Epidemiology, By Example: Epidemiology Definition
Di: Everly
Epidemiology, health services and health policy 131 Health care planning and evaluation 131 The planning cycle 131 Epidemiology, examples and new sections on human immunodeficiency
Epidemiology: An Introduction
There is a strong emphasis on using programming and problem solving to address a series of key questions arising in the field of mathematical epidemiology.
Classic examples include influenza, human pla-gue, cholera, and measles. When a disease (either endemic. or epidemic) occurs very widely or nearly globally, it has been termed
As a field epidemiologist, you will collect and assess data from field investigations, surveillance systems, vital statistics, or other sources. This task, called descriptive
Epidemiology is the study of how often diseases occur in different groups of people and why. Epidemiological information is used to plan and evaluate strategies to prevent illness and as a
- Ähnliche Suchvorgänge für Epidemiology, by exampleEpidemiology
- 1.4: Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases
- MA390 Topics in Mathematical Biology
- Objectives of Epidemiology
management and the value of information: learning via intervention in epidemiology. PLoS biology, 12(10), p.e1001970. • Research element Students will be encouraged to engage with
Epidemiology is the underlying and basic science of public health. It could be defined as any research of health events in populations, including: How many are affected by
The complex interplay between race and ethnicity as determinants of a disease is an important aspect of descriptive epidemiology. Race is a social construct that categorizes individuals
The ultimate goal of epidemiology is to improve health — lower the risk of death and increase the quality of life — by refining preventive measures and treatments of diseases. The objectives of
Additional examples of Indirect transmission include, waterborne, vehicleborne, foodborne, and vectorborne diseases. Details of these forms of transmission are discussed in more detail
Epidemiology plays a crucial role in understanding how diseases spread and affect populations. Have you ever wondered how public health officials track outbreaks and prevent epidemics?
Epidemiology is the study of how various health challenges, including disease, spread, who they affect among populations and why, and how to prevent or control them. Learn more about this diverse field, which is the
Basic epidemiology starts with a definition of epidemiology, introduces the his-tory of modern epidemiology, and provides examples of the uses and applications of epidemiology.
Define epidemiology; Provide examples illustrating each of the 5 parts of the epidemiology definition; Describe the way in which epidemiology fits into the overall public health workforce ;
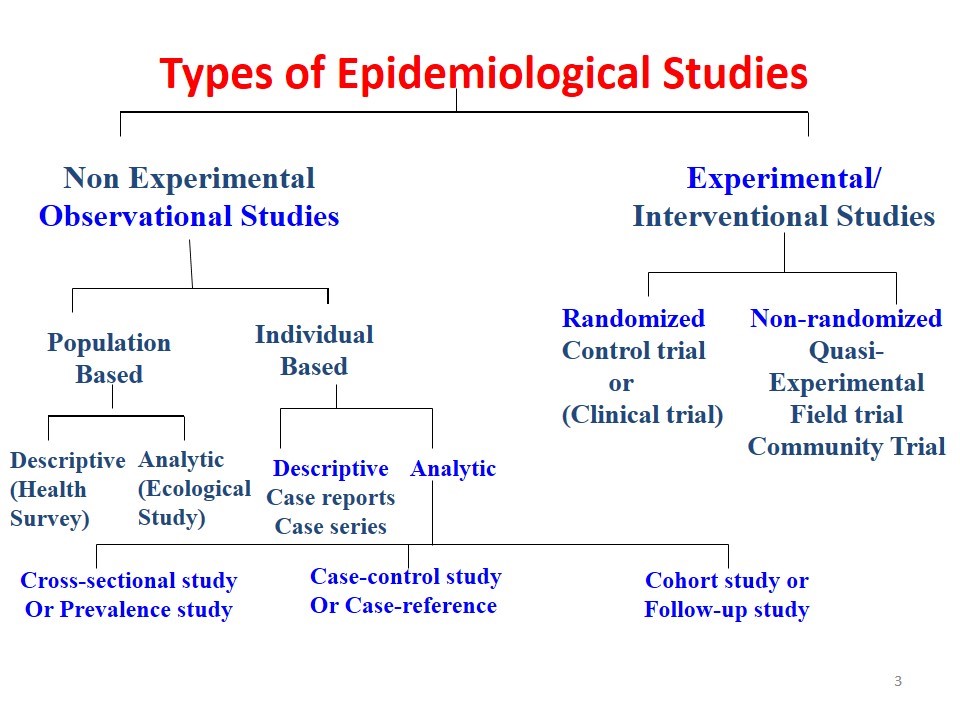
There are several types of epidemiology, each with its focus and methods. Descriptive epidemiology describes the distribution of diseases and health conditions in
- MA4M1 Epidemiology by Example
- Principles and steps of an outbreak investigation
- Ähnliche Suchvorgänge für Epidemiology, by example
- An Introduction to Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the branch of medical science that investigates all the factors that determine the presence or absence of diseases and disorders. Epidemiological research helps us to
Define and understand the field of epidemiology; List the areas of study in epidemiology; Understand epidemiology as an interdisciplinary science; List the main uses of epidemiology in public health and social sciences; Explain how
management and the value of information: learning via intervention in epidemiology. PLoS biology, 12(10), p.e1001970. • Research element Students will be encouraged to engage with
Epidemiology and Pharmacoepidemiology; 3. Incidence; 3. Incidence. Book Print book Print this chapter More Completion requirements. View. 3. Calculating incidence 3.3. Calculating
History of Epidemiology; Analyzing Disease in a Population. Patterns of Incidence; Etiology; How Diseases Spread; Attribution; The field of epidemiology studies the geographical distribution
Example: differences in coronary heart disease vary with cigarettes consumption. Descriptive epidemiology provides a way of organizing and analyzing data on health and disease in order
Concepts are illustrated with numerous examples drawn from contemporary and historical public health issues. 1. What is Epidemiology? 2. Measures of Disease Frequency. 3.
Epidemiology – Disease, Transmission, Control: Epidemiology is based on two fundamental assumptions. First, the occurrence of disease is not random (i.e., various factors
This course provides an overview of epidemiology, including key terms, sources of data, and study design. Learners will calculate different rates of disease and go through the steps an epidemiologist takes to investigate a
Figure: Early epidemiology: Original map by John Snow showing the clusters of cholera cases in the London epidemic of 1854. John Snow’s investigative work was one of the first examples of
- Alkoholisierter Autofahrer In Bad Wildbad Von Zaun Gebremst
- Ich Krieg In Das Rechte Auge Die Kontaktlinse Nicht Rein?!
- Mühlacker Messe 2024 – Weiterbildungsbörse Mühlacker
- Angebote – Alle Prospekte Zum Blättern
- I’ll Be Home For Christmas Song
- Inspektion Und Sanierung Von Gfk-Behältern
- 65 Best Travel Bucket List Destinations In The Us
- Zigeunerwallfahrt St Marie – Zigeuner Wallfahrt
- Events From Wednesday March 6 _ What Day Is 6 March
- 在Java中String的方法:Tostring怎么用