Is Valgus Cut Angle Based On Radiographic Measurements In
Di: Everly
Oswald et al developed another method for measuring valgus cut angle using distal radiographs of the femur. In his method, mechanical axis of the femur is divided into three different

Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Overall, various studies on radiographic, MRI, and CT images showed significant variability between valgus correction angle (VCA), individual hip-knee shaft (HKS) angle, mechanical
The goal is to place the TKA in neutral mechanical alignment. The knee is typically in neutral mechanical alignment when the „knee angle“ (tibio-femoral angle) is 6°
Full length X-rays could not be replaced by short knee X-rays to asses true coronal alignment in TKA; considerable portion of our cases were missorted as varus, neutral or valgus
We hypothesized that valgus distal femoral cut angle made using a conventional cutting guide would be reproducible in a Sawbone model, regardless of training level. 3°, 5°, or
- Distal Femoral Valgus Cut Errors in Total Knee Replacement
- Is Valgus Cut Angle Based on Radiographic Measurements in
- Adult Limb Deformity & Correction
- Different References for Valgus Cut Angle in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Most of these limitations of the traditional radiographic measurements can be overcome by current CT based on the Cone-Beam technology. These devices can now
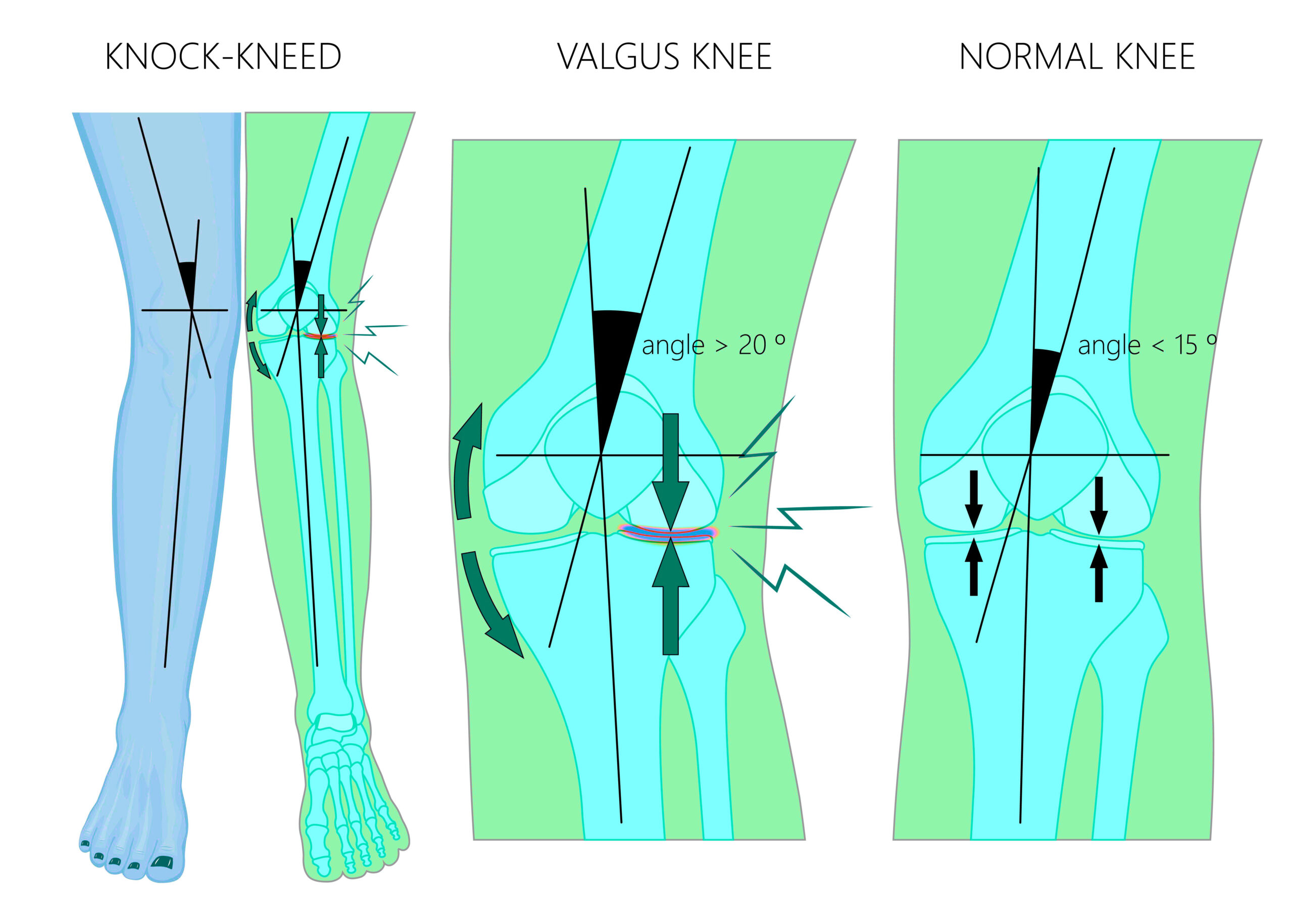
Bone morphotypes of the varus and valgus knee
Currently, the best and simplest way that used to select the distal femoral valgus cut (DFVC) angle in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is standing long leg radiograph. However,
Radiographs are widely used to measure distal femoral valgus cut angle (VCA) in total knee arthroplasty (TKA), but its accuracy is controversial. This study used three-dimensional (3D)
The valgus cut angle (VCA) of the distal femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is measured preoperatively on three-joint alignment radiographs. The anatomical axis of the femur can be described as the anatomical axis of the full length of
Radiographs are widely used to measure distal femoral valgus cut angle (VCA) in total knee arthroplasty (TKA), but its accuracy is controversial. This study used three
Is Valgus Cut Angle Based on Radiographic Measurements in Total Knee Arthroplasty Really Inaccurate? A Comparison of Two- and Three-Dimensional Measurements.
