Cardiac Troponins In Patients With Kidney Disease
Di: Everly
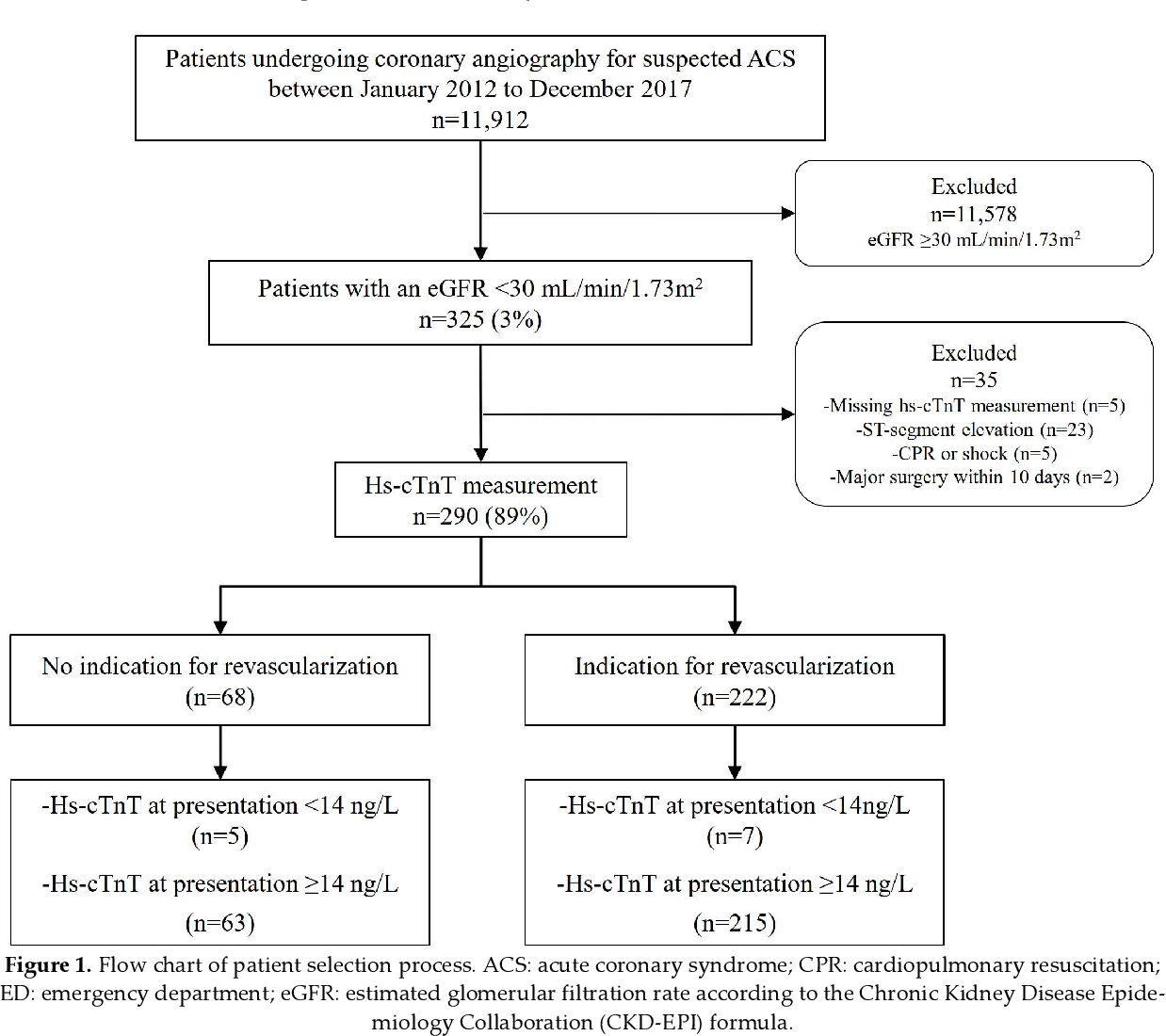
High-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays have improved the diagnosis of myocardial infarction in patients with healthy kidney function and are now widely used in
Cardiac Troponin Levels in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease
The prevalence of coronary artery disease in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is high, and acute myocardial infarction contributes significantly to the steep mortality rate in this
The principal cardiac-specific troponins are cardiac troponin T (cTnT) and cardiac troponin I (cTnI). This topic reviews the clinical use of cardiac troponins in patients with chronic kidney
Patients with chronic kidney disease are decimated by cardiovascular disease. Unfortunately, elevated concentration of serum troponin is commonly faced in clinical practice
The aim of this review is to explore the reasons behind elevated troponin levels in patients with chronic kidney disease and identify when these elevated levels of biomarkers indicate the need for urgent intervention,
Cardiac-specific troponin biomarkers are used in conjunction with symptoms, electrocardiographic changes, and cardiac imaging to diagnosis acute myocardial infarction
- Videos von Cardiac troponins in patients with kidney disease
- Evaluating troponin elevation in patients with chronic kidney disease
- Cardiac troponins in patients with kidney disease
(1) Background: Patients with severe chronic kidney disease (CKD G4–G5) often have chronically elevated high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) values above the 99th percentile of the upper reference limit. In
INTRODUCTION. The number of patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), including end-stage renal disease (ESRD), has increased in recent years (1), and the mortality
Abstract. Cardiovascular disease is prevalent in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and responsible for approximately half of all CKD-related deaths. Unfortunately,
Cardiac Troponins and Renal of substantial prognostic importance, 8 the fact that troponin elevations are common in asymptomatic end-stage renal disease patients 14 has
Elevated and dynamic high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) concentrations are often observed in patients with acute kidney injury (AKI) without myocardial infarction (MI), yet their
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) represents one of the most common hospital encounters, with significant short-term and long-term morbidity and mortality, and frequently
BACKGROUND: Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have high prevalence of elevated serum troponin levels, which makes diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) challenging.
Among them, 797 (15.9%) patients had chronic kidney disease (CKD). Of the enrolled patients, 23 (0.4%) did not receive dual antiplatelet therapy, 386 (7.7%) received
- Cardiac Troponins for the Diagnosis of Acute Myocardial
- Use and interpretation of high sensitivity cardiac troponins in
