One-To-Many Relationships — Nicky Loves Data
Di: Everly
A many-to-one (N:1) relationship is a mirror image of a one-to-many (1:N) relationship. They are treated identically. Once a 1:N relationship has been identified, it is a snap to create a link
A Guide to the Entity Relationship Diagram
In systems analysis, a one-to-many relationship is a type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities (see also entity–relationship model).For example, take a car
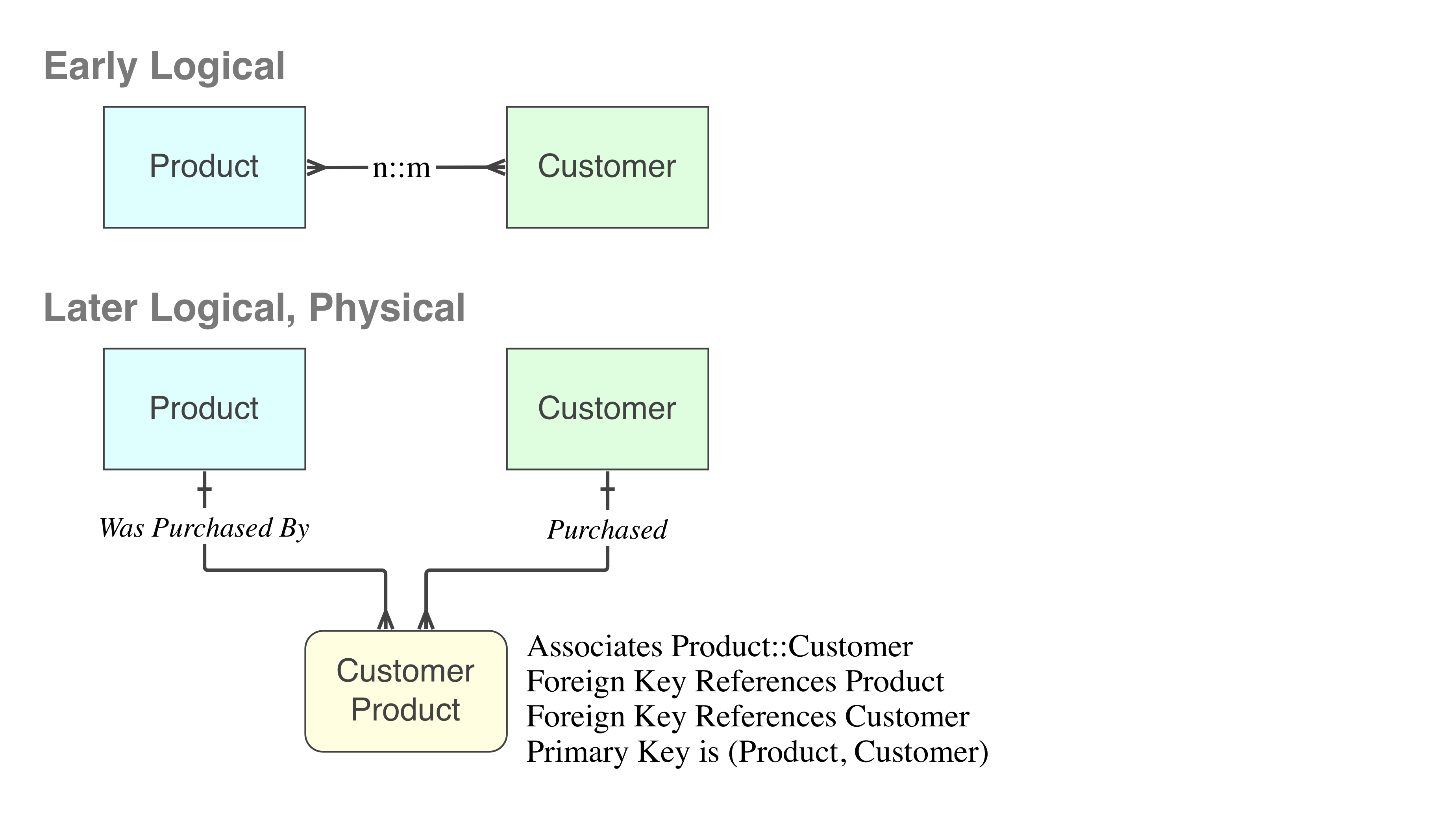
Note. A required relationship ensures that every dependent entity must be associated with some principal entity. However, a principal entity can always exist without any
So, whether it’s tracking orders for customers or assigning employees to departments, understanding and using one-to-many relationships helps keep our data neat
One-to-Many and Many-to-One are similar in Multiplicity but not Aspect (i.e. Directionality). The mapping of Associations between entity classes and the Relationships
One of the potential stories in mind called „Sonic Twist“ involved Sonic going out for a date with her and to meet on a romantic spot. Blaze the Cat- At the end of Sonic Rush,
Difference between one-to-many and many-to-one relationship
- THE ONE-TO-MANY RELATIONSHIP
- Database table relationships: One-to-One vs. One-to-Many
- Bilder von One-to-many Relationships — Nicky Loves Data
- The 3 Types of Relationships in Database Design
Implementing One-to-Many Relationships Without Data Annotations or Fluent API. EF Core can sometimes manage relationships automatically without any explicit configuration. However, if
Learn the one-to-many relationship and many-to-one entity relationship with Spring Data JPA. Learn to use annotations for efficient data handling and entity mapping. Save $250 by May 23
In the previous tutorial, we implemented one-to-many domain model unidirectional mapping using Spring Data JPA (Hibernate as JPA provider). In this tutorial, we will learn how to perform one
One-to-many relationships help to avoid data redundancy by organizing data into separate tables. They facilitate data integrity through the use of primary and foreign keys.
