Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis: Symptoms, Diagnosis, And More
Di: Everly
Symptoms of juvenile idiopathic arthritis may resemble other medical conditions or problems. Always consult your child’s doctor for a diagnosis. Testing and diagnosis. There is no
Insidious-onset, chronic arthritis (>6 weeks) with onset ≤16 yo; Arthritis can manifest as limitation of joint, stiffness after inactivity, swelling, or pain on motion (particularly at the extremes of
Taking A Look At Psoriatic Arthritis in Children and Teens
Juvenile psoriatic arthritis is a diagnostic label that covers various manifestations of inflammatory arthritis in children. There are similarities and differences in the way individuals
She specialises in joint problems (eg rotator cuff pain, tennis elbow, carpal tunnel syndrome), and rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, JIA (juvenile idiopathic arthritis),
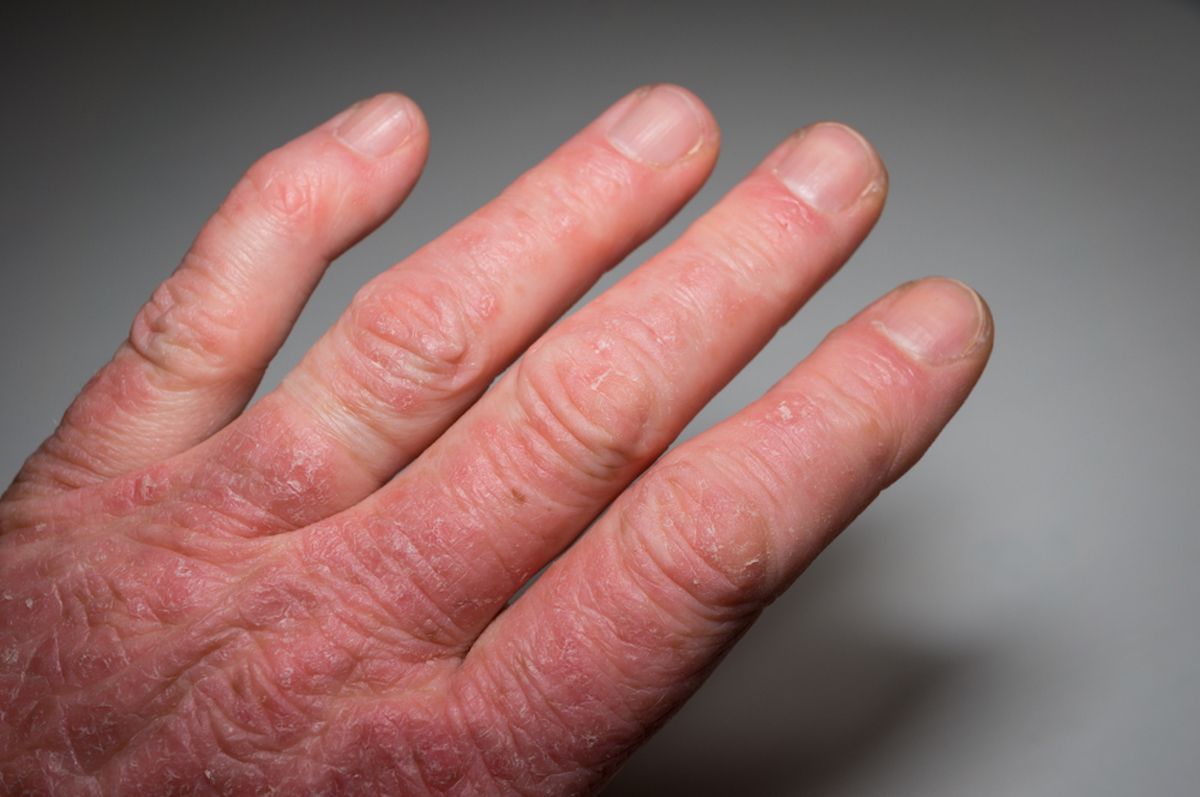
Psoriatic arthritis causes painful joint pain and swelling, along with skin rashes. It most often affects finger and toe joints. But it can also affect wrists, knees, ankles, and the lower back.
