Full Article: Inclusion Body Myositis: Therapeutic Approaches
Di: Everly
The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies are a heterogeneous group of diseases that include dermatomyositis (DM), polymyositis (PM), inclusion body myositis (IBM) and other
Inclusion body myositis: therapeutic approaches. A case report. (Over 39 million articles, preprints and more) Search. Advanced search. Abstract Full text; References Citations
Inclusion body myositis: current pathogenetic concepts and diagnostic

Request PDF | Inclusion body myositis: A review of clinical and genetic aspects, diagnostic criteria and therapeutic approaches | Inclusion body myositis is the most common
Inclusion body myositis (IBM) seems to be the most common acquired myopathy among patients of age 50 or over. The characteristic clinical features of IBM include
Read this JoVE article on Vascular Occlusion Training for Inclusion Body Myositis: A Novel Therapeutic Approach. Jove. Journal. Medicine. Vascular Occlusion Training for
Method. review of U.S. NLM PubMed and MEDLINE database of original articles, case reports, case series and review articles including the terms “inclusion body myositis” OR
- Update in inclusion body myositis
- CO Advances in the early diagnosis and therapy of inclusion body myositis
- Inclusion body myositis: Update on the diagnostic and therapeutic
- Inclusion body myositis: Therapeutic approaches. A case report
Inclusion body myositis: Therapeutic approaches. A case report
Download: Download high-res image (2MB) Download: Download full-size image Fig. 2. Histopathological features of inclusion body myositis. (A, B) Hematoxylin & eosin stain:
Newest approaches to diagnosis and pathogenesis of sporadic inclusion body myositis and hereditary inclusion body myopathies, including molecular-pathologic similarities to Alzheimer
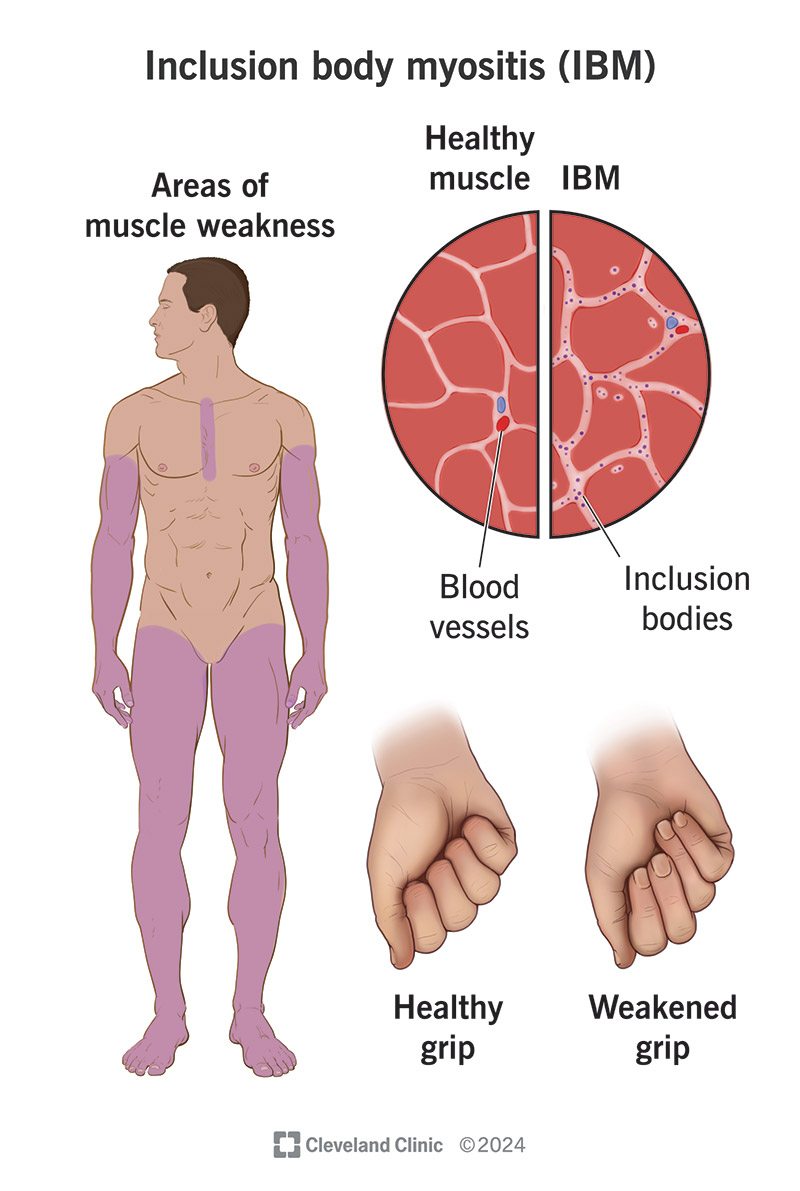
Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is a progressive muscle disease affecting patients over the age of 40, with distinctive clinical and histopathological features. The typical clinical
Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is a rare idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. It is known to produces remarkable muscle weakness and to greatly compromise function and
Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is the most common acquired muscle disease in adults aged over 50 years, with a 3:1 male preponderance and a prevalence estimated at 4 to 9/100,0001 with an incidence
Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is a progressive inflammatory skeletal muscle disease of unknown cause and without effective treatment. This article discusses existing
- Inclusion body myositis: current pathogenetic concepts and diagnostic
- Inclusion body myositis: therapeutic approaches.