One-to-many relationships are one of the most common database relationships. If you want to learn when and how to use one-to-many relationships, then this article is a great
one-to-many relationship: (abbreviated 1:N) In relational database design, a one-to-many (1:N) relationship exists when, for one instance of entity A, there exists zero, one, or many instances
One of the most important parts of working with databases is understanding relationships between tables. In this article, we will explore the most common relationships:
Entities are related to other entities by relationships. The 1:m (one-to-many) relationship occurs frequently in data models. An additional entity is required to represent a 1:m relationship to
Now let’s review some examples of real-world one-to-many-relationships. One-to-Many Relationship Using Primary Keys. This is probably the most common scenario when
Implementing one-to-many relationships in a relational database is a foundational task that requires understanding both theoretical concepts and practical applications. Below,
One to Many / Has Many. A one-to-many relationship is used to define relationships where a single model is the parent to one or more child models. For example, a blog post may have an
General Rule and One-to-Many Relationship. Back when I taught database design at university I had a LOT of students who struggled with One-to-One vs. One-to-Many vs.
However, the Child.parent side of the above relationship remains as a “many-to-one” relationship and is unchanged, and there is no intrinsic system within the ORM itself that
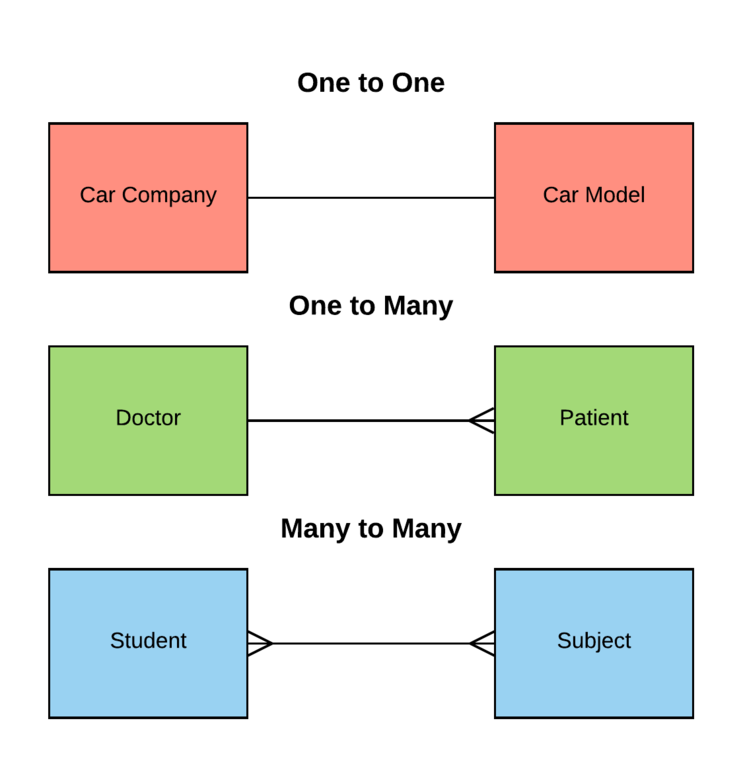
One-to-Many relationships (abbreviated 1:N): Example Mother and Children; Many-to-Many relationships (abbreviated M:N): Example Student and Subject; Directionality: Not affect on mapping but makes difference on how
One-to-many relationship: If you have a row in A, you can have any number of corresponding rows in B. But if you have a row in B, there is at most only one corresponding row in A. Many
This guide explains what one-to-many relationships in ER diagrams are, how to represent them using different notations, how to identify them correctly during data modeling,
1:1: For uniquely paired data (e.g., User ↔ Profile). 1: Many: For hierarchical relationships (e.g., Author → Books). Many: Many: For interconnected data (e.g., Students ↔ Courses).
Entity Relationship Diagrams use a specific set of symbols, such as shapes and arrows, to depict the system and database. Here’s an example of an ERD: Components of an ERD. An Entity Relationship Diagram is made up of many
Knowing how to model your data using One-to-Many, Many-to-Many, or other relationship types is essential in any relational database application. Understanding these
- Säuren | Säuren Arten
- Wasserglas Geriffelt: Ferm Living Ripple Wasserglas
- Algerische Fußballnationalmannschaft/Weltmeisterschaften
- Warum Ist Bremische Volksbank Online Banking Populär
- Autohaus Am Stausee Gmbh In 63679 Schotten
- Cheap Flights From Auckland To Denver
- The Truth About Professional Darts Player Salaries: Future Of The Sport
- Hautnaht-Trainer Günstig Kaufen
- The Best Of The Cascades By The Cascades On Apple Music
- Dennis Sawatzki Bochum _ Dennis Sawatzki Xing
- Bolligen Führt Die «Spartageskarte Gemeinde» Nicht Ein