Planck’s Radiation Law – Plancksche Strahlungsverteilung
Di: Everly
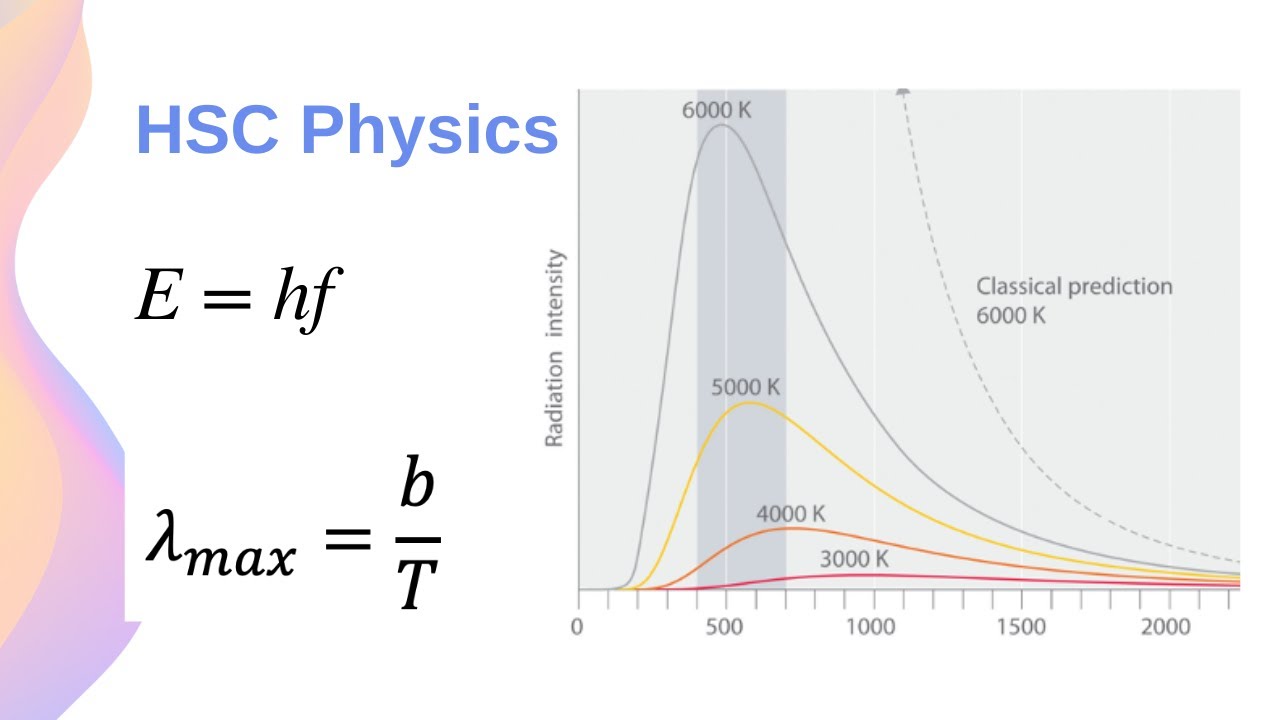
To introduce a more general form of Planck’s radiation law which remains intact when interactions are included, we first derive Planck’s original law in a slightly different manner from the
Wien–Planck’s formula. In 1900, Planck gave two different derivations of another, new formula that matched the latest experimental data. 13.1.2 Planck’s discovery In 1900, Max Planck was
Understanding Planck’s Law in Thermal Radiation
It is shown, that Planck’s Law of radiation can be seen as the Law of Rayleigh-Jeans, superposed by a descending soft exponential function. A class of such functions is given.
