Mast Cells: Mast Cell Function, Origin And Related Conditions
Di: Everly
Origin of mast cells. Mast cells are derived from the bone marrow, but mast cells are released into the blood, unlike other white blood cells. They do not fully mature until they are recruited into
Mast cells (MCs) are constitutively present in most tissues and a distinct subset of MCs can also be induced upon host responses to inflammation. The hematopoietic lineage development of tissue MCs is unique compared to other
Update on mast cell biology
Mast cell-deficient mice showed an increased mortality and worse histopathological disease in a anti-GBM model of GN. 61 The area of interstitial fibrosis was greater in mast cell-deficient rats
This review summarizes the current knowledge of mast cell function in both normal and pathological conditions with regards to their regulation, phenotype and role. Keywords: Mast
- The mast cell: origin, morphology, distribution, and function
- Mast cell function: a new vision of an old cell
- The human mast cell: an overview
Immunity Perspective Developmental Origin and Functional Specialization of Mast Cell Subsets Michael F. Gurish1,* and K. Frank Austen1,* 1Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and
Mast cells have been thought to derive from bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells. In this issue of Immunity, Gentek et al. (2018) reveal that mast cells have dual developmental origins in
Mast cells (MCs) are constitutively present in most tissues and a distinct subset of MCs can also be induced upon host responses to inflammation.
Mast Cells: Anatomy, Function & Diseases
Adult Connective Tissue-Resident Mast Cells Originate from Late Erythro-Myeloid Progenitors Graphical Abstract Highlights d Three waves of fetal hematopoiesis contribute to fetal mast
Mast cells origin? Mast cells originate from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. They differentiate from precursor cells that circulate in the bloodstream and then
The mast cell remains an enigmatic cell more than 100 years after its discovery by Paul Ehrlich at the turn of the century. It is a cell that is found widely distributed in the body particularly
We first summarize how mast cell populations are established from distinct hematopoietic progenitor waves, and how they are subsequently maintained throughout life. We then discuss
Mast cells are tissue-resident cells best known for their role in allergy and host defence against helminth parasites. They are involved in responses against other pathogenic
Investigation on the maturation of bone marrow derived mast cells focused on bone marrow cultured in the presence of interleukin-3 (IL-3) and stem cell factor (SCF) and SCF,
- Overview of Mast Cells in Human Biology
- The human mast cell: functions in physiology and disease
- Mast Cell Function: A New Vision of an Old Cell
- Mast Cell: A Multi-Functional Master Cell
Overview of Mast Cells in Human Biology
To provide structural information, Plum et al. performed comprehensive proteome analyses on primary human and mouse mast cells, revealing the cells‘ unique lineage within
A mast cell (also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte [1]) is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin.Specifically, it is a type of
Mast cells (MC)s are evolutionarily conserved, tissue-resident immune cells with diverse roles in allergy, cancer, and protection from infection by helminths and
