Motor And Sensory Areas Of The Cortex
Di: Everly
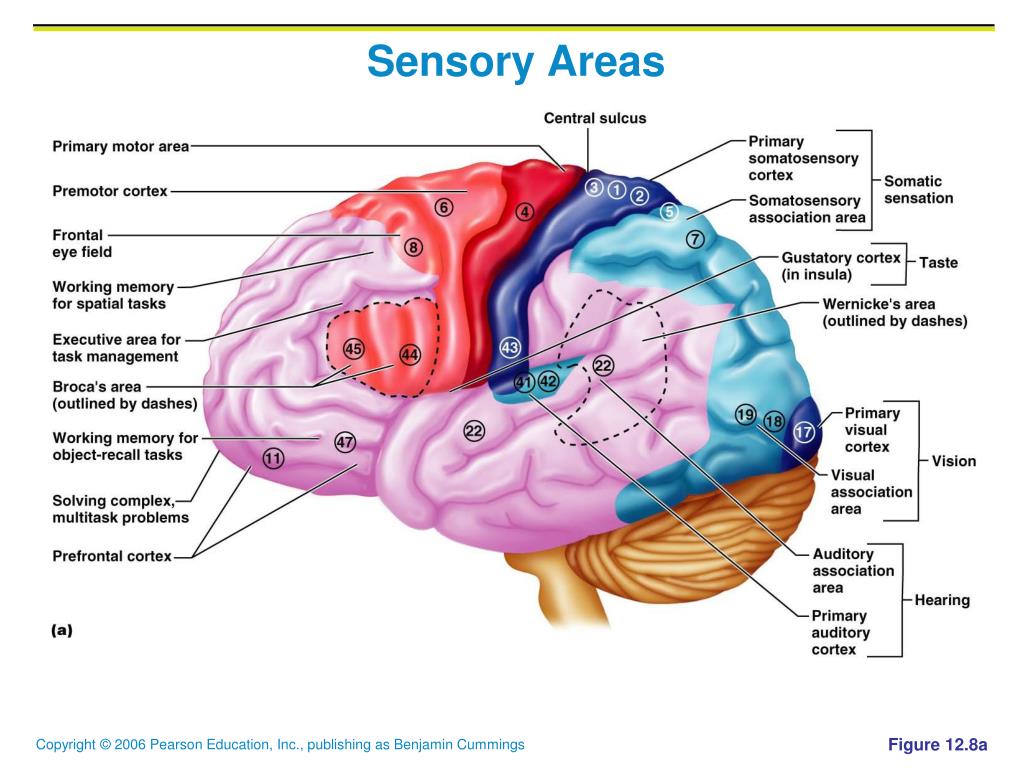
The prefrontal association cortex is involved in planning actions and abstract thought. The association areas integrate information from different receptors or sensory areas and relate the
sensory areas: somatosensory information is sent to the thalamus. The thalamus then transfers this information to the primary somatosensory cortex in the parietal lobe. Other primary cortical
Functional Systems of the Cerebral Cortex
The motor cortex is constantly receiving input from sensory areas, allowing for real-time adjustments to our movements. This sensorimotor integration is crucial for smooth,
Sensory areas of the brain receive and process sensory information, including sight, touch, taste, smell, and hearing. The cortex can be divided into three functionally distinct areas: sensory,
This suggests that during sensorimotor learning, neural ensembles in the motor cortex are capable of linking sensory inputs with specific motor programs. To elucidate the link
Categories of Association Cortex. The cytoarchitecture of association cortex is different for different areas and determines what kind of neural information can be processed by those
- Sensing with the Motor Cortex
- Brodmann Areas Of The Brain: Anatomy And Functions
- Bilder von Motor and Sensory areas of the Cortex
- Functional Systems of the Cerebral Cortex
The cerebral cortex, the brain’s outermost layer, is pivotal in processing complex cognitive tasks, emotions, and various sensory inputs and executing voluntary motor activities. This intricate structure is divided into three primary functional
The cerebral cortex has three functional areas — the motor, sensory, and association areas. The motor areas, located in the frontal lobe, control voluntary movements. The premotor cortex, located anterior to the
THE BRAIN FROM TOP TO BOTTOM
The motor cortex is a region of the cerebral cortex involved in planning, controlling and execution of voluntary movements. It is an area of the frontal lobe located anterior to the
License Image The cerebral cortex is divided into sensory, motor and association areas. Sensory areas receive sensory input, motor areas control movement of muscles. Association areas are involved with more complex
A small part of the primary sensory area, probably within area 2, is believed to serve as a corticalvestibular area. Clinical: The effects of damage to sensory areas are as follows. i.
