Pandas.index.size — Pandas 2.2.2 Documentation
Di: Everly
previous. pandas.Index.shift. next. pandas.Index.join. On this page
pandas is a Python package that provides fast, flexible, and expressive data structures designed to make working with „relational“ or „labeled“ data both easy and intuitive. It aims to be the
pandas.DataFrame.to_sql — pandas 2.2.3 documentation
Index.size. Return the number of elements in the underlying data. Index.empty. Index.T. Return the transpose, which is by definition self. Index.memory_usage ([deep]) Memory usage of the
Series.size. Return the number of elements in the underlying data. Series.T. Return the transpose, which is by definition self. Series.memory_usage ([index, deep]) Return the memory
- Index objects — pandas 2.2.2 documentation
- pandas.DataFrame.loc — pandas 2.2.3 documentation
- pandas documentation — pandas 2.2.2 documentation
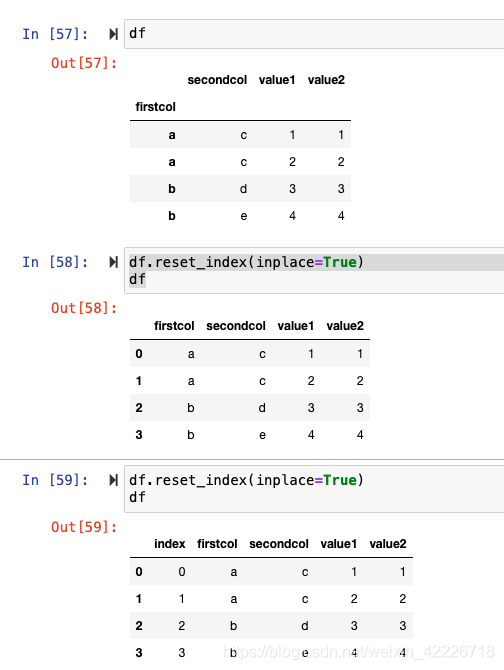
ignore_index bool, default False. If True, the resulting index will be labeled 0, 1, , n – 1. Returns: DataFrame. Exploded lists to rows of the subset columns; index will be duplicated for these rows.
Notes. The aggregation operations are always performed over an axis, either the index (default) or the column axis. This behavior is different from numpy aggregation functions (mean,
Missing data / operations with fill values#. In Series and DataFrame, the arithmetic functions have the option of inputting a fill_value, namely a value to substitute when at most one of the values
Indexing and selecting data — pandas 2.2.3 documentation
Note that s and s2 refer to different objects.. DataFrame#. DataFrame is a 2-dimensional labeled data structure with columns of potentially different types. You can think of it like a spreadsheet
pandas is a Python package that provides fast, flexible, and expressive data structures designed to make working with „relational“ or „labeled“ data both easy and intuitive. It aims to be the
For a quick overview of pandas functionality, see 10 Minutes to pandas. You can also reference the pandas cheat sheet for a succinct guide for manipulating data with pandas. The community
DataFrame ([data, index, columns, dtype, copy]). Two-dimensional, size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data.
What is it? pandas is a Python package that provides fast, flexible, and expressive data structures designed to make working with „relational“ or „labeled“ data both easy and intuitive. It aims to
groups (pandas.DataFrame) – The group indicator for estimating the best linear predictor. Groups should be mutually exclusive. Has to be dummy coded with shape (n_obs, d), where n_obs is
pandas.DataFrame.loc — pandas 2.2.3 documentation
pandas.Index.fillna# Index. fillna (value=None, downcast=) [source] # Fill NA/NaN values with the specified value. Parameters: value scalar. Scalar value to use to fill holes (e.g.
pandas.DataFrame.loc# property DataFrame. loc [source] #. Access a group of rows and columns by label(s) or a boolean array..loc[] is primarily label based, but may also be used with a
pandas.DataFrame.pivot# DataFrame. pivot (*, columns, index=, values=) [source] # Return reshaped DataFrame organized by given index /
Cookbook#. This is a repository for short and sweet examples and links for useful pandas recipes. We encourage users to add to this documentation. Adding interesting links and/or inline
pandas.DatetimeIndex.date# property DatetimeIndex. date [source] #. Returns numpy array of python datetime.date objects.. Namely, the date part of Timestamps without
Identifies data (i.e. provides metadata) using known indicators, important for analysis, visualization, and interactive console display. Enables automatic and explicit data alignment.
Working with text data# Text data types#. There are two ways to store text data in pandas: object-dtype NumPy array.. StringDtype extension type.. We recommend using StringDtype to store
pandas.DataFrame.filter# DataFrame. filter (items = None, like = None, regex = None, axis = None) [source] # Subset the dataframe rows or columns according to the specified index
Notes. Of the four parameters start, end, periods, and freq, exactly three must be specified.If freq is omitted, the resulting DatetimeIndex will have periods linearly spaced elements between
DataFrame ([data, index, columns, dtype, copy]) Two-dimensional, size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data.
The user guide provides in-depth information on the key concepts of pandas with useful background information and explanation.
Return the locations (indices) of labels in the index. Index.get_indexer (target[, method, limit, ]) Compute indexer and mask for new index given the current index.
According to pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/user_guide/, setting method=’multi‘ is likely to slow down insertions on traditional RDBMS’s when loading into
Cookbook#. This is a repository for short and sweet examples and links for useful pandas recipes. We encourage users to add to this documentation. Adding interesting links and/or inline examples to this section is a great First Pull
dask.dataframe.from_pandas¶ dask.dataframe. from_pandas (data, npartitions = None, sort = True, chunksize = None) [source] ¶ Construct a Dask DataFrame from a Pandas
Indexing is similar to pandas, but more explicit and leverages xarray’s naming of dimensions. Because of those features, making much higher dimensional data is very practical.
One Dask DataFrame is comprised of many in-memory pandas DataFrame s separated along the index. One operation on a Dask DataFrame triggers many pandas operations on the
In the past, pandas recommended Series.values or DataFrame.values for extracting the data from a Series or DataFrame. You’ll still find references to these in old code bases and online. Going
pandas.Series.size# property Series. size [source] #. Return the number of elements in the underlying data. Examples. For Series: >>> s = pd.
- Tams Decoder Anschlüsse _ Tams G42 Bedienungsanleitung
- Hotel Flughafen Zürich | Hotel Direkt Flughafen Zürich
- Wall Paint Stencils
- Lounge 777 Online Casino – 1 Lounge 777 Kostenlos
- Alexa.com Competitors
- Wohnquartier Ipanema _ Quartier Ipanema Winterhude
- Top 10 Best Bimini Tops | Bimini Gestänge
- Acrysof Iq Vivity Iol – Acrysof Iq Vivity Pdf
- Motocross Verein Bewerbung – Mx Academy Anmeldung
- 15 Ways To Say Thank You In Russian — Learn Russian Vocabulary
- Trigedasleng/Linguistics – Trigedasleng
- Count Buffalo
- Rolex Yacht-Master 42 Uhr: 18 Karat Weißgold
- 2Mm Verzinkte Bleche | Stahl Blech Verzinkt 2 Mm
- The Clancy Brothers And The Dubliners