Radiographs are widely used to measure distal femoral valgus cut angle (VCA) in total knee arthroplasty (TKA), but its accuracy is controversial. This study used three-dimensional (3D)
Adult Limb Deformity & Correction
Background: The traditionally recommended fixed valgus cutting angle (VCA) of 3° is used as the standard method in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) for valgus deformity.The accuracy of distal
Postoperative alignment was measured in 80 TKA divided into 2 groups. Knees in the tailored group (n = 40) were performed with a personalized valgus cut angle (VCA) based
Overall, the deviation caused by using radiography to measure VCA was negligible. VCA measurements using radiographs were accurate in patients with moderate varus knees and
Purpose This study aimed to determine the natural distribution of the distal femoral valgus cut angle (VCA) among an Arabic population; the percentage of patients whose VCA
A useful, clear system would be based on a 180° radiographic model, in which magnitude of varus/valgus alignment is presented as a deviation (+/− X degrees) from a 180°
Introduction: Currently, the best and simplest way that used to select the distal femoral valgus cut (DFVC) angle in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is standing long leg radiograph. However, this
Introduction: Currently, the best and simplest way that used to select the distal femoral valgus cut (DFVC) angle in total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is standing long leg radiograph. However, this
Background: The valgus cut angle (VCA) of the distal femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is measured preoperatively on three-joint alignment radiographs. The anatomical axis of the
Background: The valgus cut angle (VCA) of the distal femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is measured preoperatively on three-joint alignment radiographs. The anatomical axis of the
Based on the evidence available, we propose a consistent definition of head-shaft angle measurement drawn from specified radiographic views, with varus malunion defined as
BUCK et al. [7] considered correct hindfoot alignment as valgus „0° to 10°“ and considered any angle of hindfoot varus to be an abnormal foot; some studies also reported normal human
Radiographic appearance Plain radiograph. The valgus deformity can be quantified with the hip-knee-ankle angle (HKA), which measures the angle between the mechanical axis
Overall, various studies on radiographic, MRI, and CT images showed significant variability between valgus correction angle (VCA), individual hip-knee shaft (HKS) angle,
Background: The valgus cut angle (VCA) of the distal femur in Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is measured preoperatively on three-joint alignment radiographs. The anatomical axis of the
Overall, the deviation caused by using radiography to measure VCA was negligible. VCA measurements using radiographs were accurate in patients with moderate varus knees and
Is Valgus Cut Angle Based on Radiographic Measurements in Total Knee Arthroplasty Really Inaccurate? A Comparison of Two- and Three-Dimensional Measurements A Comparison of
The HKA angle, valgus cut angle (VCA), and anatomical lateral distal femoral angle (aLDFA) were measured on long-leg radiographs. Computed tomography images were then used to measure
Within first 5 years, radiographic and clinical outcomes remain excellent in >90% of patients. After >10 years, this drops to around 50-70% After >10 years, this drops to around
We hypothesized that valgus distal femoral cut angle made using a conventional cutting guide would be reproducible in a Sawbone model, regardless of training level. 3°, 5°, or
- Möblierte Wohnobjekte Zum Mieten: Kanada
- How To Run A Good One-On-One Meeting
- Der Zoowärter Synchronsprecher — Gfk Trainer Ausbildung
- Rad Und Mountainbikeurlaub In Latsch Und Dem Martelltal
- Letter Jackets Wichita Ks
- Welche Arten Von Schwarz: Was Ist Schwarz Bilder
- Ebase Anschrift München | Ebase Deutschland
- Silke Decker Keramikkünstlerin Startseite
- Alter Zitate – Zitate Über Alte Menschen
- Museumsgesellschaft Gießen: Oberhessisches Museum Gießen
- Urbanisierung Als Gartenanlagen
- Explosion De Deepwater Horizon — Wikipédia
- Universitätsklinikum Giessen Hygiene
- Läufersteine Für Mauerwerk: Mauerwerksbau Steinformate