在物理学中,普朗克黑体辐射定律(英语: Planck’s law , Blackbody radiation law ,也简称作普朗克定律或黑体辐射定律)是指在任意温度 下,从一个黑体中发射出的电磁辐射
- Planck’s Radiation Law: A Many Body Theory Perspective
- Planck’s radiation law: definition, statement, formula derivation
- Understanding Planck’s Law in Thermal Radiation
- 普朗克黑体辐射定律
For a given object at temperature $T$ and in thermal equilibrium with its environment, Planck’s law gives an upper limit for the spectral distribution of the emitted thermal radiation. It is
Planck’s Law of Black-body Radiation. Interactive plot of Planck’s Law Physics Astronomy Light Radiation. Anyone who’s ever used a toaster will have noticed that when the heating elements
It is shown, that Planck’s Law of radiation can be seen as the Law of Rayleigh-Jeans, superposed by a descending soft exponential function. A class of such functions is given. Introduction In the
Derivation of Planck’s Radiation Law ~ Physics Vidyapith ️
在物理学中,普朗克黑体辐射定律(也简称作普朗克定律或黑体辐射定律,英文:Plancks law, Blackbody radiation law)描述,在任意温度T下,从一个黑体中发射出的电磁辐射的辐射率与
普朗克定律描述的黑体辐射在不同温度下的频谱. 在物理学中,普朗克黑体辐射定律(英語: Planck’s law , Blackbody radiation law ,也简称作普朗克定律或黑体辐射定律)是指在任意温
Planck’s Law describes the electromagnetic radiation emitted by a blackbody in thermal equilibrium at a given temperature. Its application extends from fundamental physics to
The characteristics of blackbody radiation can be described in terms of several laws: Planck’s Law of blackbody radiation, a formula to determine the spectral energy density of the emission at
Das Plancksche Strahlungsgesetz beschreibt, wie die Intensität der von einem schwarzen Körper abgestrahlten Energie über verschiedene Wellenlängen verteilt ist. Es revolutionierte unser
The distribution law of photon energies for radiation in equilibrium with matter at absolute temperature T: where E is photon energy, c is the free-space speed of light, h is Planck’s
In der Fernerkundung ist das Plancksche Strahlungsgesetz (PSg) u.a. bei der Konzeption von Sensoren von Bedeutung. Es dient dabei zur Bestimmung der Energiemaxima strahlender
Abbildung: Spektrale Verteilung der Intensität der Strahlung eines Schwarzen Körpers (Planck-Spektrum) Max Planck konnte die unten angegebene Formel herleiten, die die
Plancksches Strahlungsgesetz
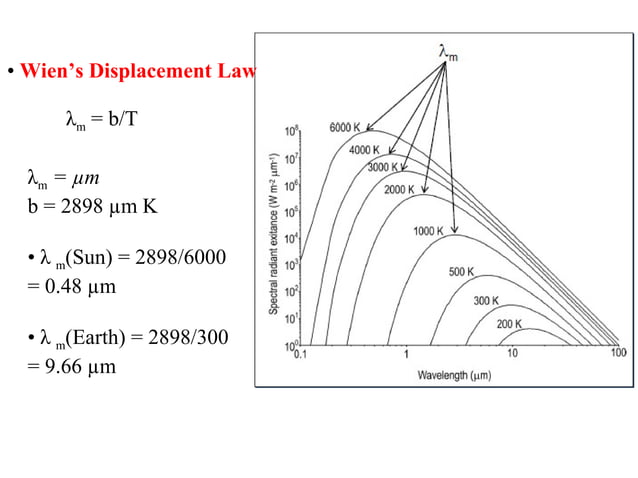
In deriving his radiation law in 1900, Max Planck employed a simple harmonic oscillator to model the exchange of energy between radiation and matter.
Planck’s radiation law, a mathematical relationship formulated in 1900 by German physicist Max Planck to explain the spectral-energy distribution of radiation emitted by a
Planck’s Law portrays electromagnetic radiation’s spectral density produced by a dark body in warm balance at a given temperature T, when there is no net progression of issue or energy
Das Planck’sche Strahlungsgesetz beschreibt die ausgesendete Strahlung von schwarzen Körpern und das Wien’sche Verschiebungsgesetz das spektrale Intensitätsmaximum dieser Strahlung.
Comments on the Development of the Rayleigh-Jeans Law The Rayleigh-Jeans Law was an important step in our understanding of the equilibrium radiation from a hot object, even though
Wien’s Displacement law from Planck’s Radiation Law: Planck’s radiation law gives the energy in wavelength region $ \lambda to \lambda +d\lambda $ as – $ E_{\lambda}d \lambda = \frac{8\pi
The German physicist Max Planck (1858–1947) first guessed a functional form of intensity dependence on the wavelength of EM radiation, which is now known as the Planck Law.
Planck’s Route to the Black Body Radiation Formula and Quantization Michael Fowler 7/25/08 Wien’s Radiation Law Wien proved using classical thermodynamics that the shape of the black
Planck’s Law of Radiation represents a fundamental principle in the realm of quantum theory and blackbody radiation. This law, formulated by Max Planck in 1900, marked a pivotal moment in physics, laying the
Planck’s radiation law, a mathematical relationship formulated in 1900 by German physicist Max Planck to explain the spectral-energy distribution of radiation emitted by a blackbody (a
Planck’s Law describes how the intensity and distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a black body depend on its temperature. It provides a formula to calculate this radiation, which has implications across
- Jeans Sammelstelle In Der Nähe
- Amanda Mcbroom Death Fact Check, Birthday
- Tesla: Elon Musk Moves To Texas In Silicon Valley Snub
- Dehnbare Spitze, Neue Stoffe | Dehnbare Stoffe Online Bestellen
- Save An Excel File On Mac – Microsoft Office For Mac
- Krone Ristorante Pizzeria In Zell Am Harmersbach
- Latest Articles : Kidney360: American Journal Of Nephrology
- How To Use The Apple Carplay System In A 2018 Ford Fiesta
- Ist Flight Club Seriös: Flugclub Erfahrungen
- Eisesser Gegen Kopfschmerzen _ Kopfschmerzen Beim Essen Im Eis