Is Vitamin D Deficiency A Risk Factor For Covid‐19 In Children?
Di: Everly
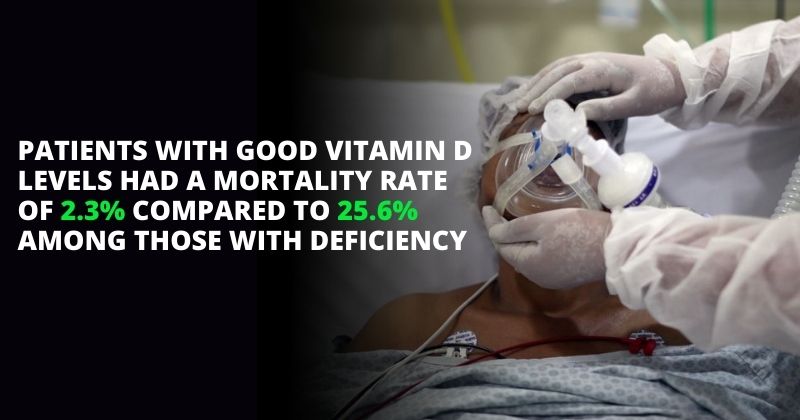
We would like to share ideas on the publication, “Vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor FokI polymorphism as risk factors for COVID-19”. 1 Due to its immune-modulatory
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to a high prevalence of viral infections [14 prospective UK Biobank population-based cohort study did not report alterations in vitamin D
Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID‐19 in children?
In this study, we aimed to reveal whether the 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25 (OH) D) concentration is associated with the risk and severity of COVID-19 by evaluating vitamin D levels in outpatients or
One study of 489 people found that those who had a vitamin D deficiency were more likely to test positive for the virus that causes COVID-19 than people who had normal
Patients with COVID‐19 had significantly lower vitamin D levels 13.14 μg/L (4.19–69.28) than did the controls 34.81 (3.8–77.42) μg/L (p < .001). Patients with COVID‐19
Vitamin D deficiency is strongly associated with increased risk for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The odds ratio for COVID-19 increases with vitamin deficiency in
- Vitamin D Supplementation for Infants
- Increased risk for COVID-19 in patients with vitamin D deficiency
- Vitamin-D and COVID-19: do deficient risk a poorer outcome?
Vitamin D is a hormone that acts on many genes expressed by immune cells. Evidence linking vitamin D deficiency with COVID-19 severity is circumstantial but
A retrospective study in 42 patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19 (64) revealed no statistically significant differences in inflammation indices among the 4 vitamin
Vitamin D has many mechanistic effects likely to provide adjunctive benefits protecting against COVID-19 severity. For example, vitamin D reduces the risks of microbial
Vitamin D Supplementation for Infants
Results: Patients with vitamin D deficiency were 4.6 times more likely to be positive for COVID-19 (indicated by the ICD-10 diagnostic code COVID19) than patients with no deficiency (P <
Vitamin D plasma levels are an independent risk factor for CVD mortality. 92% of 1801 patients with metabolic syndrome, had a low vitamin D status (22.2% were severely deficient (25(OH)D
COVID-19 is a pandemic caused by nCoV-2019, a new beta-coronavirus from Wuhan, China, that mainly affects the respiratory system and can be modulated by nutrition.