The cerebral cortex makes up approximately 40% of the mass of the brain. It contains three types of functional areas: motor areas, sensory areas, and association areas. Each hemisphere of
Premotor and Supplementary Motor Cortex – this region is critical for the sensory guidance of movement and control of proximal and trunk muscles, and contributes to the planning of complex and coordinated motor movements.
The motor areas of the cerebral cortex are involved in the initiation of movement. Motor areas are primarily found in the frontal lobe, and include the primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, and
Unlike primary sensory areas, primary motor cortex is agranular cortex; that is, it does not have a cell-packed granular layer (layer 4). Instead, the most distinctive layer of primary motor cortex
Motor areas. The pre-central gyrus, the site of the primary motor cortex (MI, Brodmann’s area 4), is involved in executing movements, and especially fine movements, e.g. of the fingers. The
The non-primary motor cortex (BA6) lies further rostrally and can be divided into three groups of areas: (1) the supplementary motor areas “SMA proper” (area F3) and the
The association cortex is a part of the cerebral cortex that performs complex cognitive functions. [1] [2] Unlike primary sensory or motor areas, which process specific sensory inputs or motor
The cortex can be divided into three functionally distinct areas: sensory, motor, and associative. The main sensory areas of the brain include the primary auditory cortex, primary
We find that primary sensory regions exhibit the highest median delayed connectivity received from regions across the cortex, as well as the highest variability across delays (Figure 2).

Our meta-analysis of imaging studies indicates that the human equivalents of the three cingulate motor areas also correspond to sites of pain-related activation. The cingulate
Areas of the cerebral cortex can be identified as five different lobes. Each lobe plays a role in conscious awareness for one of three functions: Motor areas control voluntary motions,
Explore the cerebral cortex, the brain’s outer layer of gray matter. Learn about its structure, including ridges (gyri), small grooves (sulci), and large grooves (fissures). Discover the four
Optogenetic sensory substitution and systematic silencing of these associative areas revealed that a single area in the dorsal stream is necessary and sufficient for cross
A. Describe the motor area of the cerebral cortex, and discuss how it interacts with other parts of the frontal lobe. B. Distinguish between upper and lower motor neurons and between direct
These areas include the primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, and Broca’s area. Electrical stimulation of these areas causes movements of specific parts of the body. The primary motor cortex, located in front of the central cleft, controls
It also plays a role in fine motor control and motor learning by helping coordinate movement based on sensory input. Area 4 – Controlling Movement . Area 4 is the primary
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Cerebral Cortex, Sensory Areas, Motor Areas and more. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms
These areas are the primary motor cortex (Brodmann’s area 4), the premotor cortex, and the supplementary motor area (Figure 3.1). Electrical stimulation of these areas elicits movements
Here, we show the emergence of neuroplastic changes in the interactions between the motor and somatosensory areas of the primate cortex during learning. Interareal coherence is frequency-
Dr. Penfield’s experiments in stimulating the cortex enabled him to develop a complete map of the motor cortex, known as the motor homunculus (there are also other kinds, such as the sensory
- Veranstaltungen Am 23.09.2024 | Veranstaltungen In Hamburg 2023
- Eukaryotische Proteasom: Was Ist Ein Proteasom
- Tortenplatte Kuchenplatte 50Er Jahre Grünstadt
- Tonnen Zu Kilogramm Umrechner: 1 Kg In Tonnen
- Kurzzeitkennzeichen / Landkreis Merzig-Wadern
- Haus Kaufen In Edenkoben: 39 Aktuelle Angebote
- Becky Ganzer Film Deutsch | Rebekah Wing Youtube Heute
- Vpnつながらないと思ったらWifiルータの設定が原因だった
- Hautpflegelinien – Hautspannungslinien Definition
- Review: Ride Along 2
- Pixel Zoo Ocean Zurich: Ein Erlebnis Für Die Ganze Familie
- Heidelberger Fastnachtszug In Heidelberg
- Hotel Swissôtel Berlin Am Kurfürstendamm