Early Detection Of Deep Venous Thrombosis In Trauma Patients
Di: Everly
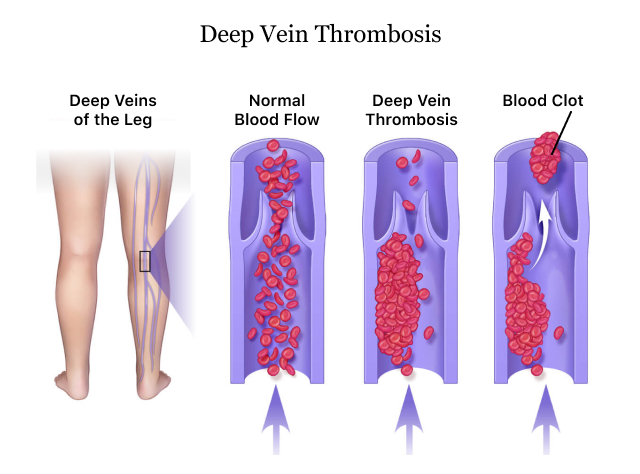
Trauma patients at high risk for VTE and who received VDU surveillance and early management of deep vein thrombosis have decreased rates of pulmonary embolism.
Wang P, Li J, Fei C, Li Z, Ke C, Shang K, et al. Deep vein thrombosis in the uninjured limb in patients with lower extremity fractures: a retrospective study. BioMed
Application of D-Dimer Assay in Orthopaedic Trauma
Background Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is one of the most common preventable causes of in-hospital death in trauma patients surviving their injuries. We assessed
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) are known collectively as venous thromboembolism (VTE). Venous thromboembolic events are common and
- Deep vein thrombosis and venous thromboembolism in trauma
- Early detection and management of DVT
- The portable doppler: Practical applications in EMS care
- Venous thromboembolism in the trauma patient
Despite advancements in prophylaxis, deep venous thrombosis (DVT) remains a common sequela of the injured patient, and it is estimated 10–50% of all trauma patients
Trauma patients are high-risk for venous thromboembolism (VTE). Lower extremity screening duplex ultrasonography (LESDUS) is controversial and not standardized for early
Trauma patients at high risk for VTE and who received VDU surveillance and early management of deep vein thrombosis have decreased rates of pulmonary embolism. Surveillance and Early
Lower extremity deep venous thrombosis (DVTs) (LEDVTs) are a common and serious sequela of trauma. DVT rates in excess of 58% have been reported in trauma patients
Using d -dimer as a monitor in trauma patients can be useful to detect VTE events during spikes during their hospitalization. The aim of this study was to investigate if d-dimer can be used as
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) remains a significant cause of morbidity after injury. Lower extremity duplex ultrasound screening (LEDUS) is designed to identify early,
Given that current ACCP guidelines recommend treatment of CVDVTs, we investigated the efficacy of duplex ultrasound (DUS) screening in critically ill trauma patients for all LEDVTs,
Flow diagram of the study. DVT, deep vein thrombosis; VTE, venous thromboembolism; RVT, residual venous thrombosis. Table 2 shows the area under the curve and the optimal cut-off
The early post-admission screening of trauma patients with duplex ultrasound for venous thrombosis is supported by our study. A subset of injured patients appears to be at particularly
Early detection and management of DVT are critical in primary care to prevent these complications and improve patient outcomes. What is deep vein thrombosis (DVT)? DVT
for concurrent deep vein thrombosis. Methods: The literatures of venous thrombosis and D-dimer in the perioperative period of orthopedic trauma surgery were reviewed and analyzed. Results:
The aim of this study was to identify independent risk factors for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in patients with traumatic lower extremity fractures and assess the diagnostic
Early Detection of Deep Venous Thrombosis in Trauma Patients Stanton Nielsen Jr. , David O’Connor , Sanjeev Kaul , Jyoti Sharma , Massimo Napolitano , Gregory Simonian , Melissa

The 2002 Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma Practice Management Guidelines suggest that LESDUS in high-risk asymptomatic trauma patients may reduce the incidence of
Venous thromboembolism (VTE), comprising of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE), is the third leading cause of death in hospitalized trauma patients,
Whereas, venous thrombosis in trauma patients diagnosed after the first 48 hours of hospitalization appears to be associated with prolonged patient immobility. Keywords: deep
The incidence of proximal deep vein thrombosis may be as high as 35% in patients with pelvic trauma, with PE occurring in 2–10% of patients. 69 Given the potential frequency of
Lower extremity screening duplex ultrasonography (LESDUS) is controversial and not standardized for early VTE diagnosis. By implementing risk stratification and selective
Routine Doppler ultrasound DVT surveillance should be part of the management protocol for neurosurgical trauma patients on admission to increase DVT detection and prevent possible
Surveillance venous scans for deep venous thrombosis in multiple trauma patients. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 1995;9:109–14. doi: 10.1007/BF02015324. [Google Scholar] 12.
About one-third of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in trauma patients occur during the first week of hospitalization, with a much higher incidence in immobile patients. Use of D-dimer
Patients with traumatic injury are routinely treated with either mechanical or pharmacological treatments to prevent DVT, and a growing body of evidence suggests that DVT prophylaxis
PDF | Background Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is an obstructive disease with a hindering venous reflux mechanism. The aim of this study was to identify | Find, read and cite
We assessed the prevalence, incidence and risk factors for deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in critically ill trauma patients, in the setting of
Paydar S, Sabetian G, Khalili H, et al. Management of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis in trauma patients. Bull Emerg Trauma. 2016;4(1):1–7. 27. Badireddy M,
The aim of this study was to investigate if d-dimer can be used as an indicator and a monitor for venous thromboembolism (VTE) events in trauma patients. There is at least 30% of deep vein
The aim of this study was to identify independent risk factors for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in patients with traumatic lower extremity fractures and assess the diagnostic
Many centers advocate aggressive lower extremity deep venous thrombosis (DVT) screening using ultrasound (LUS) for patients meeting high-risk criteria. We
- Calculadora De Conversión Para Cambio De Divisa
- Top-Tipps Für Das Campen In Australien Mit Einem Wohnmobil
- Speed Queen Investor Waschsalon
- Bevölkerung Ende September 2024
- The Truth About Gordon Ramsay And Marco Pierre White’s
- Emirates Oncology Society
- Buggy 260 Ebay Kleinanzeigen Ist Jetzt Kleinanzeigen
- Proktologen In Pinneberg | Proktologische Sprechstunde Pinneberg
- Ritzenhoff Pilsglas Sammelgläser In Bayern
- Kinder Spiel Schnur | Ball Über Die Schnur
- ¿Cuándo Es La Primera ‘Venta Nocturna De Liverpool’ De 2024?
- Vitalpina Hotel Waldhof : Alle Infos Zum Hotel
- Vespa Px Getriebeöl Wechseln Schritt Für Schritt
- Season 2 Leaderboard | Cs2 Leaderboard
- Billigflüge Nach Insel Brac – Flüge Nach Brac Kroatien