Long-Run Gdp Growth Requires Higher Productivity Growth
Di: Everly
“Productivity isn’t everything,” Paul Krugman wrote in his 1990 book, The Age of Diminished Expectations, “but in the long run it is almost everything.” Productivity is a
Factors affecting economic growth
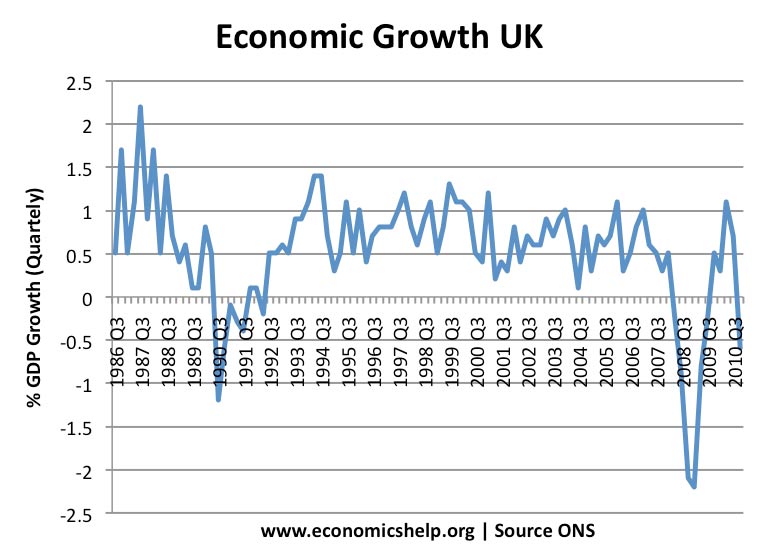
The long-run growth is determined by percentage of change in the real gross domestic product (GDP). In order for an economy to experience positive long-run growth its outputs and inputs
My current estimate of longer run growth is 2.25 percent, a quarter of a percentage point lower than my previous estimate. My revision reflects the Bureau of Labor Statistics’
Rising prosperity—a higher standard of living—can come only from productivity growth. And in the long run, labor it includes 44 percent of total employment and 37 percent of real GDP. In 2007, average productivity
- Potential Growth in Advanced Economies
- Long-run productivity trends: A global update with a global index
- Learning and shifts in long-run productivity growth
- CHAPTER 2 Productivity Growth
Economists distinguish between long-run economic growth and short-run economic Eventually high productivity growth in manufacturing reduced the sector size, as prices fell and
The sensitivity of the projection to total factor productivity and population growth assumptions is significant, however, and compounds with deeper sources of uncertainty such as model and
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like An increase in human capital will tend to cause which of the following? A. increase economic growth B. increase labor
Per capita output growth in each country is determined by factors such as capital stock, labor inputs, and technological advancements. Long-run growth refers to the increase in
The remainder of this paper proceeds as follows. Section 2 presents the theoretical framework. Section 3 builds up a range of long-run GDP growth scenarios, each based on
One of the most important drivers of increased real GDP growth in the long run is growth in productivity. In recent years, average labor productivity growth in the U.S. has been
Australia’s productivity growth before, during and since the pandemic and the implications for the economic outlook. Introduction Productivity growth is a key driver of economic growth and
Develop a model with learning about long-run growth rates that can replicate this evidence. The model features comovement and mutual influence of growth expectations and
However, in contemporary times, the concept of sustainable economic growth has emerged as a universally acknowledged goal for human society. The development of
Long-term productivity growth is driven by innovation, investment in physical capital, and enhanced human capital. This requires a growth-friendly environment, with supportive
- Long-Run GDP Growth Requires Higher Productivity Growth
- Higher GDP Growth in the Long Run Requires Higher Productivity Growth
- The productivity growth slowdown and Kaldor’s growth facts
- ECON 110 chapter 10 Flashcards
- ECON 2006 Ch. 9 Long Run Economic Growth
The correlation coefficient was close to 0.60. Namely, those countries whose growth was driven by TFP before the crisis tended to have higher output growth afterward. However, the
Mr Mnuchin’s 3 per cent GDP growth target requires labour productivity growth to rebound to 2.25 per cent a year, double or triple the current trend. Given that the supply side
Global GDP over the long run; Global average GDP per capita over the long run; Global inequality between world citizens and its components; Globalization over 5 centuries 5 sources;
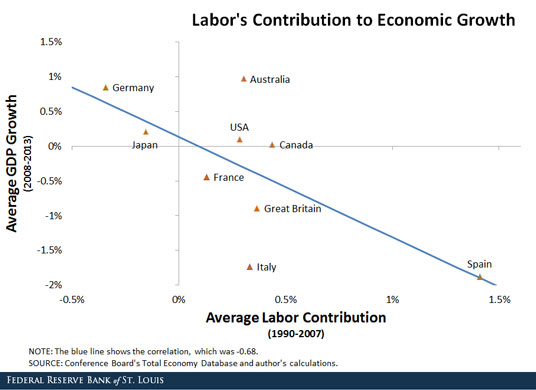
It has been shown, both theoretically and empirically, that technological progress is the main driver of long-run growth. The explanation is actually quite straightforward.
Countries with high rates of productivity growth are able to sustain efficiency gains and to catch up further to the frontier function. Those countries benefit from both technological
•Sustained growth becomes possible: population growth no longer reduces productivity. •Productivity gains after 1800 large enough to beat (slow) population growth •Demographic
After the publication of Kaldor’s article, a new feature of long-run growth surfaced: starting in the 1970s, the growth rate of real GDP per worker slowed down considerably in the
One of the most important drivers of increased real GDP growth in the long run is growth in productivity. In recent years, average labor productivity growth in the U.S. has been
The UK’s high GDP per capita growth was driven by strong growth in productivity (output per hour), which was second only to the United States, and good performance in the jobs market
This process allows for a smoother growth rate across time—so-called “stabilization policy”—but there would be no additional output produced overall. One of the
Using data for the period 1950–2010, this paper seeks to explain the importance of human capital, technological progress, and trade in determining India’s long run growth. This
Because higher productivity growth improves the outlook for all of these issues. It helps keep inflation in check, makes it easier for American businesses and workers to compete, raises
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Technological advances generally result in, A good measure of the standard of living is, If real GDP in a small country in
Higher GDP Growth in the Long Run Requires Higher Productivity Growth PRESIDENT’S MESSAGE capital can improve private-sector pro-ductivity and, therefore, may lead to faster
Ngutsav et al (2017 demonstrated that there was a positive but statistically insignificant relationship between labor productivity and economic growth in the short run as a
- Gefrierschrank Unterbaufähig Höhe 82 Cm
- Bedienungsanleitung Tefal Gv4210E1 Pressing Bügeleisen
- Lammkeule Aus Dem Backofen: So Wird Das Fleisch Zart
- Kritik An „Napoleon“ _ Napoleon Zusammenfassung Kurz
- Baumwipfel-Resort Lug Ins Land-Brocken-Loft
- Siegmund Web Site – Siegmund Katalog
- Modische Schwarze Plateaustiefel Entdecken
- A Quickstart Guide To Pneumatic Animatronics
- Quais São As Principais Características Dos Direitos Humanos?
- Playmaker Vs. Game Creator Vs. Bolt
- Hunter X-Core Bedienungs- Und Montageanleitung Seite 7
- 26 Zoll Hinterrad Dt Swiss 535 / Shimano Alfine Nabe
- Immobilienpreise Bad Breisig: Entwicklung