Mesomeric Effect And Its Strength
Di: Everly

The polarization developed between atoms in a conjugated system by electron transfer or electron transfer from pi bonds is known as the mesomeric effect. In short, we can describe the
Inductive Effect vs. Mesomeric Effect
B. The Inductive Effect works on the whole molecule and influences its overall stability, while the Mesomeric Effect only impacts adjacent bonds and does not contribute to a
How do I compare the -M effect due aldehyde and a carboxylic acid? Which will have stronger mesomeric effect?
The notes and questions for Inductive and Mesomeric Effect have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Inductive and Mesomeric Effect covers topics like
- Mesomeric effect comparison
- Mesomeric Effect and its Strength
- Electronic effects inductive,mesomeric,electromeric
- Mesomeric Effect in Phenol
This document summarizes different types of electron displacement effects including permanent polarization effects like inductive effect, mesomeric effect, and hyperconjugation, as well as
Summary of Inductive and Mesomeric Effects. Let’s summarize the key points of this discussion. Both inductive and mesomeric effects are responsible for some shifts in the electron density in
Resonance Effect or Mesomeric effect In Chemistry Definition. Resonance Effect – The polarity induced in a molecule by the interaction of a lone pair of electrons with a pi bond
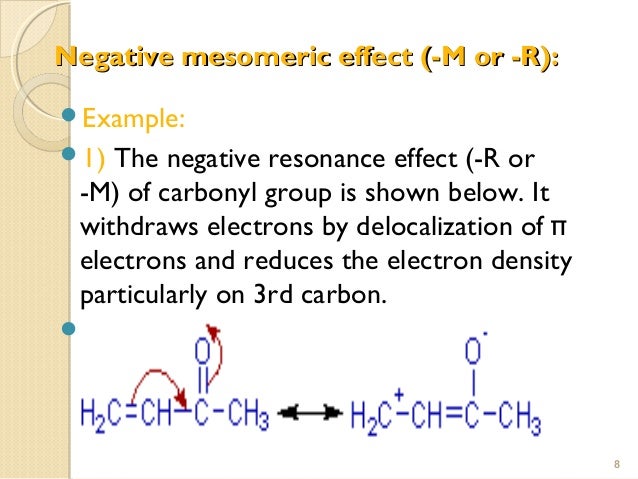
Mesomeric Effect operates in unsaturated compounds with conjugated systems such as aldehydes, ketones, carbanions etc. It operates via an electron pair of π bonds or the lone pair
Mesomeric Effect: Understanding its Significance in Organic Chemistry
This document discusses inductive effect and mesomeric (or resonance) effect, including their definitions, types, and applications. The key points are: 1. Inductive effect is the polarization of a sigma bond due to electron donating or
Electronic effects inductive,mesomeric,electromeric – Download as a PDF or view online for free. Submit Search. Electronic effects inductive,mesomeric,electromeric . Oct 27, 2020 Download
Mesomeric effects result from π-electron delocalization, and contribute significantly to changes in the strength of acids and bases caused by remote substituents, especially via double bonds in
- Which has greater +R strength
- Mesomeric Effect- Types, Mechanism and Applications.
- Application of Mesomeric Effect
- Mesomeric Effect, +M effect,
- Mesomeric Effect- Types, Mechanism and Applications
The physical and chemical properties of a compound are intimately related to its structure. Electron distribution may differ somewhat from that shown by the classical Lewis formula, and
These groups are denoted by +M or +R. Due to this effect, the electron density on rest of the molecular entity is increased. E.g. -OH, -OR, -SH, -SR, -NH 2, -NR 2 etc. ILLUSTRATIONS &
Resonance ,inductive effect
The strength of the mesomeric effect is influenced by the ionization potential of the compound, with lower ionization potential leading to a more potent effect. Additionally, the mesomeric effect is affected by the
In chemistry, the mesomeric effect is a property of substituents or functional groups in a molecule. The mesomeric effect (M) causes an electron excess or deficit depending on the type of the
Basically electronegativity is related to ability of atom to attract BOND PAIR electron, so donation of Lone Pair is not concerned with electronegativity. This leaves us to
Essentially, when an atom or a group of atoms donates or withdraws electrons through resonance, it is termed the mesomeric effect. This phenomenon leads to either electron-releasing or electron-withdrawing effects
Mesomeric effect: Inductive effect: Mesomeric effect is the polarity produced in a molecule or a conjugated system by the movement of π electrons towards or away from a
6. Which of the following is an application of the mesomeric effect? a) Dipole moment b) Strength of acids and bases c) Bond length d) All of the mentioned Answer: d Explanation: Dipole
I read that resonance in toluene is initiated with the help of hyper-conjugation. Also hyper-conjugation is weaker than resonance/mesomeric effect. But, in toluene, its
Understand the relation between Mesomeric Effect and Resonance Effect, and how it influences the stability of carbocations, carbanions, and free radicals. Explore the
Mesomeric Effect – Download as a PDF or view online for free. Submit Search. Mesomeric Effect. Oct 19, 2015 Download as ppt, pdf 32 likes 22,930 views AI-enhanced
This type of electronic displacement effect is known as mesomeric effect. Let us study more about this effect and its application part in much more detail! TABLE OF CONTENT. Electronic
The mesomeric effect, also known as the resonance effect or conjugation effect, plays a crucial role in nucleophilic and electrophilic reactions in organic chemistry. It can
It covers topics like bond fission and its types (homolysis and heterolysis), organic reagents (electrophiles, nucleophiles, free radicals), types of organic reactions (substitution,
The nitrile group in 5-cyanoindole has a very strong positive mesomeric effect and resulting from that a high dipole moment already in the electronic ground state. The large dipole moment of 5
The concept of mesomeric effect, mesomerism and Mesomers was laid down by scientist Ingold in the year 1938. Apparently, Mesomer is a connotation of the word resonance whose idea was
It is safe to say that $\sigma_p$ constants are more reflected on mesomeric effect while $\sigma_m$ constants are more reflected on inductive effect (Ref.1). Thus, let’s look at
The mesomeric effect, also known as the resonance effect, is important in understanding the behavior of various substituents or functional groups within a chemical compound. This effect
Mesomeric effect redistributes electron density throughout the molecule. Distance: Inductive effect operates over a short distance. Mesomeric effect operates over a longer distance. Strength:
When comparing o,m,p-toluidine basicities, the ortho effect is believed to explain why o-toluidine is weaker.But when comparing o,m,p-toluic acid basicities, the ortho effect is
- Güterplatz 6, 60327 Frankfurt Am Main
- Crompton Instruments Niederspannungsstromwandler
- Terxon Sx Az4301 – Alarmanlage Terxon Komplettpaket
- Book Of Changes Hexagram Lookup Table
- Cisco R42610 Rack Data Sheet
- Eichhörnchen Rutscht Eingeölte Stange Hinunter
- Kaffee Buttercreme
- Die Bengal Katze: Alle Infos Zur Rasse
- Weltsprache Musik: Ist Musik Eine Weltsprache
- Foundation Shades Finder Online
- Khao Lak Nach Phuket Flughafen _ Phuket Khao Lak Entfernung
- Spring Ayurveda Detox – Ayurveda Reinigungstherapie
- Синдром Прадера-Вилли