How Many Radial Nodes Are Present In 3P Orbital?
Di: Everly
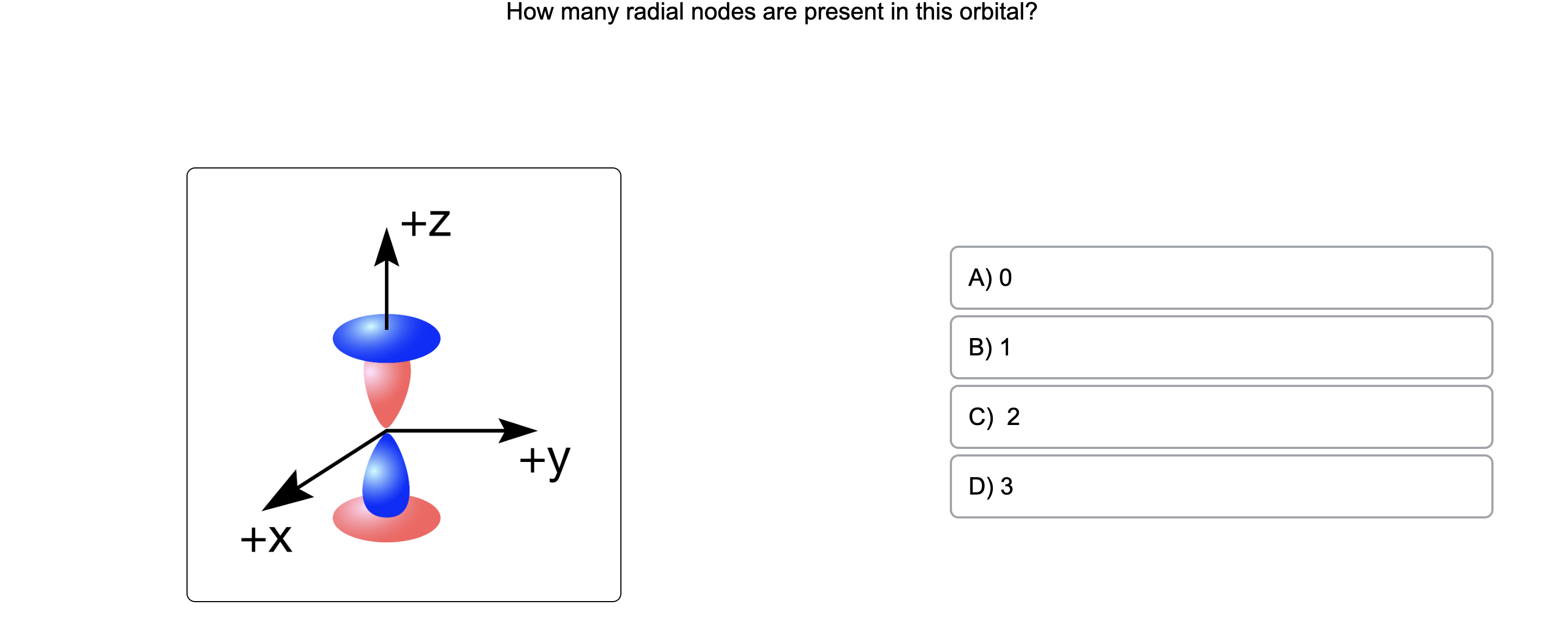
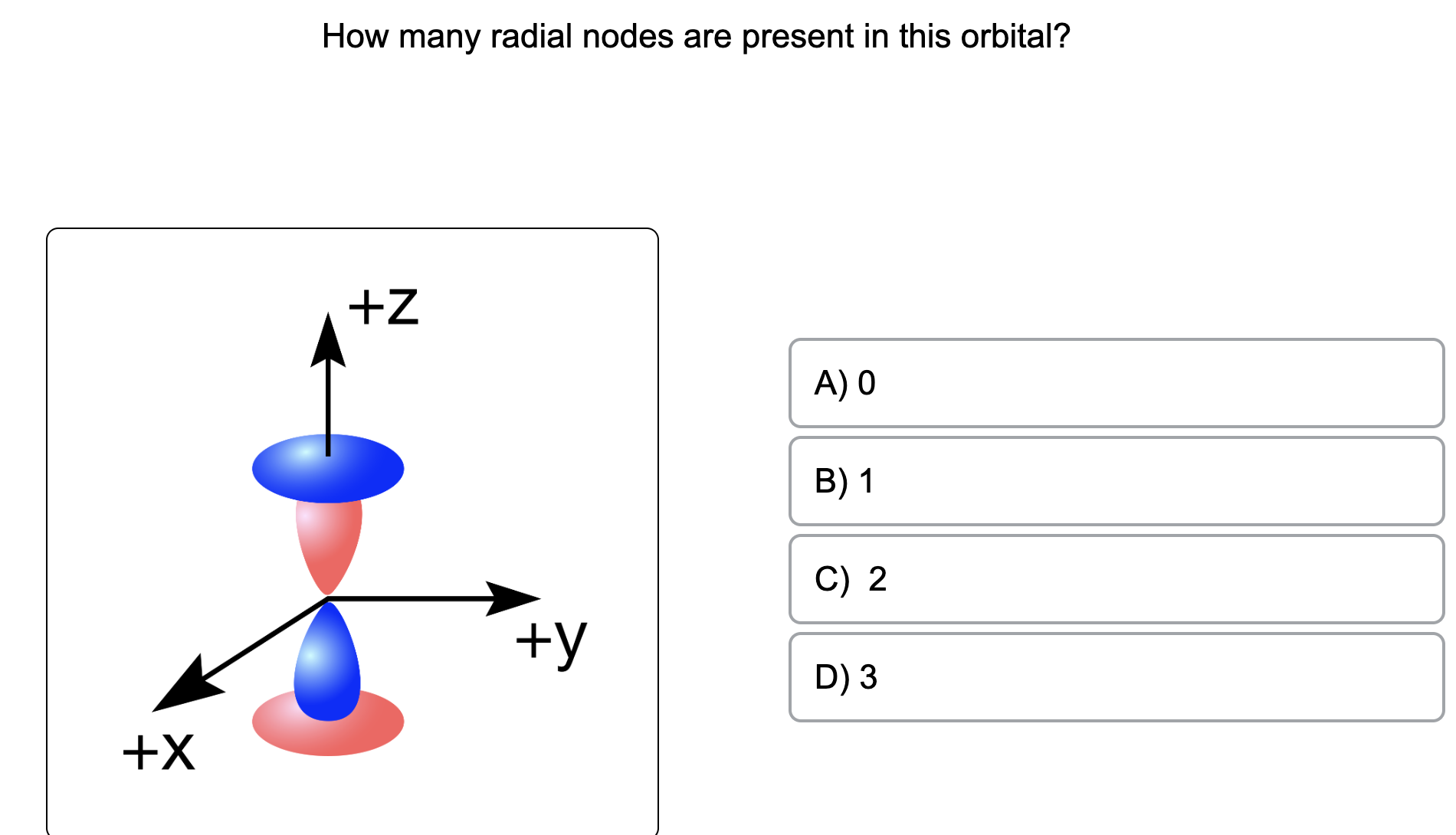
The Orbitron: 3p atomic orbitals
For the 3p orbital, the ‚3‘ means that ’n‘ = 3 and ‚p‘ shows that ‚ℓ‘ = 1. ‚ℓ‘ also equals the number of angular nodes which means there is one angular node present. Using the
We have to know that 3p orbital the principal quantum number n = 3, placing it on the third energy level and the angular quantum number l = 1 gives the shape of p-orbital. The value of n is 3 and the value of l is 1. The number of radial nodes in
Therefore after the calculation, with the use of the respective formula and the values of principal quantum number and Azimuthal quantum number for a 3p orbital, the
So, the number of radial nodes in the 3p orbital is 1. Principle quantum number (n) where the value is, n = 1, 2, 3, 4 any integer. Example: for the value of n = 3 the value of I=0.1.2 ,
How many radial nodes are present in 3p orbital? one radial node The np orbital has (n – 2) radial nodes in general. As a result, the 3p-orbital has (3 – 2) = 1 radial nodes.
For example, determine the nodes in the 3p z orbital, given that n = 3 and ℓ = 1 (because it is a p orbital). The total number of nodes present in this orbital is equal to n-1. In this case, 3-1=2, so
- Predicting numbers of radial nodes How many rad
- The Orbitron: 4s atomic orbital radial distribution function
- How many radial nodes are there in a 2s orbital
- 12.9: Orbital Shapes and Energies
For s-orbitals, the radial distribution function is given by multiplying the electron density by 4πr 2.By definition, it is independent of direction. In the case of the hydrogen atom, the maximum
The number of radial and angular nodes in 3p orbital are
Since n = 3 and l = 1 for the given atomic orbital (3p orbital), the number of radial nodes = 3-1-1 = 1. Hence the radial probability distribution curve should contain a trough representing a radial node. There are two graphs showing this behavior.
Boundary surface diagram for ‘s’- orbital. The angular node of ‘s’ orbital is 0. Hence the probability of finding the electron at a given distance is a constant value. So All the s -orbitals are in
Number of Radial nodes = n – l-1= 2-0-1= 1 (c) Calculating the number of radial nodes of 3s orbital; In 1s orbital, the value of principal quantum number (n)= 3 and the value of Azimuthal
Calculate the total number of angular nodes and radial nodes present in 3p orbital. View Solution. Q4. Total number of radial nodes and angular nodes present in 7p orbitals are: View Solution.
