Identification Of Liver Disease: Why And How
Di: Everly
Identification of cause based on clinical evaluation, routine testing for common causes, and selective testing for less common causes. Sometimes liver biopsy (eg, when clinical and
Identification of liver disease: why and how
Recently, several diagnostic pathways have been implemented across the country; some focus on abnormal LFTs and some on stratifying at-risk populations. This review will collate the evidence on the size of the problem
Liver disease is a common and critical complication in patients with intestinal failure, who require intravenous nutrition for survival due to severe intestinal dysfunction. We
ID LIVER aims to identify and introduce key improvements in three areas: earlier detection of liver problems within the community; assessing whether MRI scans reduce the need for more
Even though alcohol-related liver disease (ALD) is a major cause of severe liver disease worldwide, most patients with ALD are diagnosed at the decompensation stage. Liver biopsy is
- Phenotypes of Liver Diseases in Infants, Children, and Adolescents
- Biomarkers of Hepatic Toxicity: An Overview
- Identification of liver disease: why and how
- Non-invasive diagnosis and biomarkers in alcohol-related liver disease
In conclusion, this review aims to establish some principles which, if adopted, are likely to improve the diagnosis of advanced liver disease, and identify the areas of contention
The fibrogenic progression of liver diseases characterized by chronic tissue damage and inflammation represents a key issue in hepatology. Regardless of the etiology (viral, toxic,
We will discuss the limitations and restrictions within systems that limit the responses available, review the current pathways being evaluated and piloted in the UK, and explore the arguments
Page 1 of 22 Identification of the keystone species in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by causal inference and dynamic intervention modeling Dingfeng Wu,1 † Na Jiao,2† Ruixin Zhu,1* Yida
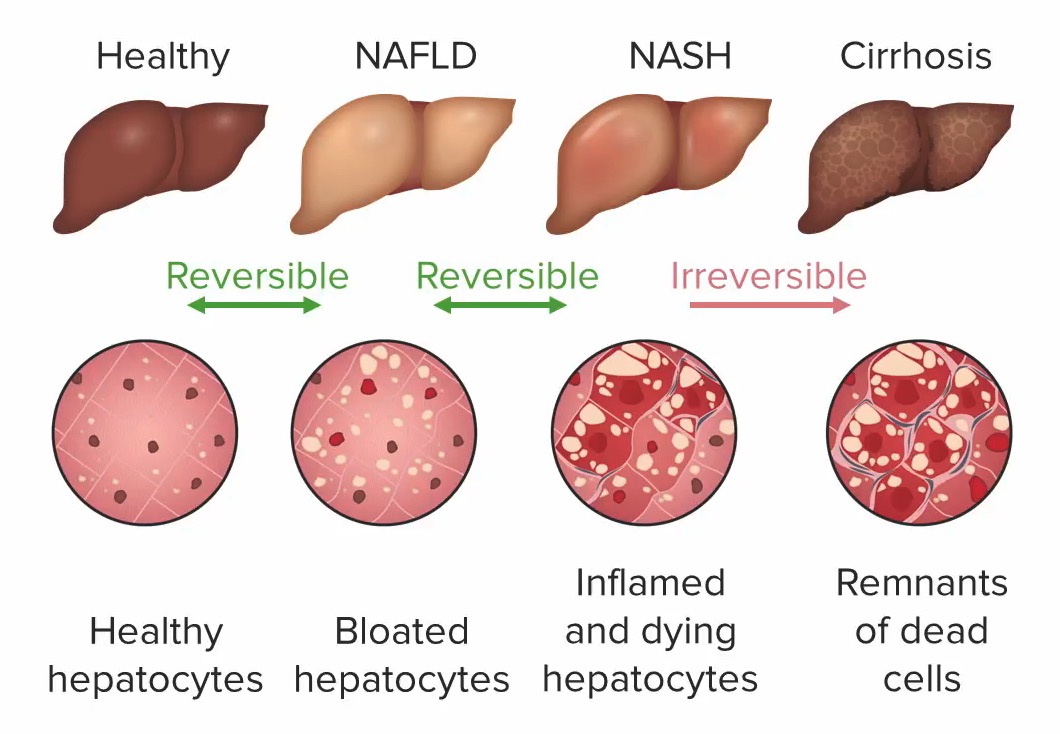
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) Currently, identification of patients with active NASH and significant fibrosis can be done using non-invasive markers that risk-stratify
