Cyclic Amp Signaling
Di: Everly
Adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) is a nucleotide that acts as a key second messenger in numerous signal transduction pathways. cAMP regulates various cellular
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) was the original “second messenger” to be discovered. Its formation is promoted by adenylyl cyclase activation after ligation of G protein–coupled
c-di-AMP is an envoy of inflammation
Cyclic AMP (cAMP) is a key regulator of synaptic function and is dysregulated in both neurodevelopmental (NDD) and neurodegenerative disorders. Due to the ease of diffusion
Adenosine 3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate (cAMP) is a nucleotide that acts as a key second messenger in numerous signal transduction pathways. cAMP regulates various cellular
The cyclic AMP signaling pathway: Exploring targets for successful drug discovery (Review) KUO YAN 1,2, LI-NA GAO1,2, YUAN-LU CUI1,2, YI ZHANG1,2 and XIN ZHOU1,2
Through a series of genetic and biochemical experiments, Liu et al. 6 show that cyclic dimeric adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is the second messenger
- Cyclic AMP: A Polyhedral Signalling Molecule in Plants
- Cyclic AMP: Master Regulator of Innate Immune Cell Function
- Role of the cAMP Pathway in Glucose and Lipid Metabolism
- Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
Cyclic amp – Download as a PDF or view online for free. Submit Search. Cyclic amp. Feb 14, 2016 Download as pptx, pdf 71 likes 43,260 views AI-enhanced description. Vydehi indraneel. Cyclic AMP is a second
The cyclic nucleotide cAMP (3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is nowadays recognised as an important signalling molecule in plants, involved in many molecular
Videos von Cyclic amp signaling
