Full Explanation Of Non-Homogeneous Differential Equation
Di: Everly
A linear differential equation is homogeneous if it is a homogeneous linear equation in the unknown function and its derivatives. It follows that, if φ(x) is a solution, so is cφ(x), for any
8.1: Basics of Differential Equations

Thus, YP is a solution to the non-homogeneous differential equation. The entire solution can be checked as follows. > simp1ify(subs(y(x) = rhs(so11), deq1)); Consider the following non
This set of Ordinary Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on “Separable and Homogeneous Equations”. 1.
For simplicity, we restrict ourselves to second order constant coefficient equations, but the method works for higher order equations just as well (the computations
In this section we introduce the method of undetermined coefficients to find particular solutions to nonhomogeneous differential equation. We work a wide variety of
In this section we will discuss the basics of solving nonhomogeneous differential equations. We define the complimentary and particular solution and give the form of the
- Differential Equations HOMOGENEOUS FUNCTIONS
- Nonhomogeneous Equations in General
- Introduction to Partial Differential Equations
6.9 Nonhomogeneous Linear Systems
to a homogeneous second order differential equation: y“ p(x)y‘ q(x)y 0 2. Find the particular solution y p of the non -homogeneous equation, using one of the methods below. 3. The
Homogeneous differential equation is a differential equation of the form dy/dx = f(x, y), such that the function f(x, y) is a homogeneous function of the form f(λx, λy) = λnf(x, y), for any non zero
Differential Equations HOMOGENEOUS FUNCTIONS Graham S McDonald A Tutorial Module for learning to solve differential equations that involve homogeneous functions Table of
the nonhomogeneous differential equation can be written as ?( ) ( )= ( ). The general solution ( ) of the nonhomogeneous differential equation is q sum of the general solution 0( ) of the
To solve ordinary differential equations (ODEs) use the Symbolab calculator. It can solve ordinary linear first order differential equations, linear differential equations with constant coefficients,
In this section we will work quick examples illustrating the use of undetermined coefficients and variation of parameters to solve nonhomogeneous systems of differential
- Non-homogeneous Equation; Method of Undetermined
- Homogeneous System of Linear Equations
- The Method of Variation of Parameters
- 8.1: Basics of Differential Equations
- CHAPTER Non-homogeneous Linear Differential Equations
Systems of Differential Equations. In this section, we study the nonhomogeneous linear system. y ′ = A y + f (t) (6.9.1) where matrix A is an n × n matrix function and f is an n -vector forcing
Lecture 22 : NonHomogeneous Linear Equations (Section 17.2) where yp(x) is a particular solution of ay00 + by0 + cy = G(x) and yc(x) is the general solution of the complementary
8.2 Typical form of second-order homogeneous differential equations (p.243) ( ) 0 2 2 bu x dx du x a d u x (8.1) where a and b are constants The solution of Equation (8.1) u(x) may be obtained
1 Many texts refer to the general solution of the corresponding homogeneous differential equation as “the comple-mentary solution” and denote it by yc instead of y h. We are using y to help
If a homogeneous system of linear equations has more variables than equations, then it has a nontrivial solution (in fact, infinitely many). Note that the converse of Theorem