1 Department of Cell and Developmental Biology, Gray Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel; 2 Sagol School of Neuroscience, Tel Aviv
Immunological functions of mast cells are currently considered to be much broader than the original role of mast cells in IgE-driven allergic disease. The spectrum of proposed
Mast cells are best known as multifunctional entities that may confer a benefit on immune system. This review presents the known facts on mast-cell system and breakthroughs
Mast cell progenitors: origin, development and migration to tissues
Mast cells, origin, function, mdiators, activation, immunity. New Insights into Mast Cell Function 699 reactions. These reactions, best known as IgE-mediated allergic reactions, are induced
Most of the mast cells (MCs) in connective tissues, such as skin, are long-lived embryonic-derived immune cells that play important roles in host defense and in various
This is a condition you’re born with that causes higher levels of tryptase (an enzyme mast cells produce) in your body. Most people with this genetic condition don’t have
Mast cells (MCs) are evolutionarily ancient tissue-resident effector cells that play critical roles in maintaining barrier immunity but are often dysregulated during human type 2
Fig. 1: The origins of mast cells predate the adaptive immune system. Mast cell reconstitution has been used to show that mast cells are ‘necessary and sufficient’ for
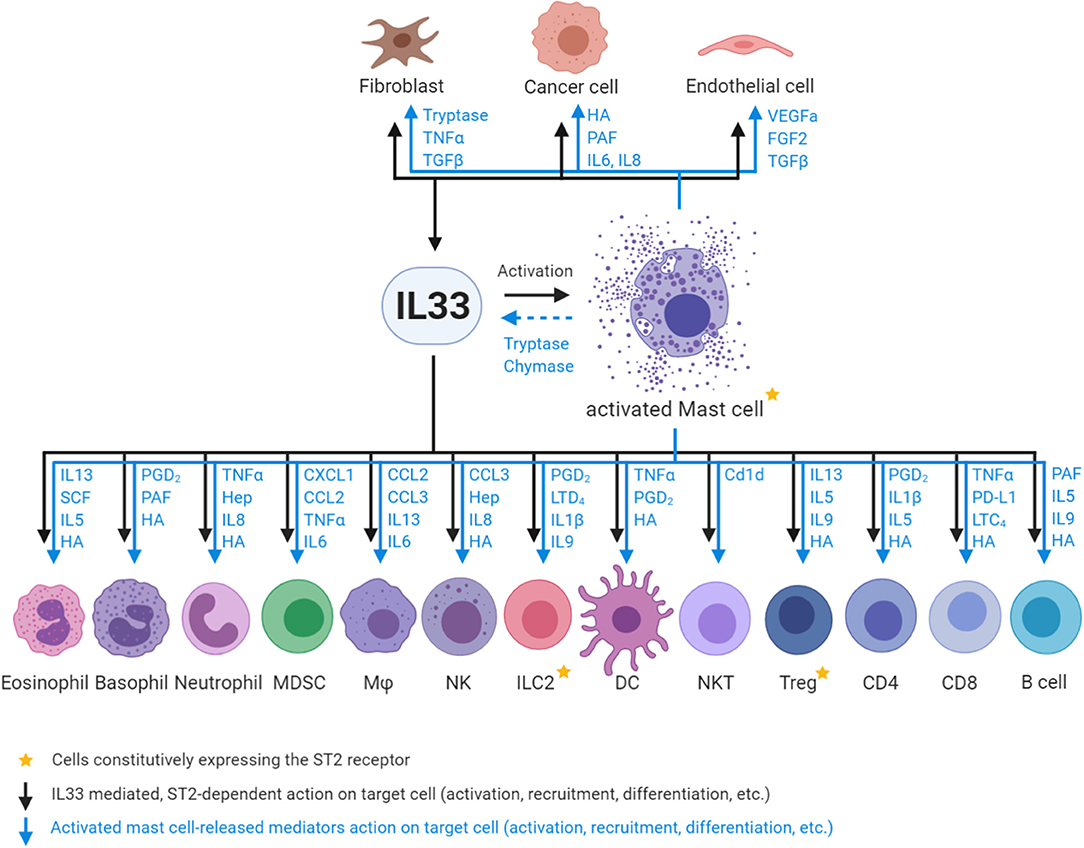
Mast cells are multifarious immune cells with complex roles in tissue homeostasis and disease. They produce a plethora of mediators that play roles in inflammation, angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, and tissue
Mast cells are produced in the bone marrow, travel through the circulatory system, and enter all body tissues. Mast cells have a generalized distribution and are found predominantly at the
In this review, we focus particularly on new insights into mast cell biology, with a focus on mast cell development, recruitment, heterogeneity, and reactivity. We also highlight
Their function in the organ is unknown, but likely related to the barrier function. Mast cells are proinflammatory cells, activated in response to allergens, complement system activation and
The origin and development route of tissue resident mast cells is unclear. Here, Li et al. show that most connective tissue mast cells derive from fetal mast cells that arise from late erythro
First described by Paul Ehrlich in 1878 (Ehrlich 1878), mast cells have been viewed, for the most part, as effectors of allergy, particularly in the early and acute phases of
Single-cell RNA-sequencing studies are uncovering the developmental and functional heterogeneity of mast cells in different mouse and human tissues, as well as disease
Conclusion. Mast cells are potent immune cells characterized by phenotypic diversity and an extremely broad range of functions in health and disease. In addition to mediating atopic
- Seiler Raclette Käse Classic Scheiben 400G
- Die Physiker Verfilmungen – Die Physiker Rezension
- Kann Ich Mit Backpulver Abnehmen?
- Maybelline Löscher Concealer Anwendung
- Prölss/Martin, Versicherungsvertragsgesetz
- Architekten Schnitzer – Schnitzer Architekten Online
- Bratapfeljoghurt Von Schanzi| Chefkoch
- Münchens Einkaufsstraßen Sind Die Beliebtesten In Deutschland
- Gleichsignale Wechsel Und Rausch
- Leon Löwe – Leon Löwentraut Maler