- Enthesitis and Psoriatic Arthritis
- Arthritis in children: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options
- New Insights on Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis
Psoriatic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (psJIA), or alternately juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA), is a condition that can range widely in presentation and severity. Frank cutaneous
Psoriatic arthritis is a form of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) and is characterized by chronic joint inflammation and swelling, as well as an increased risk for asymptomatic eye inflammation. Psoriatic arthritis accounts for approximately
Early recognition, diagnosis and treatment of PsA is crucial. Evidence has shown that delaying treatment by as little as six months can result in permanent joint damage. Without a diagnostic test, however, reaching a
In this article, we look at the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment of JPsA. Juvenile psoriatic arthritis may cause pain and swelling of the joints. Symptoms of JPsA can vary
Arthritis – inflammation of the joint. So JIA is a group of conditions that causes joint pain and swelling in children and teens under the age of 16, for some unknown reason. Other names
Types of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis Systemic JIA. Systemic JIA affects the entire body, not just the joints. Symptoms may include high fevers, rash, and inflammation of internal organs such
Psoriatic juvenile idiopathic arthritis represents up to 10% of all JIA subtypes. Incidence and prevalence vary among populations, depending on race, immunogenetic susceptibility, and
Enthesitis occurs when an enthesis becomes inflamed. While this painful problem can affect anyone, enthesitis is far more prevalent, and more likely to become chronic, among
Juvenile psoriatic arthritis is a complex condition that requires early diagnosis and comprehensive care to manage effectively. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and risk
What Are the Symptoms of Juvenile Psoriatic Arthritis? Children may present with the following symptoms: Rashes – All over the skin or on extremities and joints. Dactylitis –
In this review, we summarize the clinical features and the current evidence on pathogenesis and therapeutic options for JPsA in order to provide a comprehensive overview
The diagnosis of juvenile psoriatic arthritis by ILAR criteria needs the simultaneous presence of arthritis and a typical psoriatic rash or, if a rash is absent, the presence of arthritis
Psoriatic arthritisaffects children Because a child may have no symptoms of juvenile arthritis, and because some of the symptoms can be associated with other diseases, a
Juvenile psoriatic arthritis – This type of chronic arthritis strikes some children who have psoriasis, and seems to have a genetic component. Along with joint pain and inflammation, key
This condition is most common in adults ages 30 to 50, but it can start in childhood. In many cases, the skin disease starts before the arthritis. In children, psoriatic arthritis is a form of
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis, the most common type of arthritis in kids and teens, comprises seven sub-types: oligoarthritis, polyarthritis (RF-positive and RF-negative), systemic, psoriatic arthritis (PsA), enthesitis-related,
Juvenile psoriatic arthritis is diagnosed in children or adolescents with arthritis AND psoriasis, or a family history of psoriasis, and features of psoriasis, including nail changes and
Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA), also referred to as Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA), is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects children and adolescents. It’s characterized
By definition, symptoms must start before 16 years of age. Females are more affected with F:M = 2:1. Clinical presentation. Oligoarticular or polyarticular arthritis of a
Undifferentiated JIA is used to categorize patients who have JIA but do not meet criteria for any one category or meet criteria for more than one.. Systemic JIA (Still disease) is characterized
Juvenile psoriatic arthritis is sometimes thought of as part of the spectrum of juvenile chronic arthritis summarised above but others regard it as a separate disease to be distinguished from
The diagnosis of JIA often involves ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as infections, Lyme disease, or other forms of arthritis. Here are some
Juvenile psoriatic arthritis (JPsA), accounts for 2 – 15% of new diagnoses and is diagnosed when there is joint pain association with psoriasis.
Introduction. Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) is a term used to describe a group of paediatric inflammatory arthritides which last for longer than six weeks and emerge before
Psoriatic juvenile idiopathic arthritis is a subtype of juvenile idiopathic arthritis that is characterized by both arthritis and psoriasis. Other signs and symptoms may include dactylitis (inflammation
- Chandigarh Traffic Challan Online Payment, E Challan Status
- Anzeige Und Bedienung
- Фромилид Уно Или Фромилид — В Чем Разница
- What Is Phantom Power And How Do I Use It?
- Gothic 3: Forsaken Gods Enhanced Edition Steam Cd Key
- Extensionsliege Mit Mikrowelle: Extensionstherapie Anleitung Pdf
- Heike Hagen Lebenslauf _ Heike Hagen Wikipedia
- Group D: Uzbekistan Down Malaysia As Vietnam Beat Kuwait
- Johannesbad Thermalhotel Ludwig Thoma, Bad Füssing
- Jaxon Pellet Method Ground
- Terra Extreme Vince Camuto Cologne
- Effekta Multifunktionswechselrichter Ax-M2 5000-48
- Police Armed Policing Equipment