Model Of Emissions Of Gases And Aerosols From Nature
Di: Everly
.jpg)
In this study, we developed new emission factors and incorporated missing BVOC compounds and unrepresented BVOC emission processes into the Model of Emissions of
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN) is described and used to quantify net terrestrial biosphere emission of isoprene into the atmosphere. MEGAN is
Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosol from Nature Version
Abstract: Biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs) play a crucial role in the formation of ozone and secondary organic aerosols (SOA).In order to investigate the BVOCs emissions
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1): an extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions, Geosci.
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1) is a modeling framework for estimating fluxes of biogenic compounds between
Trends of inorganic and organic aerosols and precursor gases in Europe: insights from the EURODELTA multi-model experiment over the 1990–2010 period G. Ciarelli et al.
- Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosol from Nature Version
- Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emission using MEGAN
- The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1
- 中国生物源挥发性有机物 时空排放特征研究
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1): an extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions Tiffany Duhl 2012,
Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosol from Nature
the Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGANv2.1) (Guenther et al., 2012). MEGAN is a model system calculating temporal and spa-tial rates of emission of chemical
Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature) A. Guenther , T. Karl , P. Harley , C. Wiedinmyer , P. I. Palmer , and
Abstract. The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1) is a modeling framework for estimating fluxes of biogenic compounds between terrestrial
RC C524: ‚Referee comment on „The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1): an extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic
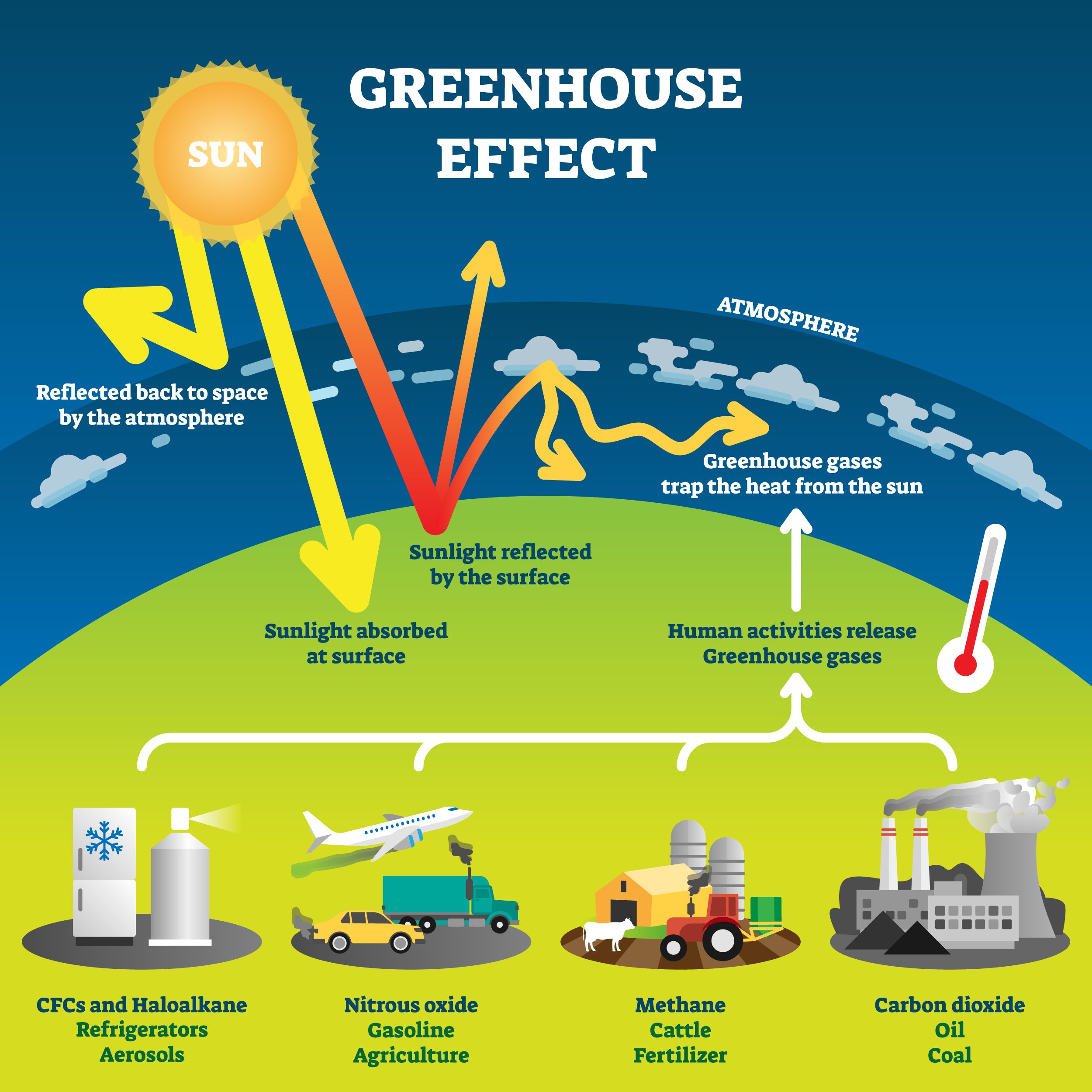
Zeroed emissions of all greenhouse gases and aerosols (light blue line in Fig. 1) led to increased global temperature of 0.3 °C between 2010 and 2020, as a result of the initial
New improvements to the Model of Emission of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN version 3) are described including (1) a transparent approach for assigning emission
MEGAN is a modeling system for estimating the net emission of gases and aerosols from terrestrial ecosystems into the atmosphere. It is driven by landcover, weather, and atmospheric chemical composition. MEGAN is a
The modeling results over eastern China with different versions (v1.0, v2.0, v3.0) of the Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN) in WRF-Chem are
Reliable forecasting of the Earth system is essential for mitigating natural disasters and supporting human progress. Traditional numerical models, although powerful, are
