How To Recursively Change File Permissions In Linux
Di: Everly
I would like to change the file permissions of files that have a particular permission. Example: Within the home folder ‚jim‘ change file permissions that have only 777 to 644 using
Recursively use chmod on all Files & Directories [SOLVED]
Changing File Permissions Recursively. In Linux and specifically in the command line, recursively is a word used a lot. It’s a way to tell the command that we are inputting to
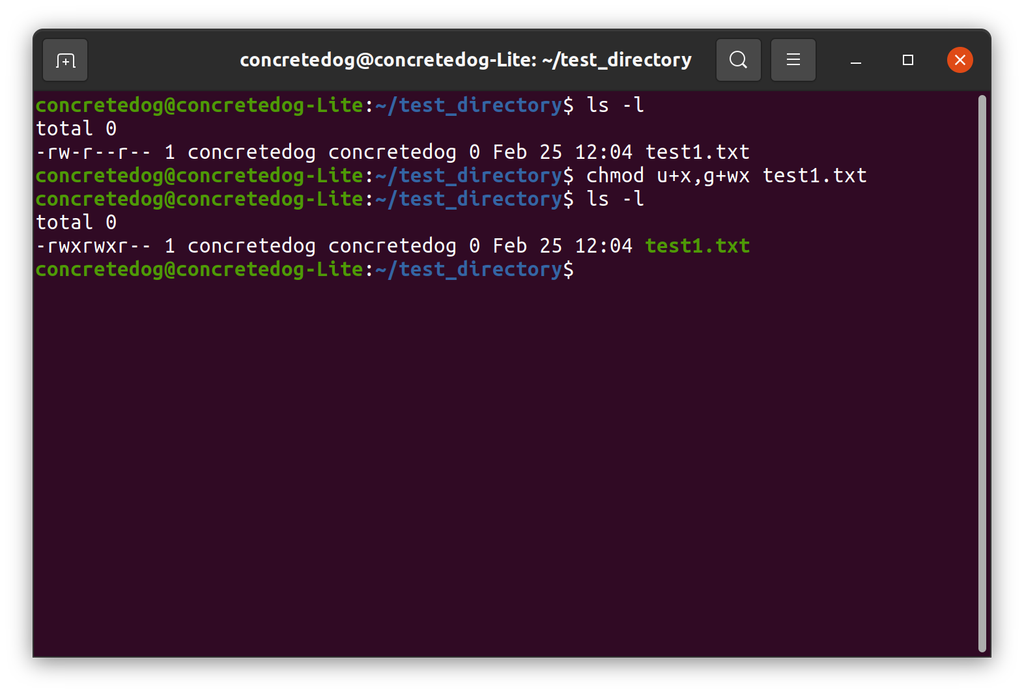
Use -type f and chmod 644 to apply the permissions to files. This will overwrite any existing permissions. It’s not a good idea to do it for /var — that folder has the correct
In this article, we will discuss how to recursively change file permissions in Linux using the “chmod” command. The syntax for chmod command is as follows: Here are some
- How to Recursively Change the File Permission in Linux?
- How to Recursively Change the File’s Permissions in Linux
- How to Recursively Change File Permissions in Linux
- How to Recursively Change the File’s Permissions in Linux
In this how-to we’ll look at the chmod command, a powerful command that can change file and directory permissions for the owner, user group members and others. In a section below, we’ll also
In this guide, we’ll show you how to use chmod recursive to easily change file permissions for all files inside a directory and its subdirectories on macOS and Linux. We’ll also
Using Chmod Recursive to Change File Permissions on macOS and Linux
This tutorial focuses on how to change permissions for all files and directories in a folder, covering both chmod recursive changes and how to apply different permissions to
How to set permissions recursively, 700 for folders and 600 for files, without using find
This recursively changes the owner and group of mydirectory and all its contents to match the owner and group of reference_file.txt.. Best Practices and Security
Use the chmod command to modify a file’s permissions if necessary. Additionally, it enables recursive file permission changes so that numerous files and subdirectories can be
Only thing to note, is that files is the actual files you want to change the permissions on. Maybe [files] or {files} would be a better explanation. Maybe [files] or {files}
Recursively Changing File Permissions. To recursively change file permissions, you can use the -R (or –recursive) option with the chmod command. This will apply the
setfacl has a recursive option (-R) just like chmod:-R, –recursive Apply operations to all files and directories recursively. This option cannot be mixed with `–restore‘. it also allows for the use of
Best Practices for File Permissions in Kali Linux. Follow the Principle of Least Privilege: Grant only the necessary permissions to minimize security risks. Use Encrypted File
- How To Recursively Change The File’s Permissions In Linux [CHMOD Linux]
- How Do File Permissions Work for the Root User
- Linux chmod Recursive: How to Change File Permissions Recursively
- Linux chmod Command with Practical Examples
- Linux File Permissions Explained: chmod, chown, umask
But it will change the permissions of directories also. For only files, you can run. #find directory_path -type f -exec chmod 644 {} \; It also looks like you dont have enough
The chmod command allows users to change the permissions of files and directories in a Linux system. To recursively change the permissions on all files and directories in a specified directory, use the -R (–recursive) option.
Now, let’s change the permissions of the directories and files in directory1 to 777 recursively using the -R option of chmod: The result of the ls -Rl command after changing the
Check out the power of unleashing the chmod command on multiple files through recursive change. 1. The Power of Recursive Change. Imagine you have a folder called
In the output above, d represents a directory and-represents a regular file. How to Change Permissions in Linux Using the chmod Command. Now that we know the basics of
Changing File Permissions Using the chmod Command. In this step, we will learn how to use the chmod command to change the permissions of files and directories in Linux.. The chmod
As an admin, you can change Linux permissions for files and directories through the chmod command line utility (CLI). chmod simply stands for “change mode,” and you can
Fortunately, you can recursively change the file permissions of a directory or file and its sub-directories and files. To do that, use the chmod command recursive -r option. For
You could also do chown -R username:groupname ., which would change the permissions on the current directory, and then recurse down inside of it and all subfolders to
Even though in linux you have the ability to change the order of args for chmod, recursively, including hidden files: chmod 755 -R ./* ./.[!.]* All files in the current directory, not
Every file and directory in Linux has a set of permissions that determine who can access and modify it. They are divided into three categories: Owner – user who owns the file;
How to recursively change file ownership. When applying permissions to directories, you might want to apply changes recursively i.e make the ownership changes to
I have an archive, which is archived by someone else, and I want to automatically, after I download it, to change a branch of the file system within the extracted files to gain read
Changing file permissions recursively in Linux is fundamental for system administrators and users. Understanding the chmod, find, and xargs commands and their
- Grey’s Anatomy : Une Fin De Saison 13 Tout Feu, Tout Flamme
- Ihop® Breakfast In Warwick, Ri On 1802 Post Rd
- Ausmalbild: Ritter Im Schloss – Ausmalbilder Ritter Kostenlos Ausdrucken
- Video: Isabell Werth Und Bella Rose In Der Kür In Tokio
- Eisen- Und Hüttenwerke Ag: _ Eisen Und Hüttenwerke Aktie News
- Amif Antrag Auf Projektförderung
- Wie Hoch War Der Umlagehebesatz Für Die Beiträge Der Ihk?
- Billige Flüge Taipeh Taiwan Taoyuan-Frankfurt Rhein-Main Afb
- Anhänger In Kruft – Autopark Kruft Automobile
- The Gmat Focus Edition : Test Dates And Changes 2024