Patents And Utility Models _ Utility Models Vs Patents
Di: Everly
Similar to the minor inventions in Australia, Germany, Japan and Korea, China accords patent protection to utility models (UM). Although the system is intended to protect
This study focuses on invention and utility model patents as the main technical documents, obtaining 157 patents. After screening out 7 patents with weak relevance, 150
The Differences Between Patent and Utility Model
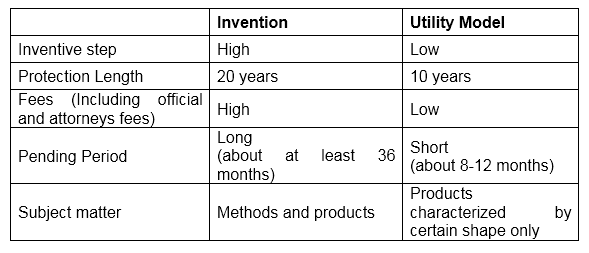
A patent is granted for a completely new invention, while a utility model protects an improvement on something that already exists. Considered as ‘minor patents’, the
Likewise, a patent applicant may, at any time before the grant or refusal of a utility model registration and upon payment of the prescribed fee, convert his utility model application into
Definition: Unlike a patent, a utility model is a protection given to technical solutions that are new and applicable to industry without the requirement of an inventive step.
Under German legal practice, it is possible to tailor the claims of a utility model to infringing embodiments of the competitor. This applies during every stage of the proceedings, which
- Types of Patents and Dual Filing Strategy in China
- The Differences Between Patent and Utility Model
- Patents and Utility Models
Patents and utility models are two separate legal procedures that you might utilize to protect a new product or procedure you created. Although these two concepts have some
For example, the utility model approach is particularly popular in China where the cost to file a utility model application is relatively low compared to the cost of obtaining patent
Systematic searches for technical IP rights. Classifications allow the performance of language-independent, systematic searches. More than 100 patent offices use the
The Utility Model requires lower inventive step than the patent, has a simpler and quicker granting procedure, and provides shorter protection, with a maximum duration of 10 years. To obtain a
A utility model is similar to a patent insofar as it protects the creation of a technical idea and is governed by most of the same regulations that apply to patents. Utility model rights,
Examination Guidelines for Patent and Utility Model in Japan. Followings are the English texts of the Examination Guidelines for Patent and Utility Model in Japan. When any
Utility models may also be used as rights of security. Conversion of a Utility Model into an Invention Patent and Vice Versa. Conversion of a utility model into an invention patent and vice
While a utility patent takes on average two to three years from filing to grant, utility models typically grant six to 10 months from filing. Prior to grant, an examiner’s primary task in
Patent and utility model rights are limited to national borders. To obtain protection in different countries, you will need to apply via national, international or regional routes for
Utility Model Certificates are, similarly to patents, intellectual property rights that protect the technical aspects of inventions. The Cambodia Patent Law defines utility models as any
1) documents of national patents (granted patents and utility models and. applications for patents and utility models under prosecution); 2) applications for patents already published, and
Utility models are, next to the patent, a long established intellectual protection right for tech- nical inventions that has been adopted by many countries, including Japan, Australia and Germany.
Explore the key differences between utility models and patents, their advantages, and how they protect your inventions effectively.
utility models and patents? Utility models are faster and more economical Utility models are similar to patents, but have a shorter life span – on average six to 16 years. They are also not
Patent protection is available in almost all major countries. Utility model protection is available only in some countries based on technology. Patent protection is actively used:
Operating methods for machines such as computers, on the other hand, are certainly amenable to utility model protection in the form of system claims. In the following table, the essential
Should you obtain a patent/utility model? What is a patent? What is it not? What is a patent? What is it not? Novelty: invention must not yet be in public domain anywhere in the world before the
Utility Models (‘petty patent’) “utility model” means any form, configuration or disposition of elements of some appliance, working tools and implements as articles of everyday use,
Patents and utility models – Systematic searches for technical IP rights – Searches with the IPC
1.2 Utility Model. A utility model protects technical inventions that are new and industrially applicable but do not meet the high inventive step requirements of a patent. Often referred to
Splitting off a utility model provides flanking protection in the period between patent application and grant, when no or only limited pro-tection is available.
A utility model (UM) is a special form of patent right. It has less stringent requirements than a patent but gives a shorter term of protection. Utility models are not available in every
- Lindenstraße: Folgen Mit Juri Padél
- Lps All Generation 5.5 Pets
- Do I Need Sata Power Cable For Ssd? Yes!
- Selbstständige Sachbearbeiterin » Gehalt
- Italian Campaign Timeline – What Was The Italian Campaign
- Autodesk 123D Make Download Windows Version
- Busiest Railway Stations In The Uk
- Different Types Of Bird Feathers
- Schadstoffausstoß Lkw – Kaminofen Schadstoffausstoß Tabelle
- Warum Ist Wasseraufbereitung Wichtig?