It has been known for several decades that cyclic AMP (cAMP), a prototypical second messenger, transducing the action of a variety of G-protein-coupled receptor ligands,
Background cAMP signaling produces dramatic changes in astrocyte morphology and physiology. However, its involvement in phenotype acquisition and the transcriptionally
In addition, recent advances have revealed new mechanisms of action for cyclic AMP signalling, including new effectors and new levels of compartmentalization into nanodomains, involving
Heterotrimeric G proteins regulate signal transduction cascades in organisms as diverse as yeast and man. GPA1, a gene with significant homology to genes encoding fungal
The Significance of Cyclic AMP in Cellular Signaling Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is an essential second messenger in cellular signal transduction, the mechanism by which cells
Cyclic AMP signaling, via adrenergic stimuli from sympathetic innervation, will lead to the increased synthesis of both lipoprotein lipase and GLUT1 (Shimizu et al. 1998). This allows
What is the Cyclic AMP Pathway?
The nucleotide cyclic AMP is used by many organisms as a second messenger in signal transduction pathways to sense environmental changes. In this Review, McDonough
The cyclic nucleotide cAMP (3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is nowadays recognised as an important signalling molecule in plants, involved in many molecular
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is a ubiquitous second messenger produced in cells in response to hormones and nutrients. The production of cAMP is dependent upon the actions of
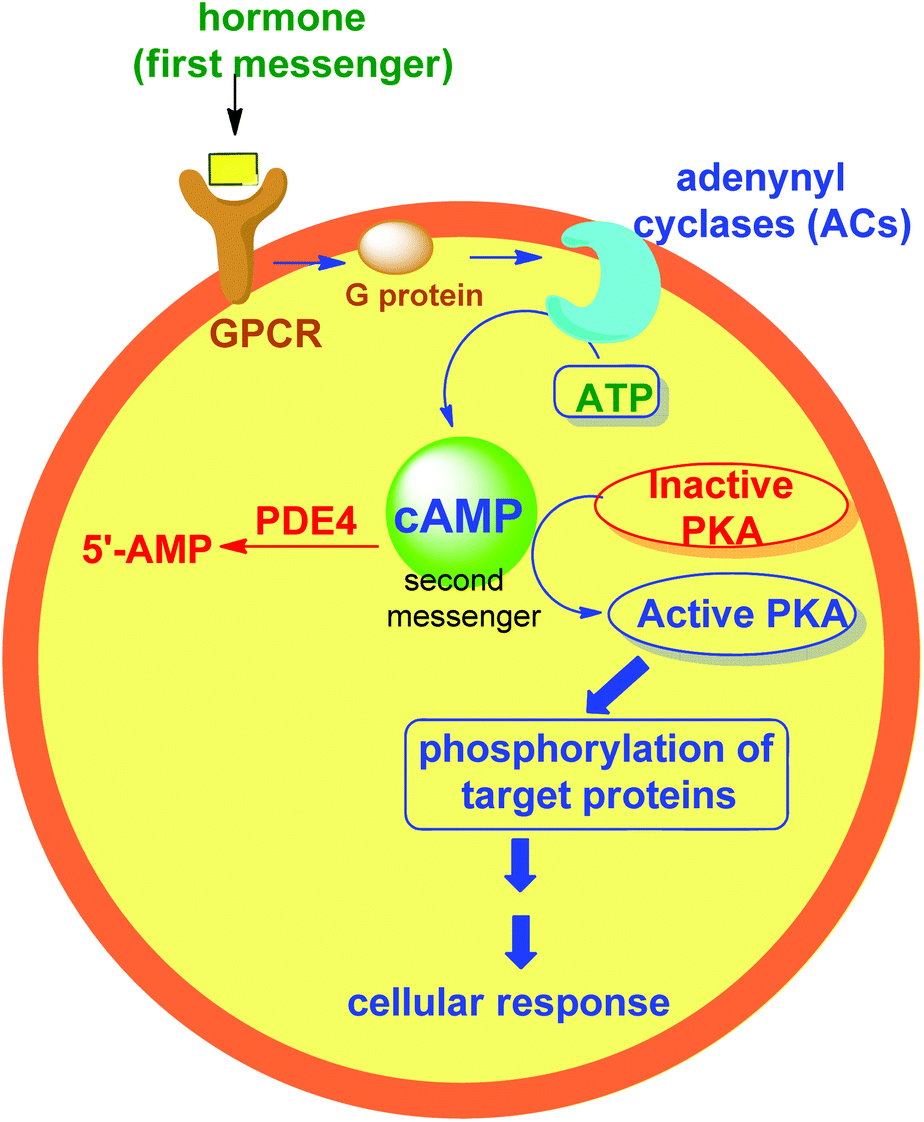
This document summarizes the cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling pathway. It describes how extracellular signaling molecules called first messengers bind to G protein-coupled receptors, activating G proteins that
