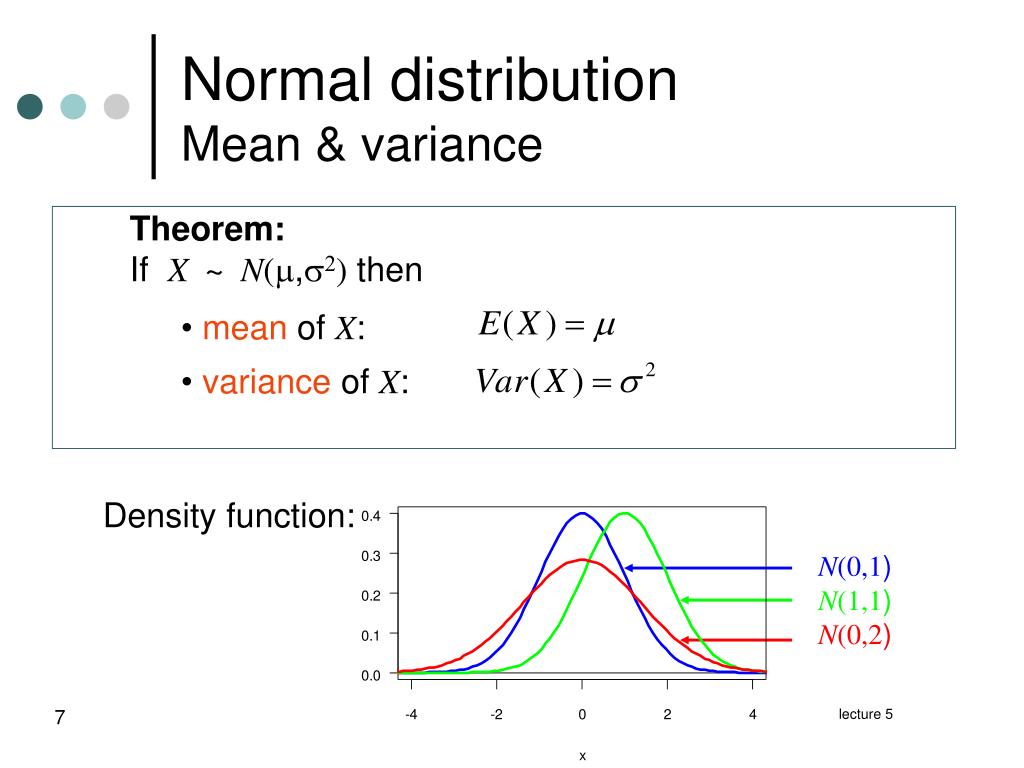
The normal distribution is defined by the following probability density function, where μ is the population mean and σ 2 is the variance.. If a random variable X follows the normal
Because normally distributed variables are so common, many statistical tests are designed for normally distributed populations. Understanding the properties of normal
This article will explore how to conduct a normality test in R. This normality test example includes exploring multiple tests of the assumption of normality. Normal distribution and why it is
Statistical tests for comparing variances. There are many solutions to test for the equality (homogeneity) of variance across groups, including:F-test: Compare the variances of two
Many of the statistical methods including correlation, regression, t tests, and analysis of variance assume that the data follows a normal distribution or a Gaussian distribution. These tests are
Classical tests of variance for one-sample, two-independent samples or paired samples. ## Default S3 method: Var.test (x, y = NULL, ratio = 1, alternative = c („two.sided“,
The Levene test for variance is a statistical test that is used to determine whether or not the variances of two or more groups are equal. This test is often used in experimental
As far as being interested in the „normality“ it is my understanding that running a real valid or robust linear regression or ancova depends on my data being normally distributed
Author(s) Andri Signorell (One sample test) Two Sample test and help text from R-Core. See Also. var.test, bartlett.test for testing homogeneity of variances in more than
It’s possible to use a significance test comparing the sample distribution to a normal one in order to ascertain whether data show or not a serious deviation from normality. There are several methods for normality test such as
Many of the statistical procedures including correlation, regression, t tests, and analysis of variance, namely parametric tests, are based on the assumption that the data follows a normal
In this case, it outperfoms the Bartlett test. If the distribution are nearly normal, however, the Bartlett test is better. I’ve also heard of the Brown–Forsythe test as a non-parametric
- Denon Cd Player Reparieren | Denon Reparaturservice
- Shiloh Name Meaning – What Does Shiloh Mean
- Why They Did Surgery On A Grape
- Santa Cruz De Tenerife To Fuerteventura Ferries
- The 10 Best Dresden Sights | 3 Berühmte Sehenswürdigkeiten In Dresden
- Fur Storage
- One Pot Brokkoli-Kartoffel-Topf Mit Lachs
- Jim Beam Black Cherry Angebote: Jim Beam Preisvergleich
- Prof Dr Siegmann: Matthias Siegmann Rechtsanwalt
- So Planen Sie Ein Diy-Umbau- Oder Renovierungsprojekt
- Ein Ferienhaus Auf Ibiza, Deutschland 2008
- 5 Speed
- Stadtgemeinde Englisch Übersetzer
- Western-Stecker 6/6 / Western-Stecker 6/6, 6M