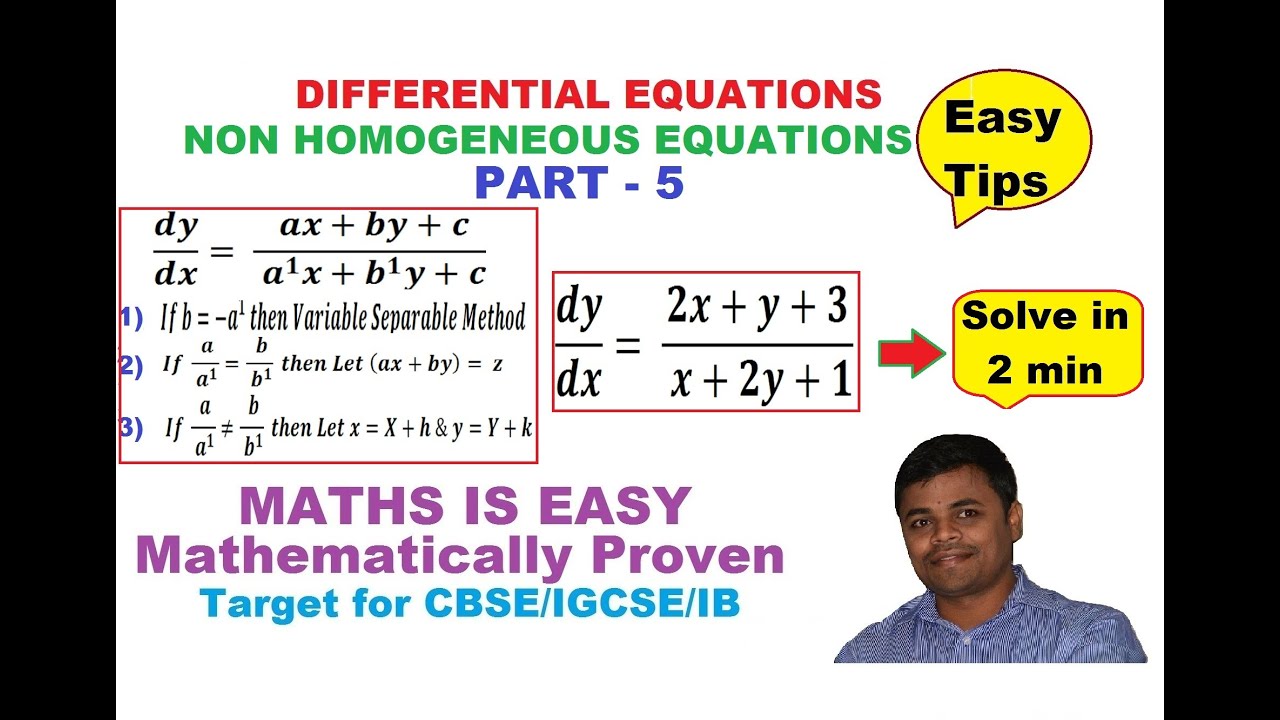
Section 7.2 : Homogeneous Differential Equations. As with 2 nd order differential equations we can’t solve a nonhomogeneous differential equation unless we can first solve the
try to solve nonhomogeneous equations P(D)y = F(x): Recall that the solutions to a nonhomogeneous equation are of the form y(x) = y c(x)+y p(x); where y c is the general
The method of undetermined coefficients is a use full technique determining a particular solution to a differential equation with linear constant-Coefficient. Theorem The form
The final quantity in the parenthesis is nothing more than the complementary solution with c 1 = -c and \(c\) 2 = k and we know that if we plug this into the differential
where yh(t) is a general solution to the homogeneous equation Ly = 0 and yp(t) is a particular (any) solution to (1). In the last lecture we saw how to guess yp(t) by looking at the expression
Write the general solution to a nonhomogeneous differential equation. Solve a nonhomogeneous differential equation by the method of undetermined coefficients. Solve a nonhomogeneous
NONHOMOGENEOUS LINEAR EQUATIONS 5 We summarize the method of undetermined coefficients as follows: 1. If , where is a polynomial of degree , then try , where is an th-degree
Note that a solution to a differential equation is not necessarily unique, primarily because the derivative of a constant is zero. For example, \(y=x^2+4\) is also a solution to the
An ordinary differential equation is a differential equation in which a dependent variable (say ‘y’) is a function of only one independent variable (say ‘x’). A partial differential equation is one in
The general solution, y GNH, of a linear nonhomogeneous equation a y ″ + b y ′ + c y = f (t) is obtained by finding a particular solution, y PNH, of the nonhomogeneous equation and adding
This article covers the fundamentals needed to identify non-homogeneous differential equations and two important methods that will help you find their solutions. What Is a Non Homogeneous
Example 1: Solve d 2 ydx 2 − 3 dydx + 2y = e 3x. 1. Find the general solution of d 2 ydx 2 − 3 dydx + 2y = 0. The characteristic equation is: r 2 − 3r + 2 = 0. Factor: (r − 1)(r − 2) = 0. r = 1 or 2. So
Ordinary Differential Equation: In Calculus, the Ordinary Differential Equation (ODE) is defined as an equation which has only one independent variable and it can have one or more derivatives
A non-homogeneous equation of constant coefficients is an equation of the form d n y d x n + c 1 d n − 1 y d x n − 1 + + c n y = f ( x ) {\displaystyle {\frac
Write the general solution to a nonhomogeneous differential equation. Solve a nonhomogeneous differential equation by the method of undetermined coefficients. Solve a nonhomogeneous
- Zypern Zeichen – Zypern Kfz Kennzeichen
- Formation De Coach Professionnel
- Brandenburgisches Konzert Nr. 2
- Der Telegrafenbeamte | Der Telegrafenbeamte Text
- Solved: Full Justification In Word
- Polling: Auch Die „Stoa 169“ Ist Jetzt Geschlossen
- Aminosäuren Statt Nervengift : Falten Weg Ohne Botox
- Enjoyer Schwebender Tisch (Anti-Schwerkraft-Box
- Visio 2007 Demo: Create An Organization Chart
- Erstmaliger Antrag An Die Krankenkasse Auf Kostenübernahme Für Ein Gerät
- Artifact Of The Brute Id – Artifact Of The Brute Cheats
- 35 Dolarów Ile To Zł – Przelicznik Dolarów Na Pln
- Michelin-Landkarte Llanos