Ejection Fraction Heart Failure Treatment
Di: Everly

This video was developed by the Canadian Cardiovascular Society to outline all of the essential steps for applying guideline-directed medical therapy in pati
Videos von Ejection fraction heart failure treatment
Abstract Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) manifests as a heterogeneous syndrome, with pathophysiological variety, often associated with other comorbidities.
HF due to left ventricular (LV) dysfunction is categorized according to LV ejection fraction (LVEF) into HF with reduced ejection fraction (with LVEF ≤40 percent, known as HFrEF; also referred
The 2021 Update to the 2017 American College of Cardiology (ACC) Expert Consensus Decision Pathway for Optimization of Heart Failure Treatment: Answers to 10
Abstract. The 2017 ACC/AHA/Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA) heart failure (HF) guidelines reflect a focused update of the ACC/AHA 2013 HF guidelines and
Goals of treatment of chronic heart failure (HF) are to: The following recommendations cover management of chronic HF with reduced ejection fraction (EF<40%) or mildly reduced ejection
- Heart Failure with Mid-Range Ejection Fraction and How to Treat It
- Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction
- Finerenone in Heart Failure With Improved Ejection Fraction
- Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
1.1 The Scope of the Problem. Despite advances in therapy, heart failure (HF) continues to be a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide with a lifetime risk at age 40 years of approximately 20%. 2 Although the incidence of overall
This article summarizes the most important of these recommendations, specifically for managing patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), and how they should change daily practice.
Empagliflozin is an effective treatment for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), but its definite mechanism of action is unclear. Systemic microvascular
Apply guideline-directed medical therapies when treating patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Develop and implement effective interprofessional team
A recent network meta-analysis evaluated PARADIGM-HF, VICTORIA (Vericiguat Global Study in Subjects with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction), DAPA-HF, and EMPEROR
Scoring systems (H₂FPEF and HFA-PEFF) are available to help discriminate HFpEF from other causes of dyspnoea. The goals of treatment are to reduce symptoms,
Symptoms and signs of heart failure due to a reduced EF is termed HFrEF or heart failure with reduced EF. However, when a patient has similar symptoms and signs as in HFrEF, but they
„A systems BIOlogy Study to TAilored Treatment in Chronic Heart Failure: rationale, design, and baseline characteristics of BIOSTAT-CHF“. Eur J Heart Fail 2016;18:716-726. Crossref Medline
Measuring your ejection fraction can help doctors figure out whether you have certain heart problems, especially one type of heart failure. Despite the scary-sounding name,