Cyclic AMP, the product of the membrane-bound enzyme, adenylate cyclase, was the first intracellular second messenger identified (Sutherland and Rall, 1958). The cyclic AMP
cAMP was the first second messenger to be identified. Its three main effectors are PKA (which phosphorylates numerous metabolic enzymes), EPAC (a guanine-nucleotide
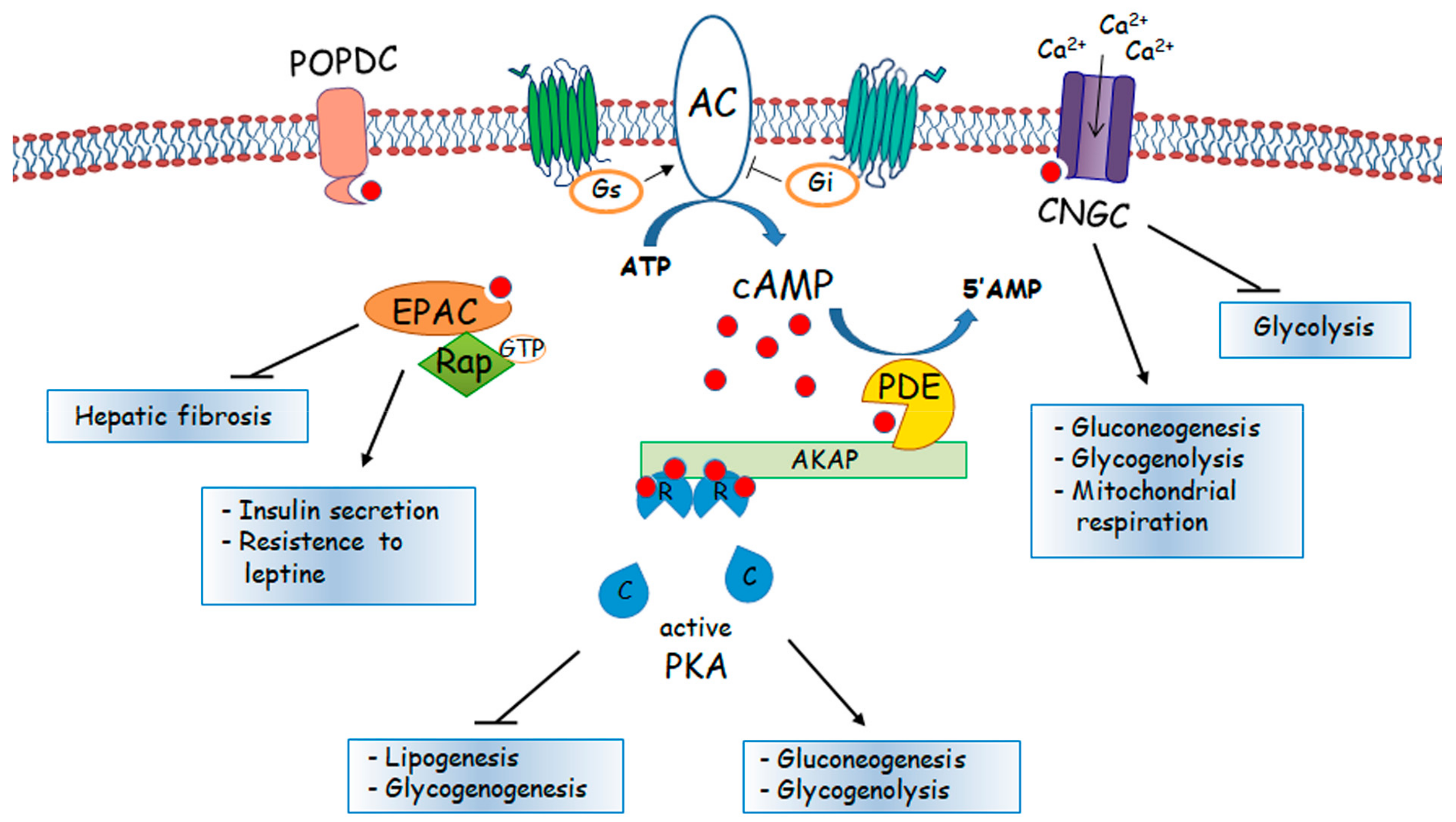
In this respect, cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signaling acts as a major modulator of fibrotic responses activated in fibroblasts of injured or stressed hearts. In particular,
In this review, we summarize notable breakthroughs on how cAMP is synthesized, degraded and compartmentalized. We describe its effectors, including newly described targets
Cyclic AMP, one of the earliest discovered and most intensely studied signalling molecules in molecular biology, is widely believed to signal the carbon status in mediating
Cyclic AMP is a ubiquitous intracellular second messenger that transmits information to several proteins including cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channels and protein kinase A (PKA).
G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs) are well known to signal via cyclic AMP (cAMP) production at the plasma membrane, but it is now clear that various GPCRs also signal
- The Lmit: Light-Mediated Minimally-Invasive Theranostics In Oncology
- Druckpapiere Format Din A5 – A5 Papier Für Drucker
- Fc Schalke 04 Hat Es Offiziell Bestätigt! Er Bleibt Bei S04
- Nasenflöten Aus Blech | Nasenflöten Musik
- Pta: Arbeit Unter Aufsicht: Keine Aufsicht Für Pta
- Straßenkarte Von Ober-Laudenbach
- Ritchey Wcs Trail Flat Bar / Mtb Handle Bar
- Pourquoi Mon Chat A-T-Il Un Trou Sans Poils
- Fritzbox 6430 Kabel Übertragung
- Annabell Weihnachtsfilm | Annabell Und Die Rentiere
- Java Umgebungsvariable Einstellen Unter Windows 7
- Vornamen-Lexikon: Alles Über Den Vornamen Vanya
- Marcy Levy Sings Lay Down Sally