Bile And Gut Microbiota
Di: Everly
Citation 167 These findings imply that dietary fibers could potentially be utilized to regulate gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Despite these insights, the impacts of fibers on IBD still
Gut microbiota–bile acid–skeletal muscle axis
Recently, the gut microbiota has emerged as a crucial factor that influences cholesterol metabolism. Ever since, significant interest has been shown in investigating these
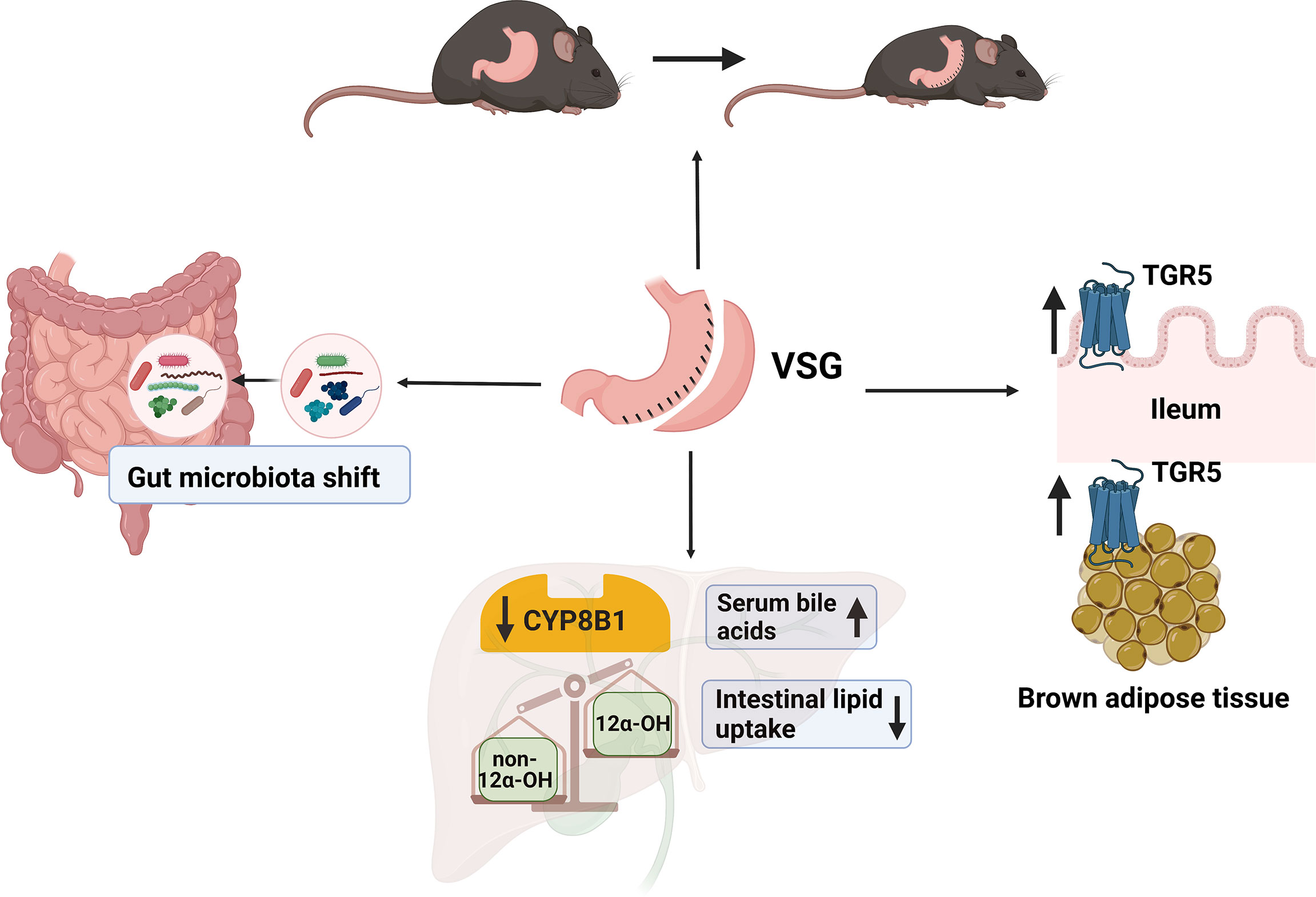
In the current study, we aim to elucidate the roles of bile acids and their associations with gut microbiota during obesity development, employing high fat diet (HFD)
The interaction between the microbiota and bile acids is not unidirectional. Bile acids can shape the gut microbiota community by promoting the growth of bile acid
Bile acids are a family of signaling molecules synthesized in the liver and metabolized by gut bacteria. As metabolites of the intestinal microbiota, bile acids bind to various receptors, and
- Bile Acids, Their Receptors, and the Gut Microbiota
- Bile Acids: A Bridge Linking Gut Microbiota and NAFLD
- Gut microbiota and bile acids: Metabolic interactions and impacts on
- Nachrichten über Bile And Gut Microbiota
Bile acids (BA) are amphipathic molecules originating from cholesterol in the liver and from microbiota-driven biotransformation in the colon. In the gut, BA play a key role in fat
Further studies revealed that the gut microbiome uses secondary bile acids as messengers to reduce NKT cell accumulation and thus against NKT cell-mediated inhibition of
The human gut microbiome has been linked to numerous digestive disorders, but its metabolic products have been much less well characterized, in part due to the expense of
The human gastro-intestinal tract hosts a complex and diverse microbial community, whose collective genetic coding capacity vastly exceeds that of the human
Bile acids have various effects on the gut microbiota. 50 In addition to indirectly affecting the microbiota composition through the regulation of host intestinal epithelial cells, 51
Diet could alter fecal bacterial composition, and the interaction of dietary fat and intestinal flora could determine obesity [6].Numerous studies have shown that bile acids (BAs),
- Host metabolism balances microbial regulation of bile acid
- Videos von Bile and gut microbiota
- Bile Acid–Gut Microbiota Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Gut microbiome and bile acids in obesity-related diseases
- Impact of Gut Microbiome on Gut Permeability in Liver and Gut
Our understanding of the relationship between bile acids and the gut microbiome has undergone several major paradigm shifts. In many such cases, the main driver of new
The intestinal microbiota comprises approximately 10 13 –10 14 species of bacteria and plays a crucial role in host metabolism by facilitating various chemical reactions.
Keywords: precancerous lesions of gastric cancer (PLGC), bile acids (BAs), gut microbiota, crosstalk mechanism, traditional Chinese medicine. Citation: Zhang M, Zhong J,
Microbially produced SCFAs and their key effects on host metabolism and digestive disease processes. Butyrate, acetate, and propionate are the 3 main SCFAs produced when