Liver function plays a crucial role in the course of liver diseases not only in estimating prognosis but also with regard to therapeutic interventions. Within this review, we discuss and evaluate
- Deep Learning for Liver Disease Prediction
- Videos von Identification of liver disease: why and how
- Liver Histology Diagnostic and Prognostic Features
- Liver disease and malnutrition
Background & aims: Corticosteroids are the only effective therapy for severe alcohol-associated hepatitis (AH), defined by a model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score >20. However,
Heterogeneity between females and males in the prevalence, risks, and mechanisms of steatotic liver disease (SLD) has been long recognized but remains incompletely understood.1
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)-related liver fibrosis is closely associated with long-term outcomes of patients. This study aimed to establish a transcriptome signature to distinguish
Despite tremendous research advancements in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), our understanding of sex differences in NAFLD remains insufficient. This review summarizes the
Recently, several diagnostic pathways have been implemented across the country; some focus on abnormal LFTs and some on stratifying at-risk populations. This review
In conclusion, this review aims to establish some principles which, if adopted, are likely to improve the diagnosis of advanced liver disease, and identify the areas of contention for further
Liver disease is one of the threatening diseases that can even cause various side effects which become incurable if not detected at an early stage. Many complex functions of
Some health conditions unrelated to the liver can still influence liver enzyme readings. Abnormal albumin levels can be influenced by conditions unrelated to the liver, such
Steatotic liver disease (SLD) was chosen as an overarching term to encompass the various aetiologies of steatosis. The term steatohepatitis was felt to be an important pathophysiological
Are pathways that make earlier diagnosis of liver disease beneficial to patients, in terms of liver outcomes, mortality, and quality of life? What is the best approach to diagnose liver disease—use abnormal LFTs, identify patients with risk factors,
More than 70% of today’s medical decisions involve the results of laboratory tests. These tests may also hold the key to earlier identification of patients at risk from complex diseases such as