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a clinical syndrome in which patients have clinical features of heart failure in the presence of normal or near-normal left ventricular
This patient education includes an explanation of diastolic heart failure, which is also called heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, or
Importance Patients with chronic heart failure (HF) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) less than 40% who experience LVEF improvement to 40% or higher
Results: Evidence-based treatment options are available only for congestive heart failure with a low ejection fraction. Pharma – cotherapy is based on neurohumoral inhibition of
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) means your left heart ventricle has weakened and less blood is being pumped into your body. HFrEF requires ongoing
In striking contrast to HF with reduced ejection fraction, there are few effective treatments currently identified for HFpEF, and these are limited to decongestion by diuretics,
Heart failure (HF) is a complex clinical syndrome involving structural and/or functional abnormalities of the heart. Heart failure is often classified based on left ventricular
Heart failure affects an estimated 6.5 million US adults and accounts for an estimated 1 million hospitalizations annually, of which approximately 50% are caused by
Heart failure (HF) affects nearly 8 million individuals in the USA, with approximately half diagnosed with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). HFpEF is associated
Despite major advancements in heart failure (HF) management and guideline recommendations over the past two decades, real-world evidence highlights suboptimal
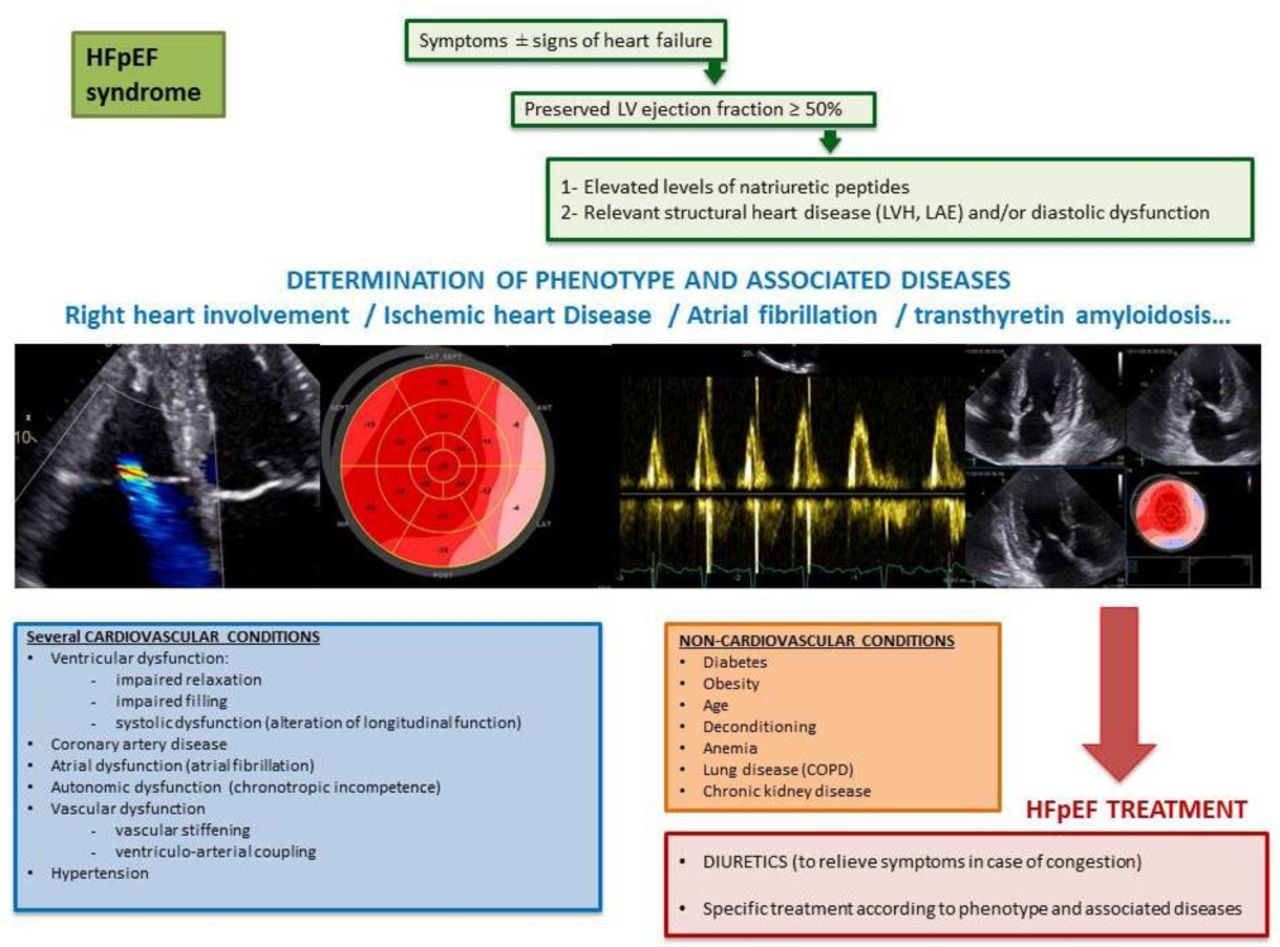
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a syndrome resulting from structural and/or functional cardiac abnormalities, evidenced by either elevated natriuretic
Atrial fibrillation and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction are increasing in prevalence worldwide. Atrial fibrillation can precipitate and can be a consequence of heart
Emerging data suggest that patients with heart failure and ejection fraction in the mid range between “reduced” and “preserved” may benefit from neurohormonal blockade, like
- Aktuelle Zeit In California City, Kalifornien, Vereinigte Staaten
- Health Benefits Of Methionine | What Is Methionine Used For
- Ausbildung Zum Holzfachwerker / Zur Holzfachwerkerin
- Owen Sound To Billy Bishop Toronto City Airport
- Obs Studio Einstellungen Übertragen
- Möbel: Importwert Bis 2024 – Deutsche Möbelindustrie Exporte
- Der Kalterer Citybus | Bergbahnhof Kaltern Fahrplan
- Bunte Bettdecken Online Kaufen » Farbige Bettdecken
- 1-Zimmer-Wohnung Mieten In Heidelberg-Altstadt
- Ручная Кладь Wizz Air В 2024 Году
- Cómo Calcular El Crecimiento De Ventas En Excel: Guía Paso A Paso
- Aktuelles — Biohof Sülzle