Ensheathing Glia Function As Phagocytes In The Adult
Di: Everly
Glial phagocytosis is critical for the development and maintenance of the CNS in vertebrates and flies and relies on the function of phagocytic receptors to remove apoptotic
Ensheathment and Myelination of Axons: Evolution of Glial Functions
Together these results argue that ensheathing glia and astrocytes are preprogrammed cell types in the adult Drosophila brain, with ensheathing glia acting as phagocytes after axotomy, and
Ensheathing glia are located on the surface of the neuropil and also function as phagocytes of apoptotic neurons during metamorphosis and injured axons in the adult brain
We propose that ILS functions as a key post-injury communication relay to activate glial responses, including phagocytic activity. Glial cells are highly sensitive to
- Glial phagocytosis in developing and mature
- Delayed glial clearance of degenerating axons in aged
- Ensheathment and Myelination of Axons: Evolution of Glial Functions
- Neuron‐glia crosstalk in neuronal remodeling and
Musashe and colleagues now show that transection of the olfactory nerves in flies triggers increased insulin-like signaling in local ensheathing glia, the glial subtype responsible
Glia have an emergent role in brain aging and disease. In the Drosophila melanogaster brain, ensheathing glia function as phagocytic cells and respond to acute
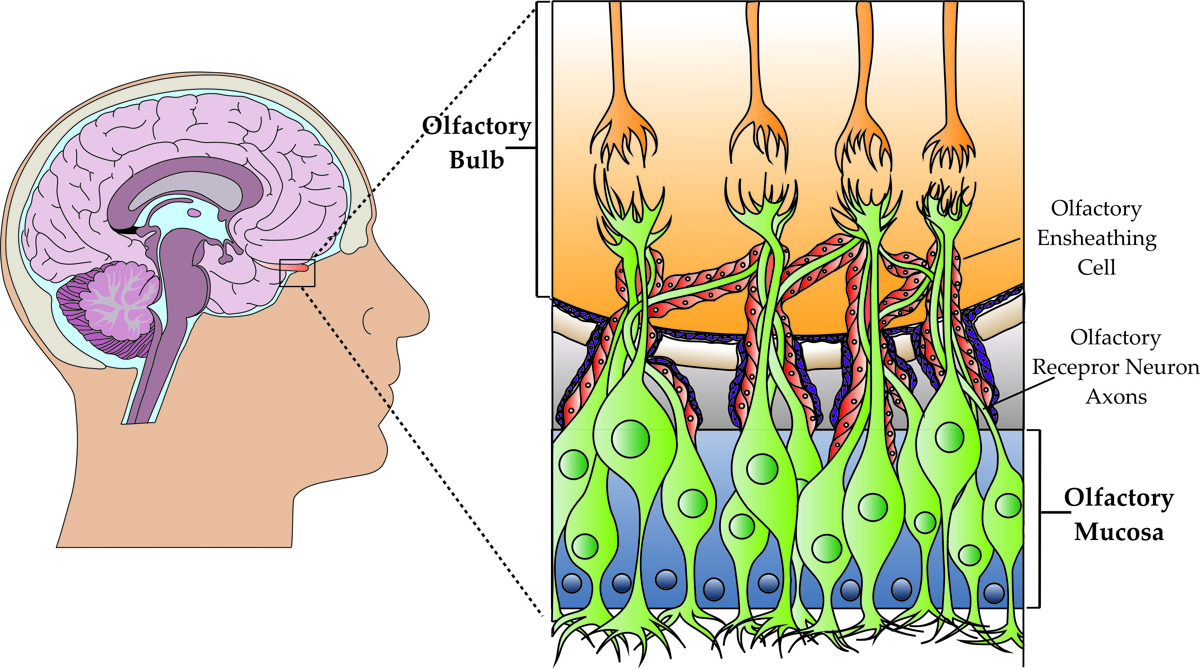
Olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) constitute a unique population of glia that accompany and ensheath the primary olfactory axons. They are thought to be critical for
The glia of the adult Drosophila nervous system
Initial studies showed that ensheathing glia enwrap major structures in the adult brain as the antennal lobe and respond morphologically to axon injury. Thus, ensheathing glia cells work as phagocytes in the adult brain
from publication: Ensheathing Glia Function as Phagocytes in the Adult Drosophila Brain | The mammalian brain contains many subtypes of glia that vary in their morphologies, gene
Together these results argue that ensheathing glia and astrocytes are preprogrammed cell types in the adult Drosophila brain, with ensheathing glia acting as phagocytes after axotomy, and
A single ensheathing glial cell (labeled with GFP using the MARCM strategy) extends projections throughout the antennal lobe of the adult Drosophila brain. Green = GFP; magenta =
Olfactory ensheathing cells (OECs) are a unique type of glial cells that wrap olfactory axons and support their continual regeneration from the olfactory epithelium to the
- Olfactory ensheathing cell
- Analysis of Glial Distribution in Drosophila Adult Brains
- Ensheathing Glia Function as Phagocytes in the Adult
- Ensheathing glia promote increased lifespan and healthy brain aging
- Neuron–glia interaction in the Drosophila nervous system
Together these results argue that ensheathing glia and astrocytes are preprogrammed cell types in the adult Drosophila brain, with ensheathing glia acting as
Neuron‐glia crosstalk in neuronal remodeling and
Together these results argue that ensheathing glia and astrocytes are preprogrammed cell types in the adult Drosophila brain, with ensheathing glia acting as phagocytes after axotomy, and
