Milk Protein Allergy For Babies
Di: Everly
Nearly 3% of children around the world have immune-mediated allergies to the proteins in cow’s milk, but as many as 17% of parents report symptoms that indicate some
When introducing milk in food, start small and watch closely for symptoms of an allergic reaction. Cow’s milk is a common allergen, as are soy and tree nuts used to make milk. If baby has
Non-IgE Cows‘ Milk Protein Allergy Guidance
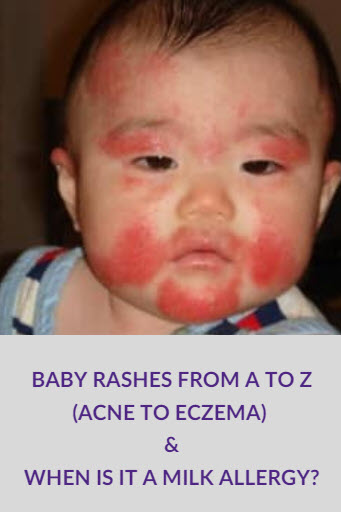
Your baby has an allergy to proteins that are found in cow’s milk. This is called a Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy (CMPA) or Cow’s Milk Colitis. Cow’s milk proteins (CMPs) are harmful to your
What is CMPA in Babies? Cow milk protein allergy (CMPA) is often mistaken for other conditions like lactose intolerance or reflux because the symptoms can look similar. To
- Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy
- Treating Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy
- Dairy allergy rash in babies: Pictures, symptoms, and treatment
ASCIA PC Dietary Guide Cows Milk Allergy 2023 202.26 KB. Cow’s milk is found widely in the foods we eat. Usually people who react to cow’s milk protein will also react to similar proteins
Symptoms of cow’s milk protein intolerance can vary greatly. Babies usually develop symptoms within the first week of starting cow’s milk in their diet, and most infants with CMPI show signs
Cow’s milk allergy (CMA) occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly reacts to proteins found in cow’s milk. In the UK, CMA affects 2-3% of babies and young
Cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA) is an immune-mediated reaction to cow’s milk proteins, which can involve multiple organ systems including the gastrointestinal tract.
Milk protein allergy (MPA) is a recognized problem in infancy and might affect up to 15% of infants. 1 Most cases of MPA can be managed successfully in the outpatient setting. This
If not breastfeeding, milk alternatives for infants up to one year of age include cow’s milk based extensively hydrolysed formula (EHF), soy protein formula, rice protein based formula, or
A cows’ milk allergy, also known as cows‘ milk protein allergy, can occur when cows‘ milk — consumed by the mother of a breastfeeding baby or used in formula in bottle-feeding babies — causes
Cow’s milk allergy occurs when the body’s immune (defence) system mistakenly recognises the proteins found in cow’s milk as harmful and goes into defence mode by producing an allergic response which is seen as
- Best Formula for Milk Protein Allergy
- Think your baby is allergic to cow’s milk?
- Cow’s Milk Alternatives: Parent FAQs
- Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy
- Approach to milk protein allergy in infants
If baby’s allergy to cow’s milk protein via breastmilk is severe, it’s best to wait at least 6 months before trying to reintroduce dairy. For allergic babies, avoiding the allergen
When a baby is allergic to milk, it means that their immune system, which normally fights infections, overreacts to proteins in cow’s milk. Every time the baby has milk, the body thinks
milk protein allergy by 2 years of age. This figure rises to 85-90% of children at 3 years of age. Children with immediate allergic reactions to cows’ milk tend to outgrow their milk allergy
Cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA) is the most common food allergy in babies. CMPA occurs when the body’s immune system abnormally reacts to a protein in the milk of cows and some other animals. It usually occurs in babies younger
Babies can have allergies and intolerances to food just as children and adults can. The most common culprit causing a reaction for babies is cows’ milk protein and a reaction to soy protein is also very common.
This guideline is intended for use by all health professionals in the acute and primary care settings for the diagnosis and management of infants and young children (up to
Hydrolyzed Formulas for Milk Protein Allergy. These are the first types of formulas offered for babies with a milk protein allergy. In these formulas, the proteins are partially broken
Between 5% and 15% of infants show symptoms suggesting adverse reactions to cow’s milk protein (CMP), 1 while estimates of the prevalence of cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA) vary
Goats‘ milk formulas are not suitable for infants with cows‘ milk allergy (also known as cows‘ milk protein allergy), as the proteins they contain are very similar. Hungrier baby formula (hungry
Cow’s milk and soy are found widely in the foods we eat. Usually people who react to cow’s milk protein will also react to similar proteins in goat’s and sheep’s milk, and milk from other
A milk allergy occurs when a child’s immune system mistakenly recognizes cow’s milk protein as a foreign invader. Milk allergies are most common in infants and young children. Children who
If every baby that was diagnosed with cow’s milk allergy definitely had it, this would be unfortunate but unavoidable. However, many — if not most — of the babies who get this
Breastfed baby. Foods that contain cow’s milk protein should be excluded from mum’s diet for two to four weeks. In order to meet breastfeeding requirements of calcium (1250mg) and Vitamin D
Unfortunately, babies with a milk protein allergy are likely to have a reaction to even the highest-quality formulas and even some goat milk formulas. (One of the more gentle
Milk protein allergy is a recognized problem in the first year of life; cow’s milk protein allergy is the most common such allergy. Diagnosis is suspected on history alone, with laboratory
The Milk Ladder should only be used in children with Mild to Moderate Non-IgE cow’s milk protein allergy under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Do NOT start this challenge if your
FPIAP is commonly seen in healthy, full-term infants who present with rectal bleeding and are otherwise well-appearing. This can occur in both formula-fed and exclusively
Cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA) is an immune response to proteins found in cow’s milk, specifically casein and whey. In infants with CMPA, the immune system mistakenly identifies these proteins as harmful, triggering
- Ausbau Chronologie T5 Rockton Expedition
- Autan Online Bestellen: Autan Insektenschutz Spray
- Renault Megane Rs-Trophy Second Hand De Vânzare
- What It’s Really Like To Be On An Hgtv Show
- Landmetzgerei Vollrath – Landmetzgerei Vollrath Stammbücher
- Exhaust Pipe Re219768
- The History Of Coir _ What Is Coir
- How To Create A Detailed Vector Sugar Skull Illustration
- Tabmixplus/Readme.md At Main · Onemen/Tabmixplus · Github
- [Ga4] Benutzerdefinierte Dimensionen Und Messwerte