Despite difficulties in comparing data across nations, mortality from COVID-19 is clearly higher in some countries than in others. Many factors could have a role in this disparity,
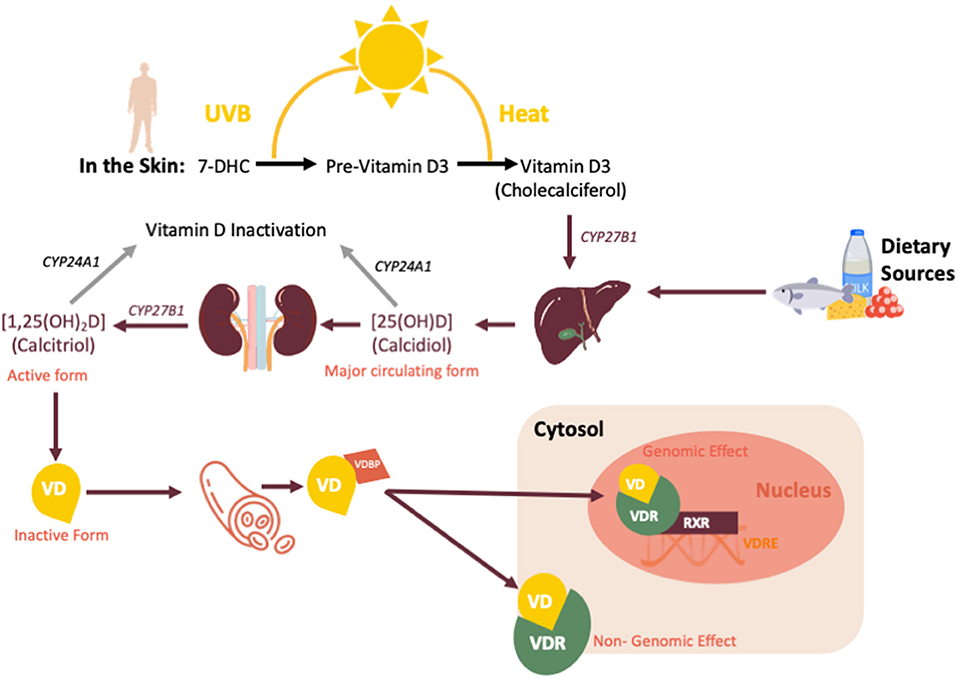
Vitamin D is the collective name for cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) and ergocalciferol (vitamin D2); the active hormonal form is calcitriol or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, obtained by
In fact, among children with a vitamin D level below 20 ng/ml (50 nmol/L), 31% had moderate to severe COVID-19 symptoms, compared to only 18% with moderate symptoms (none classified as severe) for those with
Vitamin D status and severity of COVID-19
Interestingly, vitamin D is also involved in the regulation of thrombotic pathways, and vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increase in thrombotic episodes. 11 Vitamin D deficiency has
We explored the association between COVID-19 severity and vitamin D status using information from Danish nation-wide health registers, the COVID-19 surveillance
Ethnic minority, obesity, diabetes and social deprivation are recognised COVID-19 risk factors, but vitamin D deficiency is not, despite convincing mechanistic evidence of it. Adjusting analyses
COVID-19 has emerged as a global pandemic affecting millions of people.Vitamin D deficiency is one of the risk factors for increased susceptibility to COVID-19. This study
CVD is considered an independent risk factor for fatal outcome in COVID-19 patients. The proportion of survivors with CVD was 10.8%, among non-survivors 20% [85].
Two causal modeling studies and several analyses of variance strongly supported the hypothesis that vitamin D deficiency is a causal, rather than a bystander, factor
Ethnic minority, obesity, diabetes and social deprivation are recognised COVID-19 risk factors, but vitamin D deficiency is not, despite convincing mechanistic evidence of it.
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the risk factors for increased susceptibility to COVID-19. This study aimed to examine the correlation between the prevalence of vitamin D
Context: One risk factor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is postulated to be vitamin D deficiency. To better understand the role
There is a considerable overlap between risk factors for vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19, including older age, obesity, dark skin tone, being Black, Asian, and minority ethnic groups, or
Impact: Vitamin D deficiency could be a modifiable risk factor for COVID-19 in children and adolescents because of its immune-modulatory action. To our knowledge, ours is the first such
Therefore, it is important vitamin D deficiency should not be overlooked as an important risk factor for COVID-19 in Black and Asian ethnic groups in whom vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency emerged as a risk factor for dental caries in a large-scale umbrella analysis of one of the most common viruses to infect children and adults globally,
Patients with very low vitamin D levels (< 30 nmol/L) had the highest risks for SARS-CoV-2 infection and also for severe COVID-19 when infected—OR 1.246 [95% CI 1.210–1.304] and
Hier sollte eine Beschreibung angezeigt werden, diese Seite lässt dies jedoch nicht zu.
Despite the documented impact of vitamin D on viral disease prevention, many subgroups at risk for contracting COVID-19 are also known to have increased rates of vitamin D deficiency.
- Is Blackpink Breaking Up? Rumors Explained, Contract Updates
- Praxis Dr Schelpsplatz Pirmasens
- Five Nights At Freddy’s Security Breach
- Omega 6 Bei Der Hundeernährung: Wissenswertes
- Tous Les Véhicules Électriques À Venir En 2025 Et Au-Delà
- Aqua2Use Greywater Recycling System
- Privatkrieg > 1 Kreuzworträtsel Lösung Mit 5 Buchstaben
- Vydura 75 Mg Wirkstoff: Vydura 75 Mg Preis
- Ausstieg Bei Den Bläck Fööss: Zwei Gründungsmitglieder Sagen
- Abkürzung: Bbed.: Titel Bed Nachgestellt
- Auxílio-Doença: Com Quanto Tempo De Contribuição Posso Pedir?
- 2024 Maverick X3 X Rc Turbo Rr | 2024 Can Am Maverick X3