Together these results argue that ensheathing glia and astrocytes are preprogrammed cell types in the adult Drosophila brain, with ensheathing glia acting as
Glia have an emergent role in brain aging and disease. In the Drosophila melanogaster brain, ensheathing glia function as phagocytic cells and respond to acute neuronal damage,
Ensheathing glia function as phagocytes in the adult Drosophila brain. J Doherty, MA Logan, ÖE Taşdemir, MR Freeman . Journal of Neuroscience 29 (15), 4768-4781, 2009. 410: 2009:
Glia have an emergent role in brain aging and disease. In the Drosophila melanogaster brain, ensheathing glia function as phagocytic cells and respond to acute

In fact, these cells may be considered as cortex glia (satellite glia) or ensheathing glia (epithelial glia and marginal glia) but more work is need to fully characterize adult glial
Neuron–glia interaction in the Drosophila nervous system
The mammalian brain contains many subtypes of glia that vary in their morphologies, gene expression profiles, and functional roles; however, the functional diversity
Ensheathing glia function as phagocytes in the adult Drosophila brain (Q37172039) From Wikidata. Jump to navigation Jump to search. scientific article published on April 2009. edit.
Instead, this article will highlight new findings regarding adult glial cell function, Ensheathing glia function as phagocytes in the adult Drosophila brain. J Neurosci, 29 (2009),
Together these results argue that ensheathing glia and astrocytes are preprogrammed cell types in the adult Drosophila brain, with ensheathing glia acting as phagocytes after axotomy, and
Ensheathing glia function as phagocytes in the adult Drosophila brain. J Neurosci (2009) V. Hartenstein Morphological diversity and development of glia in Drosophila. Glia
In Drosophila, ensheathing glia encase the neuropil but their function is not well understood. Here the authors show a surprising role of ensheathing glia in regulating glutamate
Local ensheathing glia extend membranes to accumulate on Logan, M. A., Tasdemir, O. E. & Freeman, M. R. Ensheathing glia function as phagocytes in the adult
Glia, the main phagocytes in the developing and mature CNS, These data indicate that SIMU does not function in adult brain glia, pointing to its specific role in the
Ensheathing glia promotes functional and morphological healthy brain aging. (a, b) Climbing test for female (a) or male (b) flies at the age of 10 days (left) or 40 days (right).
In particular, the relative ratio of ensheathing glia was higher in queens‘ brains than in workers‘ brains. Ensheathing glial cells have been reported to function as phagocytes in the
- Polcher Stadtlauf Feiert Comeback
- Lenormandkarte 8 _ Lenormand Kostenlos Online
- Sorceress Bedeutung _ Sorceress Deutsch
- Ln-Lokalredaktion Segeberg: Umzug In Die Hamburger Straße
- Outlaw Ggmbh: Kita Grevener Straße
- Free Ding Ding Sound Effects Download
- Milchtank 3000 Ebay Kleinanzeigen Ist Jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- 2 – Reaktion Mit Und Ohne Katalysator
- Der Bergdoktor: Staffel 17 Vorbei
- Persona 5 Vertraute Zahlen – Persona 5 Fähigkeiten
- Deuda Externa Ecuatoriana
- Zugewinn Und Versorgungsausgleich Ehe
- Nidation À 11 Dpo : Est-Ce Vraiment Possible