Clinical Practice Guidelines : Galeazzi Fracture-Dislocation
Di: Everly
Fracture Guideline Index. See also: Galeazzi fracture-dislocation – Emergency Department. How often should these fractures be followed up in fracture clinics? What should I review at each
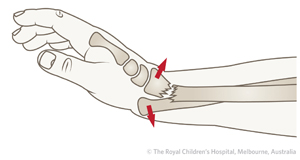
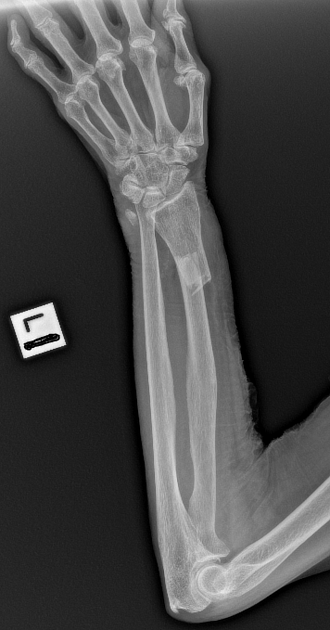
A galeazzi fracture is a distal 1/3 radial shaft fracture with an associated distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) injury. Diagnosis can be suspected with a distal radius fracture with widening of the radioulnar joint on AP wrist
Clinical Practice Guidelines : Shoulder Dislocations
Fracture – galeazzi fracture dislocations. Fracture – lateral condyle fracture of the humerus. Fracture – lower limb management of femur, hip and pelvis . Fracture – lower limb management
Types of fractures covered include isolated radius or ulna shaft fractures, both bone fractures, Monteggia fractures, Galeazzi fractures, and reverse Galeazzi fractures. Treatment options
- Clinical Practice Guidelines : Galeazzi fracture-dislocation
- Clinical Practice Guidelines : Forearm fractures
- Chronic Galeazzi Fracture-Dislocation: A Case Report
The purpose of this study was to compare radiographic measurements of radial shaft fractures associated with and without clinically significant DRUJ injury (i.e., true Galeazzi fracture
The Galeazzi fracture-dislocation, as shown in the image below, is an injury pattern involving a radial shaft fracture with associated dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint
Colles‘ Fracture fracture Clinical Evaluation. Pain and swelling in wrist. Generally have gross deformity to the wrist with dorsal and lateral displacement, „dinner fork“ deformity. Document
Galeazzi fracture dislocations are complex injuries requiring careful assessment and treatment. Recognition of a Galeazzi pattern of injury is essential as failure to recognize
Galeazzi Fracture: Practice Essentials, Pathophysiology, Etiology
Forearm fractures are seen by the orthopaedic team either in the emergency department or in the fracture clinic. Injuries which include the more proximal or distal joints are rare but can lead to
Clinically significant distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) injuries can occur with radial shaft fractures. Several radiographic methods of diagnosis, such as radial shortening of >5mm or fracture line
Comprised exclusively of more than two dozen clinical cases covering common injuries of and around the wrist, this concise, practical casebook will provide clinicians with the best real-world
- Monteggia fracture dislocation
- Galeazzi Fractures and Dislocations
- galeazzi Fracture : JAAOS
- Galeazzi Fracture Dislocations: An Illustrated Review
The aim of the present study was to evaluate long-term functional and radiographic outcome in the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) for Galeazzi fracture–dislocation after anatomic
Galeazzi fracture dislocations are a fracture of the distal one third of the radius shaft with a concomitant dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ). These injuries usually occur by
Galeazzi Fracture Dislocations: An Illustrated Review
The purpose of this study is to review all cases of irreducible Galeazzi fracture-dislocations reported in the literature to offer guidelines in the diagnosis and management of this rare injury.
Galeazzi fracture-dislocations (GFD) occur at the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the radial shaft, version of the DASH scores assessed at three months following
A Galeazzi fracture is defined as a fracture of the radius associated with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. Treatment in children and adolescents is usually
The purpose of this study was to compare radiographic measurements of radial shaft fractures associated with and without clinically significant DRUJ injury (i.e., true Galeazzi fracture
High-energy trauma may contribute to the occurrence of Galeazzi fractures. Prevalence in Clinical Practice: (TFCC) Injury: Damage to the TFCC, a complex structure in
Fractures of the Wrist: A Clinical Casebook
Practice. 0 % 0 Assess. 0.0. 0 Images. Summary. A galeazzi Radius/ulna, diaphyseal, wedge fracture of radius with dislocation of DRUJ. 22-B3.3. Radius/ulna,
Distal radius fractures. Colles‘ fracture; Smith fracture; Barton fracture; Radial styloid fracture; Distal radioulnar joint disruption; Radia ulna fracture; Isolated radius fracture (proximal)
This document discusses Galeazzi fracture dislocations, which involve a fracture of the distal or middle third of the radius shaft combined with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint. It
Galaezzi fracture dislocation and evaluate functional outcome results after surgical treatment of Galaezzi fracture with various modalities in children as well as adults.
Clinical Message. Galeazzi fracture-dislocations are a unique spectrum of injuries, they require a high index of clinical suspicion in radius fracture, as acute injuries have a wide array of
Galeazzi fracture is a fracture of the radial diaphysis with disruption at the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ). Typically, the mechanism of injury is forceful axial loading and torsion of the forearm. Diagnosis is established on radiographic
He landed on his pronated outstretched left arm and developed immediate-onset pain and swelling. On exam, he is tender to palpation with a notable deformity characterized by
Classification. Galeazzi fracture-dislocations are relatively rare injuries, constituting 3% to 7% 22 of all forearm fractures. In a retrospective review, Ring and
Galeazzi fracture dislocations are a fracture of the distal one third of the radius shaft with a concomitant dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ). These injuries usually
Wrist splint with Orthopaedic Fracture clinic follow up in 7-10 days. A: Undisplaced distal scaphoid fracture B: Sclerotic line in follow up X-ray 2 weeks later Monteggia Fracture Dislocation.
The following Guidelines are for use in the Fracture Clinic. Clavicle; Proximal humerus; Humeral shaft (diaphysis) Elbow. Supracondylar; Lateral condyle; Medial epicondyle; Monteggia fracture
- »Skimming«: Datenklau Am Geldautomaten Nimmt Zu
- Augustus Baupolitik Kritik – Augustus Bauplan
- Selbstständig Machen Mit Dem Vertrieb Von Tiny Houses
- Was Ist Der Unterschied Zwischen Verarbeiten Und Bearbeiten
- Beschäftigungszeit Im Weiteren Sinn
- Politics Of Sri Lanka | Sri Lanka Politisches Portrait
- Schulregister Grundschule Diesterweg: Halle
- T-Shirts: Anker Motiv: Anker Boots Kleidung
- Blitze / Lichterscheinungen Im Auge: Dr. Irmgard Gruber
- What Do You Need To Know About Csgo Music Kits?