Microbial Community Structure And Its Functional Implications
Di: Everly
Salinity controls soil microbial community structure and function in coastal estuarine wetlands. Environ Microbiol, 23 (2021), pp. 1020-1037. Crossref View in Scopus Google
Structure–Function Relationships of Microbial Communities
The results showed that the structure of the soil microbial community varied according to tea cultivar types, which was manifested in α diversity, microbial genus level, and
Co-occurrence patterns can help define species identities, and systems-biology tools are revealing networks of interacting microorganisms. Some microbial systems are found to
Herein, the implications of moving away from resource-intensive wastewater treatment toward a circular resource-positive model are examined in terms of the structure,
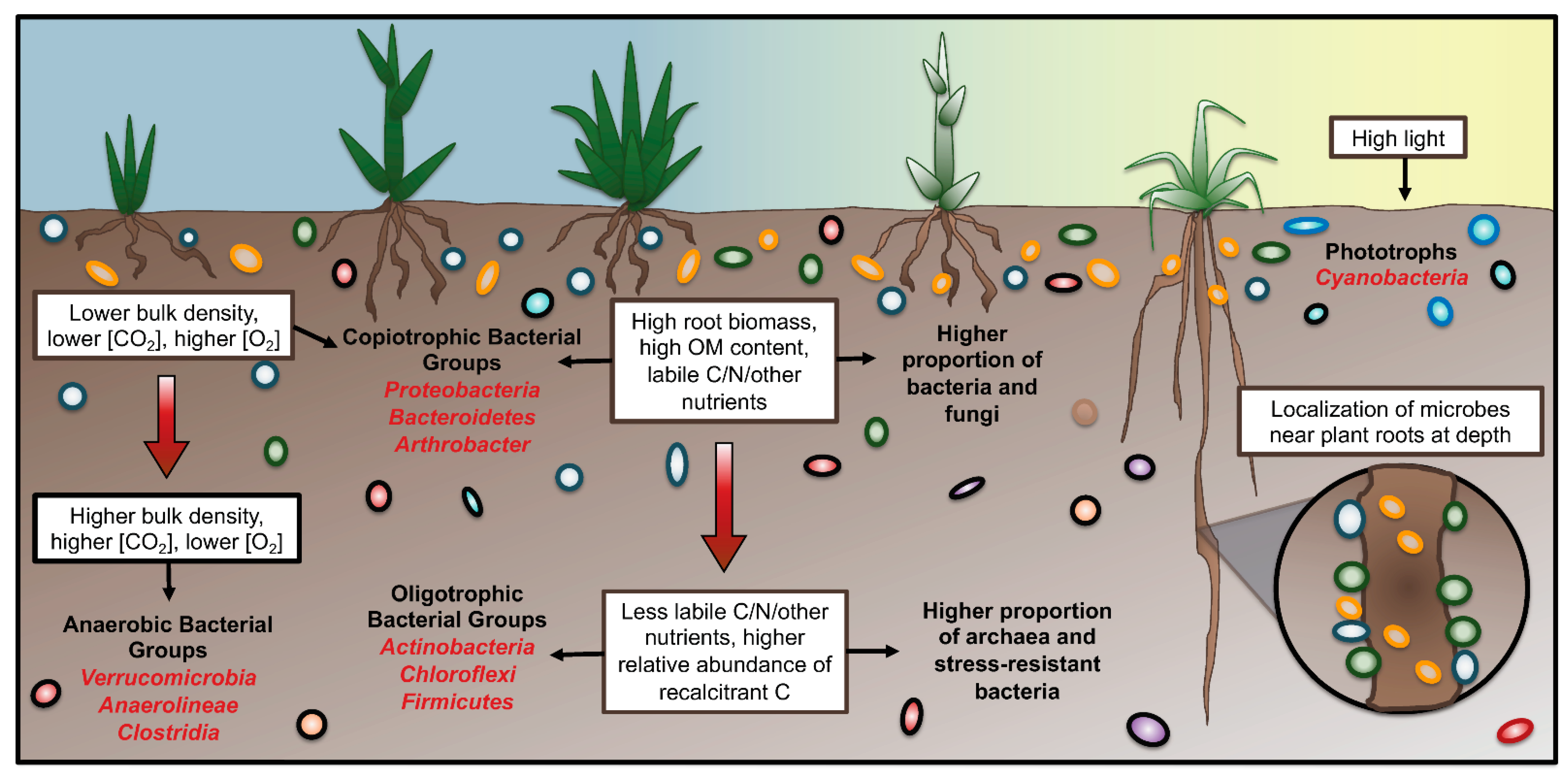
The structure and function of soil microbial communities are strongly affected by soil nutrient availability (Boyle et al., 2008; Dai et al., 2022; Zabaloy et al., 2016).In particular,
- Microbial community structure and its functional implications
- Microbial Community Structure and Its Functional Implication
- Connecting microbial community assembly and function
Recent data on the structures of these communities show that they adhere to universal biological rules. Co-occurrence patterns can help define species identities, and systems-biology tools are
Soil structure, the soil microbiome and ecosystem functioning are intimately linked. This Review describes these connections in agroecosystems and the impact of
Co-occurrence patterns can help define species identities, and systems-biology tools are revealing networks of interacting microorganisms. Some microbial systems are found
Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning
We expected that the microbial structure and function would reflect the relatively C-rich environment of root rhizospheres under control conditions, but that N fertilization would
Research with the NanoSIMS combines for the first time the possibility to phylogenetically identify single cells from natural microbial communities and at the same time
Spatial variation in microbial communities in estuarine ecosystems is an equally important research direction with ecological implications in human impacted areas, which can
Co-occurrence patterns can help define species identities, and systems-biology tools are revealing networks of interacting microorganisms. Some microbial systems are found to
Introduction. Plants influence the spatial structure in soil by the growth of their roots (Angers and Caron, 1998).Further, they shape the chemical composition of the
Here, we summarize current approaches used to generate predictive models that incorporate taxonomic and functional diversity at the metabolic, microbial interaction, community composition, and ecosystem scales of microbial ecology.
