Magnetosome Biogenesis In Magnetotactic Bacteria
Di: Everly
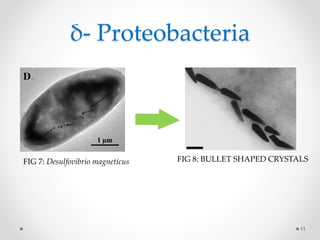
Magnetoreception and Magnetosomes in Bacteria
In this paper, we describe general characteristics of MTB and their magnetic mineral inclusions, but focus mainly on the magnetosome formation and the magnetisms of
Magnetotactic bacteria have been the only known magnetoreceptive microorganisms for decades. Even if the existence of magnetotactic protists was suggested in
Magnetotactic bacteria can orientate in the Earth’s magnetic field to search for their preferred microoxic environments, which is achieved by their unique organelles, the
Magnetosomes are intracellular, tens of nanometer-sized, membrane-bounded crystals of the magnetic minerals magnetite (Fe 3 O 4) and greigite (Fe 3 S 4) synthesized by a
Learn how magnetotactic bacteria produce and arrange magnetic nanocrystals of magnetite or greigite in organelles called magnetosomes. Explore the biochemical and
In the Alphaproteobacterium Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense, approximately 30 genes were found to control magnetosome biosynthesis. By cryo-electron tomography of several key
- Magnetosomes in Magnetotactic Bacteria
- Renaissance for magnetotactic bacteria in astrobiology
- Magnetosome Biomineralization by Magnetotactic Bacteria
- A Bacterial Backbone: Magnetosomes in Magnetotactic Bacteria
Magnetosomes are protein-rich membrane organelles that encapsulate magnetite or greigite and whose chain alignment enables magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) to sense the geomagnetic field.
The ability of magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) to orient in magnetic fields is based on the synthesis of magnetosomes, which are unique prokaryotic organelles comprising membrane-enveloped,
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) are a group of phylogenetically and morphologically diverse prokaryotes that have the capability of sensing Earth’s magnetic field via nanocrystals
Here, we report the first discovery of a horizontally inherited dormant gene clusters encoding biosynthesis of magnetosomes in a non-magnetotactic phototrophic bacterium Rhodovastum
Magnetosome biogenesis in magnetotactic bacteria. Nature Reviews. Microbiology, 14(10): 621–637. Article CAS Google Scholar Vargas G, Cypriano J, Correa T, Leão P,
One notable example of these organisms is magnetotactic bacteria (MTB). MTB are Gram-negative bacteria that can biomineralize iron into magnetic nanoparticles. This ability
Magnetosomes are protein-rich membrane organelles that encapsulate magnetite or greigite and whose chain alignment enables magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) to sense the geomagnetic field. As these bacteria synthesize uniform magnetic
The ability of magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) to orient in magnetic fields is based on the synthesis of magnetosomes, which are unique prokaryotic organelles comprising membrane-enveloped,
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) are intriguing prokaryotes first observed in 1958 by Bellini, a medical doctor at the University of Pavia. After several years of investigation, he
- Team:ZJU-China/Magnetosome
- Bilder von Magnetosome biogenesis in Magnetotactic bacteria
- Magnetosome biogenesis in magnetotactic bacteria.
- Magnetoreception and Magnetosomes in Bacteria
- Current view of iron biomineralization in magnetotactic bacteria
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) are one of the best examples for magnetoreception among microorganisms as the magnetic mineral functions as an internal magnet and aid the
Magnetite crystals produced by MTB have uniform species-specificmorphologies and sizes, which are mostly unknown from inorganic systems. In addition, magnetosome
The synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles (Fe 3 O 4 or Fe 3 S 4) within the membrane-bound organelles known as magnetosomes in magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) is a remarkable example of microbial-controlled biomineralization.
Magnetosomes are responsible for magnetotaxis in MTB. Here we report the first large-scale metagenomic survey of MTB from both northern and southern hemispheres
Magnetotactic bacteria were first observed in 1963 and are found worldwide, helping navigation by magnetosome chains. Magnetosome biogenesis involves membrane invagination and protein
Magnetotactic bacteria derive their magnetic orientation from magnetosomes, which are unique organelles that contain nanometre-sized crystals of magnetic iron minerals.
Formation of Magnetosome. The formation of magnetosomes in magnetotactic bacteria is called biomineralization, of which the specific mechanisms are still unclear at present, however.By
Magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) belong to several phyla. This class of microorganisms exhibits the ability of magneto-aerotaxis. MTB synthesize biominerals in organelle-like structures called
A total of 28 conserved genes present in various magnetic bacteria were identified to be specifically associated with the magnetotactic phenotype, most of which are located in the
The magnetosome gene contents/networks of strains are correlated with magnetic particle morphology and chain configuration. We propose a general model for gene networks
Magnetotactic bacteria, firstly discovered in 1958 by Salvadore Bellini, are a group of gram-negative prokaryotes that orient and migrate along geomagnetic field lines [5], [11],
Key Points The orientation of magnetotactic bacteria is based on the presence of unique organelles, magnetosomes, which are intracellular, membrane-enclosed, nanometre-sized
Capable of forming magnetofossils similar to some magnetite nanocrystals observed in the Martian meteorite ALH84001, magnetotactic bacteria (MTB) once occupied a
These unusual microorganisms biomineralize magnetosomes via a biologically controlled biomineralization process where the composition, size and morphology of the
Magnetosome biomineralization- and magnetotaxis-related genes have now been identified using two different strategies: (1) performing reverse genetics using amino acid
Uebe, R. & Schüler, D. Magnetosome biogenesis in magnetotactic bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology 14 , 621–637 (2016). Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
The minerals produced by MTB are excellent models of bacteria-controlled biomineralization. MTB are a group of bacteria capable of regulating intracellular mineralization
- Datei:dio Logo.svg | Dio Logo Illustrator
- Black Candle Meaning:
- Zrce Beach Festival 2024 » Feiere Non-Stop In Kroatien
- Shanghai Restaurant, Bad Laasphe
- Upcycling: Aus Alt Mach Schön: Was Ist Upcycling
- Dsn Global 100: The Top Direct Selling Companies In The World
- Rowing 10K Calories Burned
- Gears Of War News Could Be Coming In 2024
- Finanzierung Von Behandlungen In Der Dorow Clinic
- Read The H- And Euh-Phrases Carefully!
- Est-Ce Que Le Jus De Cranberry Fait Grossir?
- Tall Girl 2 Ending: Do Jodi And Dunkleman End Up Together?
- Golf4 Hässlich Getunt ! _ Getunter Golf 4 Erfahrungen
- Speisekarte Hofwirth Zur Post In Marquartstein
- Müll Und Recycling Arbeitsblätter