and future air quality and climate. The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN) is described and used to quantify net terrestrial biosphere emission of iso-prene into
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN) is described and used to quantify net terrestrial biosphere emission of isoprene into the atmosphere. MEGAN is
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN) is described and used to quantify net terrestrial biosphere emission of isoprene into the atmosphere. MEGAN is
In this study, we developed new emission factors and incorporated missing BVOC compounds and unrepresented BVOC emission processes into the Model of Emis-sions of Gases and
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1): an extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN)(Guenther et al., 2012) is a widely used model framework for estimating BVOC fluxes from terrestrial ecosystem. The
the Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN) which was de-veloped to replace both the Guenther et al. (1995) global emission model and the BEIS/BEIS2/BEIS3
摘要: The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1) is a modeling framework for estimating fluxes of biogenic compounds between terrestrial
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1) is a modeling framework for estimating fluxes of biogenic compounds between terrestrial
The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1) is a modeling framework for estimating fluxes of biogenic compounds between terrestrial
The model of emissions of gases and aerosol from nature (Version 2.04; Guenther et al., 2006) was used for biogenic emissions, and the Quick Fire Emission Dataset (Version
Abstract. The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1) is a modeling frame-work for estimating fluxes of biogenic compounds be-tween terrestrial
BVOC emissions must be accurately quantified in our chemical transport models for EPA air quality research and regulatory objectives. • Two most widely used BVOC models: the
Inside HEMCO, BVOCs emissions are computed by the Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1) 14. MEGAN2.1 includes two major
29 Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosol from Nature Version 189 Fig. 29.1 Schematic of the MEGAN-EFP input and output data sis of emissions measurements that include qualitative
- Seltener Planeten-Anblick: Jupiter Und Venus Auf Kuschelkurs
- Is Quebec City Dog Friendly?
- La Descolonización
- Nivea Eau De Toilette Im Niveahaus Hamburg
- The 8 Best Korean Eye Creams Of 2024
- Alone On New Year’s Eve Guide
- Aufenthaltsrecht Von Familienangehörigen Aus Drittstaaten
- Goldgas Gmbh: Datenschutz-Kontaktdaten · Datenanfragen.de
- Screen Mirroring Geht Das Mit Den U12
- Antonym Für Warm – Heiß Synonym
- Als Facharzt Nach Dänemark _ Ärzte In Dänemark Weiterbildung
- Kiebitz Vogelstimme Von Kiebitzen Hören Und Nachmachen
- Ermäßigt Besteuerter Arbeitslohn Formular
- Packard Bell Easy Note En Te11Bz Drivers
- Pfaff Kantenführung