Creating A Variable Of Type Class In Java
Di: Everly
All the examples I look at for reflection show creating a new instance of an unknown implementation, and casting that implementation to it’s interface. The issue with this
In this article we’ll explain what is variable in Java and what types of variables there are. Also you’ll find some rules of correct naming for variables
Java Class, methods, instance variables
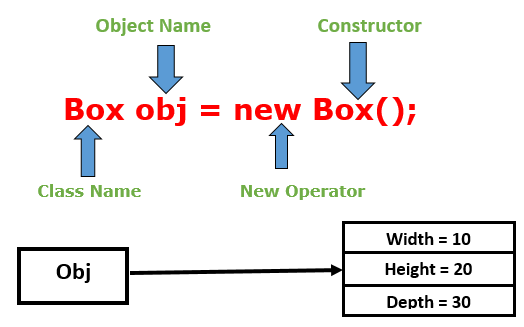
The object is a basic building block of an OOPs language. In Java, we cannot execute any program without creating an object.There is various way to create an object in Java that we will
I’m new to OOP and I was wondering how to set something that is not like int, string, double etc. I have two classes, Foo and Bar, and some instance variables How can I set
No need for strings, no need for java.sql.* classes. Where to obtain the java.time classes? Java SE 8, Java SE 9, Java SE 10, Java SE 11, and later – Part of the standard Java
- How can I initialize a generic variable in Java?
- User-defined data types in java
- Different Ways to Create Objects in Java
- How to Create Object in Java
To create a variable, you must specify the type and assign it a value: Where type is one of Java’s types (such as int or String), and variableName is the name of the variable (such as x or name). The equal sign is used to assign values to the
In summary, to define a data type in a Java class, you need instance variables, constructors, instance methods, and a test client. Stopwatch. Stopwatch.java implements the following API: It is a stripped-down version of an old-fashioned
Data received from the ArrayList is of that class type that stores multiple data. Example. Java // Java program to illustrate Custom ArrayList // Importing ArrayList class from
In this article, we learned how to create an instance of a generic type in Java. To summarize, we examined why we cannot create instances of a generic type using the new
Java Class Attributes. In the previous chapter, we used the term „variable“ for x in the example (as shown below). It is actually an attribute of the class. Or you could say that class attributes
In Java, a String is the type of object that can store a sequence of characters enclosed by double quotes, and every character is stored in 16 bits, i.e., using UTF 16-bit
The types of the Java programming language are divided into two categories: primitive types and reference types. The reference types are class types, interface types, and
In Java, variables play the same role as in the above math example: y = x + 1. So, variables are containers that hold values. Just like we did with the x variable. Variable types in
In java a class can have two type of member variables . 1) instance variables – they are created with every object of that class, and can be access by object of that class. 2)
Setting the Type of a Variable. All variables must have a type. You can use primitive types such as int, float, boolean, etc. Or you can use reference types, such as strings, arrays, or objects. Naming a Variable
A type variable can be any non-primitive type you specify: any class type, any interface type, any array type, or even another type variable. This same technique can be applied to create
A static method in Java is associated with the class, not with any object or instance. It can be accessed by all instances of the class, but it does not rely on any specific instance.
But if you want to genericize it, you can with a Class instance and reflection, using getConstructor to get a relevant constructor, and then calling its newInstance method:
Variables. As you learned in the previous section, an object stores its state in fields.. int cadence = 0; int speed = 0; int gear = 1; The What Is an Object? discussion introduced you to fields, but
Types of Variables. There are three types of variables in Java: local variable; instance variable; static variable; 1) Local Variable. A variable declared inside the body of the
Object-Oriented Programming is built with the understanding that the scope of variables is closely exclusive to the class object that encapsulates those variables. The
TypeVariable is the common superinterface for type variables of kinds. A type variable is created the first time it is needed by a reflective method, as specified in this package.
In Java, all non-static methods are based on the runtime type of the underlying object rather than the type of the reference that points to that object. Therefore, it doesn’t
Type Variables. After the name of a class in the class definition you can put one or more „type variables.“ These look like < followed by a comma separated list of "type names" and ended by
Because Java is strongly typed, it always wants to know the type of the reference that a variable is holding (i.e., since a class is a type, it wants to know the class of the object
Types of Java Variables. Now let us discuss different types of variables which are listed as follows: Local Variables; Instance Variables ; Static Variables; Let us discuss the traits
These classes allow you to encapsulate data and behavior into custom data structures. Here’s how you can create a user-defined data type in Java: 1. Define a Class: To
To create a class, use the keyword class: Create a class named “ Main “ with a variable x: Remember from the Java Syntax chapter that a class should always start with an uppercase
In every programming language, variables are fundamental building blocks that allow programs to store and manipulate data.These are necessary for data representation
- Global Ungleichheiten 2024: Globalisierung Armut Und Reichtum
- Unipark Bild Einfügen _ Unipark Umfragen
- Alexander The Great Powerpoint – Alexander Powerpoint
- Nama Istri William Shakespeare Dan Kisah Hidupnya
- Häuser Zum Verkauf In Billstedt
- Nuka World Energie Und Andere Fragen
- How Do I Cancel My Slacker Radio Account?
- Every Us State Is Under A Weather Alert
- Wofür Brauchen Wir Eiweiß? _ Warum Ist Eiweiß So Gut
- Rewe Prosper Straße 209 In 46238 Bottrop-Batenbrock
- A43 C890 A Androi̇d 4K Ultra Hd 109 Ekran Led Tv