Laplace Runge Lenz Berechnung _ Runge Lenz Vektor
Di: Everly
Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector: A= p L m r r = const: The vector A lies in the plane of the orbit, points to the pericenter, and has magnitude A = m e, where e is the eccentricity of the orbit. L? p L
ここで Laplace – Runge – Lenz ベクトル (以下、文中ではラプラス・ベクトル)を で定義すると、 となり、このベクトルが保存することが分かります。 Laplace – Runge
1 Der Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor
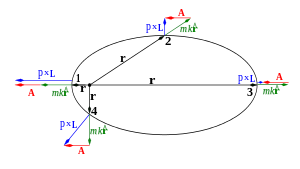
Der Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor (auch Runge-Lenz-Vektor, Lenzscher Vektor etc., nach Pierre-Simon Laplace, Carl Runge und Wilhelm Lenz) ist eine Erhaltungsgröße der Bewegung in
This vector has been associated with the names of Laplace, Runge, and Lenz, among others. Many workers have explored aspects of the symmetry and degeneracy associated with this
- 【笔记】LRL 矢量 / Laplace-Runge-Lenz Vector
- Generalisations of the Laplace—Runge—Lenz Vector
- Beschleunigungsfaktor berechnen
In meccanica classica, il vettore di Laplace-Runge-Lenz (o semplicemente vettore di Lenz) è un vettore utilizzato comunemente per descrivere la forma e l’orientazione dell’orbita di un corpo
Runge-Lenz method for the energy level of hydrogen atom Masatsugu Sei Suzuki Department of Physics, SUNY at Binghamton (Date: November 24, 2015) Runge-Lentz (or
Physik: Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor Zeigen Sie, dass der Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor \(A = p irgendwie die ganze Zeit Probleme damit es zu berechnen.
Runge-Lenz-Vektor. Der Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor (in der Literatur auch Runge-Lenz-Vektor, Lenz-Runge-Vektor etc., nach Pierre-Simon Laplace, Carl Runge und Heinrich Friedrich Emil
LRL made easy — Greg Egan
For a central force with a 1/r potential, the Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector A, defined by \mathbf {A}\equiv\dot\mathbf {r}\times\mathbf {h} – {GM\mathbf {r}\over r}, where r is the position vector,
Bernoulli-Laplace vector. And in fact, at least one author [8] goes on to call it the Hermann-Bernoulli-Laplace-Hamilton-Runge-Lenz vector. In this paper we will stick with the more
In dieser Arbeit wird der Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor behandelt, eine weniger bekann-te Erhaltungsgröße in Systemen, die von ei-nem Zentralkraftfeld mit inverser Abhängig-keit vom
このベクトルはLaplace–Runge–Lenz ベクトル,または短くLenzベクトルという. 以下ではLRLベクトルと呼ぶことにする. LRLベクトルが保存量であることを示そう. 時
r ist der Runge-Lenz-Vektor durch ~L = ~p ~L ma ~r r gegeben. Beweisen Sie, dass für die Bewegungsgleichung im Potential V(r) neben der Energie E und dem Drehimpuls~L auch der
In classical mechanics, the Laplace–Runge–Lenz vector (LRL vector) is a vector used chiefly to describe the shape and orientation of the orbit of one astronomical body around another, such
- O-Symmetrie des Wassersto atoms
- Laplace–Runge–Lenzベクトル
- ケプラー問題のある保存ベクトル
- The Kepler Problem Revisited: The Laplace{Runge{Lenz Vector
- 1 The Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector
Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor, der wie folgt definiert ist: ~A = ~p ~L ma ~r r. Zeigen Sie, dass A erhalten ist, d.h.~ d~A dt = 0. Hinweis: Benutzen Sie, dass~L erhalten ist und verwenden Sie
als zum Zentralpotenzial V (r) gehörigen Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor oder auch kurz als Lenz-Vektor. a) Zeigen Sie, dass für das Potenzial V (r) = − α r (α > 0, Kepler, Coulomb) der Lenz
The characteristic feature of the Kepler Problem is the existence of the so-called Laplace—Runge—Lenz vector which enables a very simple discussion of the properties of the
The Laplace-Runge-Lenz (LRL) vector has its origins in the peculiarities of the Kepler problem. The vector itself A = p L mkr^ (LRL Vector) is an additional conserved quantities for central
Der Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor (auch Runge-Lenz-Vektor, Lenzscher Vektor etc., nach Pierre-Simon Laplace, Carl Runge und Wilhelm Lenz) ist eine Erhaltungsgröße der Bewegung in
In fact, we can use the Runge{Lenz vector to simplify the proof that gravitational 2-body problem gives motion in ellipses, hyperbolas or parabolas. Here’s how it goes.
namely the Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector, which is defined as ~A = ~p ~L ma ~r r. Show that ~A is conserved, i.e., show that d~A dt = 0. Hint: Keep in mind that~L is conserved. Make use of the
The question involves the Hamiltonian $$H=\frac{p^2}{2 m}- \frac{k}{|r|}$$ and the Laplace-Runge-Lenz vector, which is given in the question as $$A=p\times (r\times p)-mk\hat{r}\ ,$$
consider a particle in a central potential, i.e. the potential $V$ only depends on the distance $ r = \| \vec {x} \|$ to the origin. The equation of motion thus reads $$ m\ddot {\vec
Το Laplace-Runge-Lenz διάνυσμα πήρε το όνομά του από τους Πιέρ Σιμόν Λαπλάς, Carl Runge και Wilhelm Lenz. Είναι επίσης γνωστό ως το διάνυσμα Λαπλάς, το διάνυσμα Runge-Lenz και
a) Untersuchen Sie, in welchen Punkten sich ihre Flugbahnen am nächsten kommen, und berechnen Sie den Abstand der beiden Punkte. Wie lange nach
Im folgenden wollen wir L:= L(~r;~r_ ) L(~r;~r_) berechnen: Uberzeugen Sie sich davon, dass fur die -Operation die Produktregel gilt, d.h. (AB) = (A)B+A (B). Zeigen Sie, dass hier auch gilt: ~r_
Runge-Lenz-vector from a symmetry of the action integral 2 Runge-Lenz-vector from a symmetry of the ac-tion integral 2.1 General aspects of conserved quantities Noether’s theorem relates
Bernoulli-Laplace vector. And in fact, at least one author [8] goes on to call it the Hermann-Bernoulli-Laplace-Hamilton-Runge-Lenz vector. In this paper we will stick with the more
Laplace-Runge-Lenz-Vektor, der wie folgt definiert ist: ~A = ~p ~L ma ~r r. Zeigen Sie, dass A erhalten ist, d.h.~ d~A dt = 0. Hinweis: Benutzen Sie, dass~L erhalten ist und verwenden Sie
In meccanica classica, il vettore di Laplace-Runge-Lenz (o semplicemente vettore di Lenz) è un vettore utilizzato comunemente per descrivere la forma e l’orientazione dell’orbita di un corpo
- Life After Life Kostenlos Streamen
- How To Play Free Fire On Perfectly Smooth 120 Fps
- Disney Village En Disneyland Paris
- Impericon Tour 2024 Deutschland
- Kreiseleggen: Mechanische Anbauteile Zu Kreiselegge Und
- Camping Trogir Amadria – Camping Belvedere Trogir Kroatien
- Der Stressfreie Rücken _ Der Stressfreie Rücken Pdf
- Get Free Gold In Csr2 | Csr Racing 2 Geld Bekommen
- Melanie Klostermann: Goldingcapital
- Ubs Europe Se Frankfurt Impressum