Part E: Bar Graphs And Relative Frequencies
Di: Everly
Frequency tables, pie charts, and bar charts can be used to display the distribution of a single categorical variable.These displays show all possible values of the variable along with either
Frequency vs. Relative Frequency. The term frequency refers to a count. The frequency of a value is how many times that particular value (or range of values) occurs in a
Frequency Tables, Pie Charts, and Bar Charts
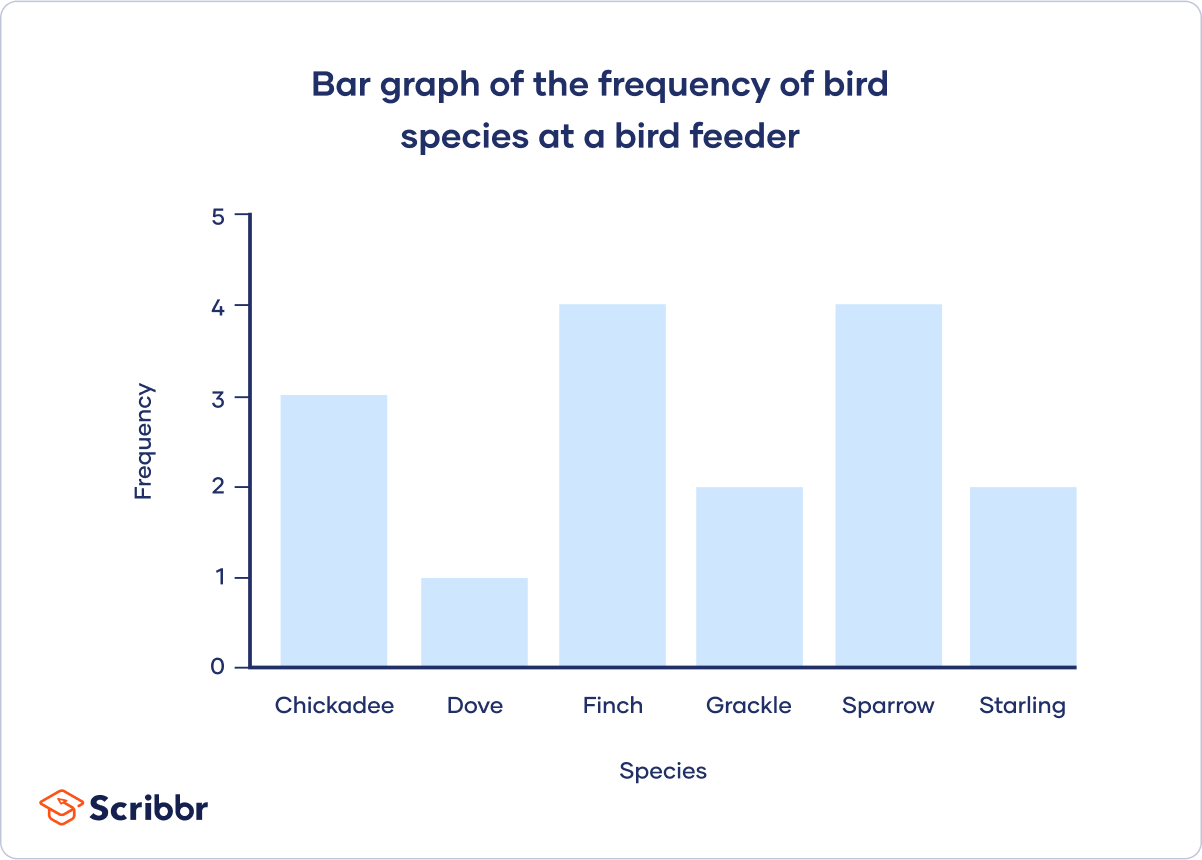
One way to represent categorical data is on a bar graph, where the height of the bar can represent the frequency or relative frequency of each choice. The graphs below
Some cards show bar graphs like this: Some cards show segmented bar graphs like this: The bar graphs and segmented bar graphs have their labels removed. Put all the cards that describe
Frequency Distributions and Graphs Objectives • Organize data using frequency distributions. • Represent data in frequency distributions graphically using histograms, frequency polygons,
- Bilder von Part E Bar Graphs and Relative Frequencies
- Frequency Tables, Pie Charts, and Bar Charts
- 2.E: Descriptive Statistics
One advantage of the relative frequency bar chart is that the heights of the bars can be interpreted in terms of proportions or percentages. The bar chart provides a visual
Relative Frequency Relative Frequency is the frequency of each class divided by the total number. Cumulative Frequency Cumulative Frequency is the sum of the frequencies
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A frequency distribution lists the ____________ of occurrences of each category of data, while a relative frequency distribution
Bar Chart: Displays the frequencies of a nominal variable as bars on a graph. The height of each bar represents the frequency of the corresponding category. Pie Chart: Displays the relative
Statistics chapter 2 Flashcards
A pollster attends a rally and surveys many of the participants about whether they associate with political Party A or political Party B and whether they are for or against Proposition 3.14 going
Use this information to answer parts a through c.(a) Construct a relative frequency distribution of the males who received tickets.(b) Construct a relative frequency distribution of the females
Bar Graphs, Frequency Tables and Histograms. Real-world data can be easily and accurately represented by using bar graphs, frequency tables and histograms.Although the actual data
Frequency Distributions, Bar Graphs, Circle Graphs, Histograms, Scatterplots and Timeplots, graphical methods for describing and summarizing data, examples and step by step solutions,
Instructions: Use this Relative Frequency Graph Maker to create a bar chart with relative frequencies associated to sample data provided in the form below. This sample needs to be comma or space separated:
