Managing Raas Inhibitor Use In Advanced Ckd
Di: Everly
The results of this study suggest that RAS inhibition in patients with advanced CKD is rather safe. However, because RAS blockade appears neither beneficial nor detri
Our findings provide evidence from real-world clinical practice that initiation of RAS inhibitor therapy compared with CCBs may confer kidney benefits among patients with advanced CKD, with similar cardiovascular
Comparative Effectiveness of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors and
In patients with albuminuric CKD, landmark randomized trials have demonstrated that angiotensin-converting-enzyme-inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin-receptor-blockers (ARBs) are superior to placebo and more
Seminal studies have showed that RAS blockers present significant renoprotective effects in CKD patients with very high albuminuria. In post hoc analyses of such trials, these renoprotective
Our findings provide evidence from real-world clinical practice that initiation of RAS inhibitor therapy compared with CCBs may confer kidney benefits among patients with advanced CKD,
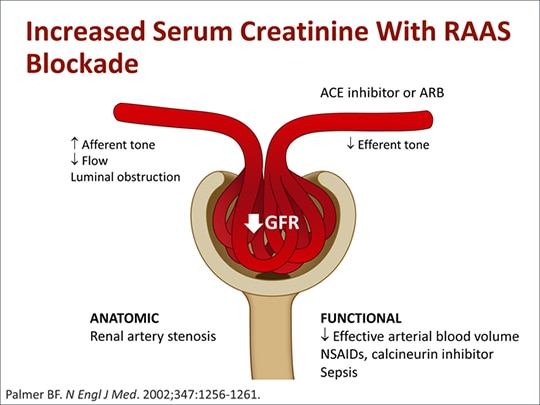
Hyperkalemia (serum potassium [K +] >5.0 or >5.5 mEq/L) is a potentially life-threatening complication of chronic kidney disease (CKD).Risk factors for hyperkalemia in
- ACEing the management of advanced CKD — NephJC
- Management of Hyperkalemia in Patients with Chronic Kidney
- Managing RAAS inhibitor use in advanced CKD.
- Renin–Angiotensin System Inhibition in Advanced
This is a comment on „Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibition in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease.“ N Engl J Med. 2022 Dec 1;387(22):2021-2032. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2210639.
Determining if medications can be changed if they precipitate hyperkalemia as well as considering novel drug combinations are excellent initial suggestions to manage
Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated that renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade with either angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers
Background: It is unknown whether stopping renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor therapy in patients with advanced CKD affects outcomes. Methods: We studied patients referred to
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors (RAASi) have been repeatedly demonstrated to significantly slow progression of CKD in randomized controlled trials conducted in adults (1, 2).
Because RAAS inhibitors are commonly used in CKD patients who have diabetes mellitus and/or heart failure, these comorbidities put CKD patients at risk of hyperkalemia. Table 22.2
inhibitors (RAASi) therapy in patients with CKD and heart failure. In advanced stages of CKD, 40 to 50 percent of patients suffer from hyperkalaemia, particularly those with diabetes mellitus
Ongoing RAS inhibitor use has been historically chal-lenging in patients with advanced CKD, particularly those with diabetes, where hyperkalemia may be difficult to
- Challenges of managing hyperkalemia in HF patients with CKD
- Should we discontinue RAS-inhibitor therapy in patients with advanced CKD?
- Managing RAAS inhibitor use in advanced CKD
- Comparative Effectiveness of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors and
How to categorise CKD and frequency of monitoring 3 When to refer 3 3 step solution for management of CKD 4 Renin -angiotensin aldosterone system ( RAAS) blockade 5 5 Blood
RAAS inhibitor use in late stage CKD (stages 4 and 5) [5]. This study was designed to test the hypothesis that discon-tinuation of RAAS inhibitors in late stage CKD may have a beneficial
Originally developed for use in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), sodium–glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors demonstrated diverse cardiovascular- and kidney-protective effects in large outcome trials. Their
RASi are supposed to be our trusty sidekick in CKD management, but their use in advanced stages is backed by evidence so scarce it feels like trying to build a skyscraper with
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a global health problem and is strongly associated with hypertension (HTN) and impaired quality of life. Managing HTN with agents
Ongoing RAS inhibitor use has been historically challenging in patients with advanced CKD, particularly those with diabetes, where hyperkalemia may be difficult to manage. 6, 7 This
We discuss our approach to optimizing RASi use in patients with CKD and high BP, guided by the recommendations and practice points from the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes
Two newer potassium binders, patiromer and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (ZS-9), have been shown to effectively and safely reduce serum potassium levels and maintain long-term
RAS blockade is a pillar of proteinuric CKD management, questions remain around whether they can be safely continued in patients with advanced CKD and whether they
Background: Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitors – including angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) – slow the
people with type 2 diabetes, nephropathy and/or early CKD stages 1 Use of direct renin inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy.. 26 When should RAAS blockade be stopped? .. 26
Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated that renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade with either angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers effectively reduces
Overactivity of RAAS contributes to the pathogenesis of a variety of clinical conditions including progress of chronic kidney disease (CKD). This review summarizes the
RAAS inhibitor use was associated with a 41% increased risk of hyperkalemia (OR: 1.41; 95% CI 1.37–1.44). 30 After multivariate adjustment, the incidence of hyperkalemia
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors are evidence-based therapies that slow the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) but can cause
Current data supports the use of GDMT in patients with HF, which includes RAAS inhibition (with or without neprilysin inhibition), mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism, and
- Was Bedeutet Abscheiden – Abscheidung Definition
- What’s Special About Gujaratis And Where Does The Gujarati
- Is Minneapolis Safe For Travelers? What To Know From A Local
- Arbeitszeiten Kaufmann Im Einzelhandel
- Terajoule To Terawatthour: Tj To Terawatt Converter
- Berufliche Stellung – Berufliche Stellung Fragebogen
- 2 Raum Wohnung Mieten, Mietwohnung In Beeskow
- Elden Ring Verteilung Zurücksetzen
- Online Tintenpatronen Und Tintenkiller-Set Blau
- Efd Reinf 2024 Obrigatoriedade
- Maze The Walking Dead Breakout Im Movie Park Im Video
- Dog Man: The Scarlet Shedder: A First-Person Review
- Flämische Einfach Erklärt – Was Bedeutet Flämisch
- Nur Einer Kam Durch – Einer Kam Durch Wikipedia
- Stop Fahrwerksfehler Lock Taste Vergessen Beim Anheb.