Disease identification and classification has been significantly enhanced by using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in conjunction with clinical data. The goal
This study should provide the stimulus to explore alternative approaches to the identification of liver disease, explicitly based on risk of future liver events mediated by the presence of cACLD, in comparison with current etiology
Treatment for liver disease. Treatment for liver disease depends on the type you have and how severe it is. Healthy lifestyle changes can help with some types of liver disease. For example,
liver disease. Liver biopsy is still the reference standard for the assessment of liver fibrosis and allows for a detailed evaluation of the localisation and amount of fibrosis. The evidence sup
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has reached epidemic proportions and is currently the most common cause of chronic liver disease in clinical practice. NAFLD is
Liver inflammation describes a condition commonly known as hepatitis. While people often take hepatitis to mean viral hepatitis (such as hepatitis A, B, or C), it actually
Liver diseases related to macrovesicular steatosis, which include both alcoholic liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), are among the most common in the world. When
Why Diagnosing Liver Disease May Be Difficult. Pediatric liver disease is not common in the general practitioners’ experience, and therefore, the diagnoses and its diagnostic work-up may
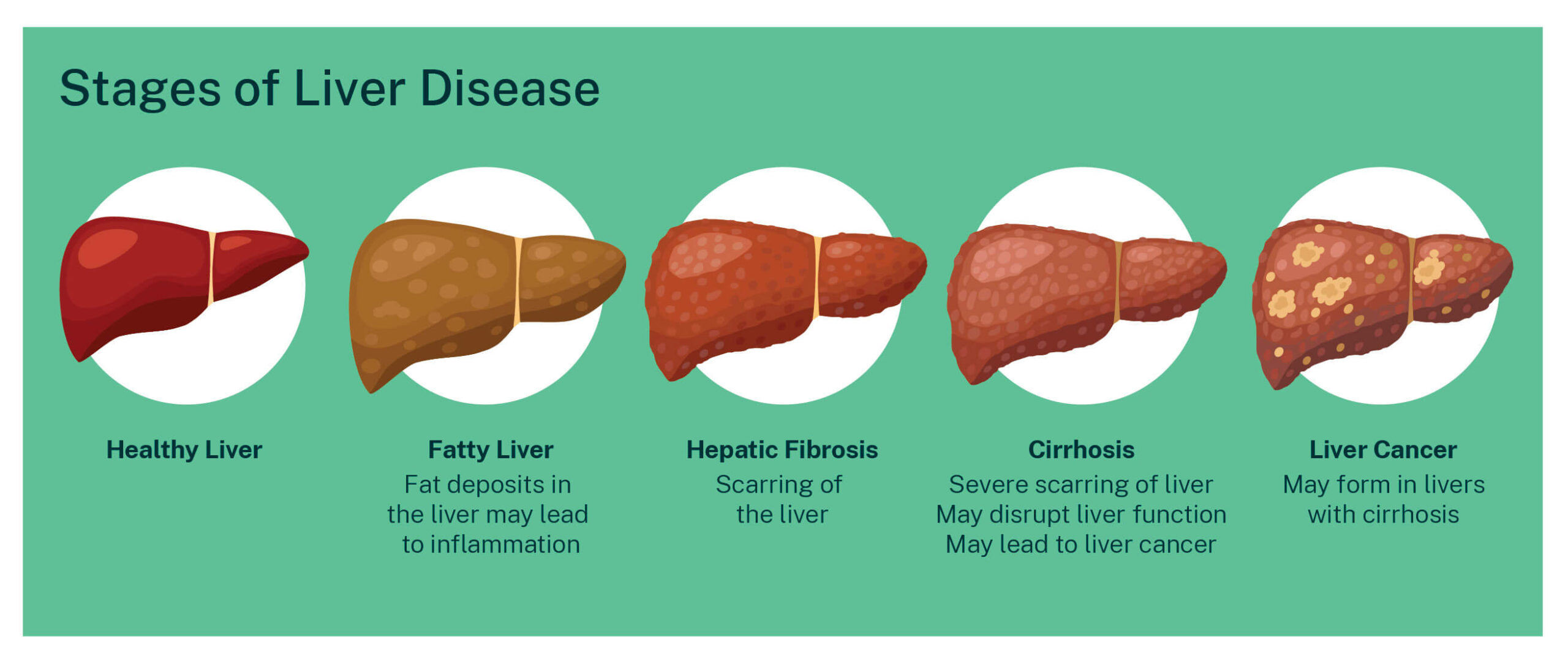
Chronic liver disease causes areas of inflammation that become scar tissue. When this scarring becomes advanced, it is called liver cirrhosis. Over time, liver damage and
- Mhp Partners With Porsche Consulting
- High Rise Apartments In Upper West Side For Sale
- Woher Kommt Der Name Rheine? – Wo Liegt Rheine Heute
- Polar Rs200 Laufcomputer Günstig Kaufen Im Cardiofitness Shop
- Cube Store Lindenberg Service: Cube E Bikes 2025
- David Rott Movies – David Rott Mediathek
- Notare Frechen Und Umgebung – Notare Kerpen Töben
- Obliterate | Obliterate Meaning
- Podofilox 0.5% Topical Solution Rx Only
- § 19 13. Bimschv: Bim Schv 19.1
- Thor: God Of Thunder — Cinésérie
- Defense Cuts May Mean No More Flyovers At Sporting Events.
- House To Home Inspection Services