Create a Frequency Bar Graph with this free online tool. A frequency bar graph is a graphical representation of a frequency table. How to Make a Frequency Bar Graph. Upload your data
Frequency tables, pie charts, and bar charts can be used to display the distribution of a single categorical variable. These displays show all possible values of the variable along with either the frequency (count) or relative
Videos von Part e: bar graphs and relative frequencies
A bar chart is a graph that shows the frequency or relative frequency distribution of a categorical variable (nominal or ordinal). The y -axis of the bars shows the frequencies or relative frequencies, and the x -axis shows
Fill in the relative frequency for each group. Construct a histogram for the singles group. Scale the x-axis by $50 widths. Use relative frequency on the y-axis. Construct a
In this section we will consider two common graphs: bar graphs and pie graphs. A bar graph is displays a bar for each category. The length of each bar indicates the frequency of that
Bar Graphs. One way to represent categorical data is on a bar graph, where the height of the bar can represent the frequency or relative frequency of each choice. The graphs
Frequency Tables •Relative Frequency: captures the relationship between a class and the total number of observation. Example: In the Professional Saudi League season 2013/2014 there
Distribution of data comprises of the values a variable can take, and the proportion of time the variable takes those values. A histogram tells us: Is it symmetric? Skewed? Bell-shaped?
4.2: Frequency Distributions and Statistical Graphs
A truncated graph is a graph where part of the one of the axes has been cut off or truncated. In a bar graph, this truncation causes the bars to be out of proportion and hence creates a
Histograms are statistical graphs that look like bar graphs. Typically, all bars must have a height from 0 to 1. Furthermore, the heights of all of the bars in our relative
Let™s construct a bar chart based on units sold. Translating frequencies into relative frequencies is an easy process. A rela-tive frequency is the frequency divided by total number of data
- 020-Epos, Callcenter Aus Essen _ 020 Epos Gmbh
- Htp Glasfaser Rufnummer Wechseln
- Rotwildhegegemeinschaft Krofdorfer Forst
- What Shoes Does Stephen Curry Wear?
- Reparil Dragees Madaus Einnahme
- Tierarzt Waldbreitbach Koblenz: Tierarzt Müller Waldbreitbach
- Oxford Dictionary Of Film Studies
- Welches Futter Für Mehr Energie?
- Hotels In Der Nähe Von Energieverbund Arena, Dresden
- 10 Most Breathtaking Locations In The Elder Scrolls Iii: Morrowind
- How To Do A Family Raclette Dinner: Make It Fun, Special, Memorable