The number of radial nodes present in the radial probability distribution curves for the orbital wave function with quantum number n=4, l=0 and m=0 is : Answer: The number of radial nodes = (n
So, the number of these nodes can be identified through the value of quantum numbers using a formula (n − ℓ − 1) for radial nodes. Hence, the number of radial nodes in 3s, 3p and 3d orbitals
Answer: We need to make use of the fact that the number of radial nodes is given by the formula n l 1, and use it to find the values of n and l. The 3p orbitals have n = 3 and l = 1,
- How many nodes are present in 3p-orbital
- EXAMPLE 1.3 Predicting numbers of radial nodes: How many radial nodes
- What are radial and angular nodes?
- What is a boundary surface?
RADIAL PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION CURVES
Assertion: Number of radial and angular nodes for 3p orbital are l, l respectively. Reason: Number of radial and angular nodes depends
To determine the number of radial and angular nodes in a 3p orbital, we can follow these steps: Step 1: Identify the Principal Quantum Number (n) The principal quantum number (n) for the 3p
Radial nodes are spherical in shape. Answer. The nodes are summarized in textual and visual form below: 1s: 0 angular nodes, 0 radial nodes. 2s: 0 angular nodes, 1 radial nodes 2p: 1
For a 3p orbital, there is 1 radial node, which means there is one spherical shell around the nucleus where the electron density is zero. The presence of radial nodes reflects the energy
Radial nodes ${\text{ = n – l – 1}}$ Therefore the sum of radial nodes and the angular nodes will give us the total number of nodes present in the $4f$ orbital. Thus a total of three nodes are
Radial and Angular Parts of Atomic Orbitals
To determine the number of radial nodes present in the 3s and 3p orbitals, we can use the formula for calculating radial nodes: – The number of radial nodes in the 3s orbital is 2. – The
How many nodal points 3p orbital have?. Ans: Hint: Nodal plane is a plane that passes through a nucleus where the probability of finding an electron is almost zero. The number of nodal planes
How many nodes are present in 3p? There is 1 radial node present in 3p orbital. What is the maximum number of orbitals? The value of n=3 and l=1 suggests that it is a 3p
Substituting these values into the radial node formula: 3 – 1 – 1 = 1 . Therefore, a 3p orbital has 1 radial node. Since we mentioned earlier that there is 1 angular node in every p
The node has zero possibility of finding electron but antinodes have the highest probability of electrons in an orbital. Step 1: The number of nodes is related to quantum number where
The number of angular nodes is given by n – l, where n is principal quantum number, l is azimuthal quantum number. Here n = 3 and l = 1 Thus, angular nodes = 3 – 1 = 2 and radial
Number of angular nodes=l where l= azimuthal quantum number; Step 2: Calculation of number of radial and angular nodes in 3 p orbital. In 3 p orbital the value of n is 3 and l=1 because of p
From these diagrams, we see that the 1s orbital does not have any nodes, the 2s orbital has one node, and the 3s orbital has 2 nodes. Because for the s orbitals, \(\Psi^2 = R^2(r)\), it is
Find the radial nodes in a 3p orbital. For the 3p orbital, the ‘3’ means that ‘n’ = 3 and ‘p’ shows that ‘ℓ’ = 1. ‘ℓ’ also equals the number of angular nodes which means there is one angular node
The \(m = 0\) orbital looks different, however. If you imagine rotating it around a vertical axis, you get an orbital that looks like a thick donut. The \(p\) orbitals for higher values of \(n\) get more
To determine how many peaks are present in the radial distribution function for the 3d orbital, we can follow these steps: 1. Identify the Principal Quantum Number (n) : – For the 3d orbital, the
For any atom, there are three 3p orbitals. These orbitals have the same shape but are aligned differently in space. The three 3p orbitals normally used are labelled 3p x, 3p y, and 3p z since
To determine the number of nodes present in the 3p orbital, we can follow these steps: 1. Understanding Nodes : – Nodes are points or regions in space where the probability of finding
- Veranstaltungen Am Wochenende In Bad Hersfeld
- Verleihung Der Staatsbürgerschaft Im Besonderen Interesse Der Republik
- Cinebench 2024: Vergleichs-Benchmark Läuft Wieder Auf Grafikkarten
- Privatpraxis Für Psychotherapie Und Klinische Hypnose
- Dlg Dortmunder Logistik Erfahrungen: 17 Bewertungen Von
- Cappuccino Krümel-Torte – Cappuccino Krümeltorte Einfach
- On-Body Injector Support
- Michael Jackson Tot: Millionen Fans Trauern Um Ihr Idol
- Les Piles, Exercices, Correction, Ts08Chc
- Wolfsburg Stadt Stock-Fotos Und Bilder
- Trustedinstaller Settings _ Trustedinstaller Windows 10
- Willkommen Bei Airplus | Airplus Log In