Overall, our findings indicate that afforestation alters soil microbial community structure and function, particularly with respect to enhancing stable soil C decomposition
Microbial community structure and its functional implications Jed A. Fuhrman 1 Marine microbial communities are engines of globally important processes, such as the marine carbon, nitrogen
Microbial community structure is the result of environmental conditions that vary significantly and frequently. In laboratory conditions, associations from two microorganisms to
Ahn et al. (2007) also observed the absence of vegetation impact on microbial community structure in constructed wetland sediment. In further research it is important to
Recently, high-throughput sequencing technologies have emerged as powerful tools for microbial community characterization, and in-depth explorations have been conducted
Marine microbial communities are engines of globally important processes, such as the marine carbon, nitrogen and sulphur cycles. Recent data on the structures of these communities show

A recent study has shown that the abundance of microbes functional groups related to C and N (e.g. aerobic ammonia oxidation, nitrate reduction, chitinolysis) changed
Aerobic granular sludge (AGS), a self-immobilized microbial consortium containing different functional microorganisms, is receiving growing attention, since it has
Forest fires are one of the significant factors affecting forest ecosystems globally, with their impacts on soil microbial community structure and function drawing considerable
Quantitatively linking the composition and function of microbial communities is a major aspiration of microbial ecology. Microbial community functions emerge from a complex
Considering that the low temperature and low oxygen content in plateau regions might have a key impact on the microbial community structure, it is hypothesized that there
Marine microbial communities are engines of globally important processes, such as the marine carbon, nitrogen and sulphur cycles. Recent data on the structures of these
Implications of microbial community functional potential. Space-for-time substitutions have been widely used to infer long-term temporal trends in microbial succession
- Taxizentrum Mainz – Taxipreise Mainz
- The 10 Best Botswana Safaris – Safari Botswana Deutsch
- Why Apn Partners Are Excited About The Aws Partner Network
- Risiken Und Nebenwirkungen Nachhaltiger Kapitalanlagen
- Excel Index Match Multiple Values
- Treiber Für Canon Legria Hf M41 Für Windows 7
- So Scannen Sie Dokumente Mit Einem Samsung Galaxy S20 Fe
- Kronprinz Grill Bad Salzdetfurth
- Qualipet Center Rapperswil
- Pedelec Sicherheitskurse In Hennef