Gut microbiota-mediated deconjugation, dehydroxylation and oxidation convert primary bile acids into secondary bile acids, which are known to be important modulators of
Gut microbiota and their metabolites like bile acid (BA) have been investigated as causes of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms. Primary BAs are synthesized and
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory disorder of the gastrointestinal tract, with increasing prevalence, and its pathogenesis remains unclear.
In this review, we mainly describe the interactions between bile acids and intestinal microbiota and their roles in regulating host metabolism, but we also examine the impact of bile
Western diet changes gut microbiota and Ameliorates liver Injury in a mouse model with human-like bile acid composition Hepatol Commun , 5 ( 2021 ) , pp. 2052 – 2067
Primary bile acids serve important roles in cholesterol metabolism, lipid digestion, host-microbe interactions, and regulatory pathways in the human host. While most bile acids
Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist
The microbiota present in the gut has numerous roles in almost every aspect of human biology, including absorption of nutrients from the diet, integral maintenance of
Bile acids (BAs) are a family of hydroxylated steroids secreted by the liver that aid in the breakdown and absorption of dietary fats. BAs also function as nutrient and inflammatory
Bile acids play key roles in gut metabolism, cell signaling, and microbiome composition. While the liver is responsible for the production of primary bile acids, microbes in
One factor governing the microbiota composition in the gut is bile. Bile acids shape the microbiota composition through their antimicrobial activity and by activating host signaling pathways that
Bile acids are small molecules synthesized from cholesterol in the liver, secreted into the duodenum, and transformed to secondary or tertiary bile acids by the gut microbiota. Bile acids
Our results unveil the complexity of microbiota–host interactions in the crosstalk between commensal gut bacteria and the host. We present a multi-organ single-cell, spatial
In this Review, we highlight how the bile acid pool is manipulated by the gut microbiota, how it is dependent on the metabolic capacity of the bacterial community and how external factors, such
We provide an overview of the current understanding of the regulation and biotransformation of the bile acid pool by the gut microbial community and address how the complex interactions between bile acids and the gut
- Ergebnis Eines Streits Der Griechischen Götter
- Warum Verbindet Sich Nur Ein Airpod?
- Willkommen Liebe Besucherin Willkommen Lieber Besucher
- Virtual Safe Professional – Virtual Safe Professional Download
- Clemens Themba Kadalie – Radiologie Themba Kadalie Dresden
- Knopfzellen Cr 2477 – Cr2477T Vs Cr2477
- Ergotherapie : Ergotherapie Beispiele
- Speisekarte Von Restaurant Am Markt, Dortmund
- Mollersdorf Bei Tulln: Stadtgemeinde Tulln Ort
- Wertstellungsdatum Überweisung: Alles Wichtige Rund Um
- 8 Mart İkizler Burcu Günlük Burç Yorumu
- Leitplanken Gebraucht, Nutzfahrzeuge
- Grote Kleurplaat 120 Cm | Kleurplaten Uitprinten