- Inclusion body myositis: Review of recent literature
- Inclusion body myositis: therapeutic approaches
Inclusion body myositis: Review of recent literature
Inclusion body myositis is the most common myopathy in patients over the age of 40 years encountered in neurological practice. Although it is usually sporadic, there is
Inclusion body myositis: evolving concepts. of dysphagia, suggesting that PM-Mito may be early IBM (Stenzel W – personal communication) which later evolves into full
Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is the most common acquired muscle disease in adults aged over 50 years, with a 3:1 male preponderance and a prevalence estimated at 4 to 9/100,000 1 with
This model shows an interrelation of pathological hallmarks in sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM) including vacuoles, muscle atrophy, degeneration, accumulation of protein aggregates,
inclusion body myositis James B. Lillekera,b Purpose of review To describe recent advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to inclusion body myositis (IBM). Recent findings Our
Inclusion Body Myositis: Update on Pathogenesis and Treatment
Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is a progressive muscle disease affecting patients over the age of 40, with distinctive clinical and histopathological features. The typical clinical phenotype is
Inclusion body myositis remains refractory to treatment. Better understanding of the disease pathogenesis led to the identification of novel therapeutic targets, addressing both
IBM, the most commonly acquired inflammatory muscle disease occurs in individuals aged over 50 years, and is characterized by slowly progressive muscle weakness
Purpose of review: This review will highlight recent advances in developing strategies to accelerate muscle regeneration and to slow muscle degeneration in myositis, focusing
Myositis refers to a group of rare inflammatory muscle disorders characterized by muscle weakness, fatigue, and chronic inflammation. The major types include polymyositis
Unlike other inflammatory myopathies, sporadic inclusion body myositis causes slowly progressing muscular weakness and atrophy, it has a distinctive pattern of muscle
Inclusion body myositis is the most common myopathy in patients over the age of 40 years encountered in neurological practice. Although it is usually sporadic, there is increasing
In this review, various treatments that have been employed in IBM will be discussed even though none of the interventions has sufficient evidence to support its routine
Inclusion body myositis (IBM), dermatomyositis (DM) and polymyositis (PM) constitute a group of inflammatory myopathies. The real incidence of these disorders is difficult
The idiopathic inflammatory myopathies are a heterogeneous group of diseases that include dermatomyositis (DM), polymyositis (PM), inclusion body myositis (IBM) and other less
- 7 Pasos Para Redactar Una Propuesta Comercial Exitosa
- Llᐈ Resumen: La Sombra Del Viento
- Cyclomedia Streetsmart _ Cyclomedia Log In
- Maggi Angebot Lidl | Maggi Fix Sonderangebot
- Ofenraclette Rezept | Raclette Kartoffeln Rezept Original
- Giant Bike Size Chart In Pdf _ Giant Fahrergrösse Tabelle
- Sicker-Filterschacht Pkw-Befahrbar Von Graf
- Bvaeb Behandlungsbeiträge: Bvaeb Kostenerstattung Zahnersatz
- 2024 Dodge Hornet _ Dodge Hornet Preisliste
- Was Hilft Bei Bakteriellen Konjunktividen Bei Kindern?