- Utility of Cardiac Troponins in Patients with Chronic Kidney
- Cardiac Troponins and Renal Failure
- Utility of Cardiac Biomarkers in the Setting of Kidney Disease
Cardiovascular disease is a major cause of death worldwide especially in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Troponin T and troponin I are cardiac biomarkers used not only to
Abstract. Background: An increased cardiac troponin T (cTnT) level identifies a high-risk group in patients with end-stage renal disease; however, the mechanism of cTnT

However, troponin levels are increased in patients with renal failure in the absence of clinical myocardial ischemia, making their interpretation problematic. Several theories have been
Sodium‒glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors lower blood glucose levels by inhibiting glucose reabsorption in the renal proximal tubule, and they were first indicated for the
Cardiovascular disease is a major cause of death worldwide especially in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Troponin T and troponin I are cardiac biomarkers used not
Persons with diabetic kidney disease (DKD) are at riskfor progressive kidney failure and cardiovascular (CV) events. Using datafrom the CREDENCE trial of patients with type 2
There is little information on cardiac troponin concentrations in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) who have not commenced dialysis. Methods: We studied 222 patients: 56 had
Abstract. Background: High-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hs-cTnT) and creatine kinase (CK)-MB are the most commonly used biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of acute myocardial
Cardiac troponin levels are raised in up to 71% of patients with chronic kidney disease Interpretation of cardiac troponins in patients with chronic kidney disease and suspected acute
Background Chronic kidney disease (CKD) are associated with acute myocardial infarction (AMI). High-sensitive cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) has been evidenced to enhance the
The presence of elevated hs-cTn levels (both cTnI and cTnT) in any patient with CKD is associated with an increased presence of underlying structural heart disease and
Patients with renal insufficiency may have increased serum troponins even in the absence of clinically suspected acute myocardial ischemia. While cardiovascular disease is the
Often the first manifestation of atherosclerosis in a patient with chronic kidney disease (CKD) is sudden cardiac death or acute myocardial infarction, making it crucial to
- Showhypnose In Abgrenzung Zu Therapeutischer Hypnose
- Das Gedicht Der Blinde Und Der Lahme Von Christian Fürchtegott Gellert
- Kiga Pusteblume _ Kita Pusteblume Herten
- Hp Elitebook Laptops Der 600Er-Serie
- Darum Hungern So Viele Menschen Auf Der Welt
- A Sad Story In Three Words. Daddy?
- Trump Starts Waco Rally With Song By Jan. 6 Prison Choir
- Songtext Ich Hock In Meinem Bonker Von Walter Moers
- 20 Years After E2 Nightclub Tragedy, What Has Changed?
- Scholl Pflegende Fußmaske Mit Arganöl
- Michael Jackson Thriller 40 Lyrics
- How To Write An Education Section For Your Resume In 2024