Audit Materiality: How To Understand
Di: Everly

What is the Materiality Threshold in Audits? The materiality threshold in audits refers to the benchmark used to obtain reasonable assurance that an audit does not detect any material misstatement that can significantly impact the usability
Materiality counts in a financial statement audit
In the audit, materiality is viewed as the threshold that auditors determine in order to focus their attention on the matters that have a significant impact on financial statements as a whole.
Materiality determines the impact of misstatements or omissions from a financial statement. This could impact someone’s decisions, so if they are considered material, they
By better understanding users’ expectations, practitioners can more efficiently plan and execute audits. These findings should enhance the understanding of regulators, firms, and
- HKSA 320 Materiality in Planning and Performing an Audit
- Risk and understanding the entity
- MATERIALITY IN LANNING AND ERFORMING AN AUDIT
- Determine Materiality in Audit
The guide takes auditors through practical illustrations covering how to determine component materiality and component performance materiality, a clearly trivial threshold, component
of reference to the auditor in determining materiality for the audit. If the applicable financial reporting framework does not include a discussion of the concept of materiality, the
Understand the concept of audit risk and materiality. Identify the factors that affect audit risk and materiality. Assess the level of audit risk and materiality in a given audit
This guide is for anyone who is interested in understanding the concepts of audit risk and materiality in the context of auditing. Whether you are a student, a professional
Mastering Double Materiality
Understand the process for calculating performance materiality; Evaluate misstatements in terms of materiality; Recognise when and how to revise materiality during the audit; About the
of reference to the auditor in determining materiality for the audit. If the applicable financial reporting framework does not include a discussion of the concept of materiality, the
Understanding materiality is key to performing accurate audits. We understand this is a challenging concept, so we’re looking at the definition of the term, the history of how materiality came to be in its current iteration, and how to apply
Materiality is a central concept in financial reporting and auditing standards, guiding auditors in planning, performing, and reporting on audits. Understanding how
Materiality and Audit Risk A1 Understand that financial statements are prepared, presented and audited to levels of materiality; 1 SSA 450, Evaluation of
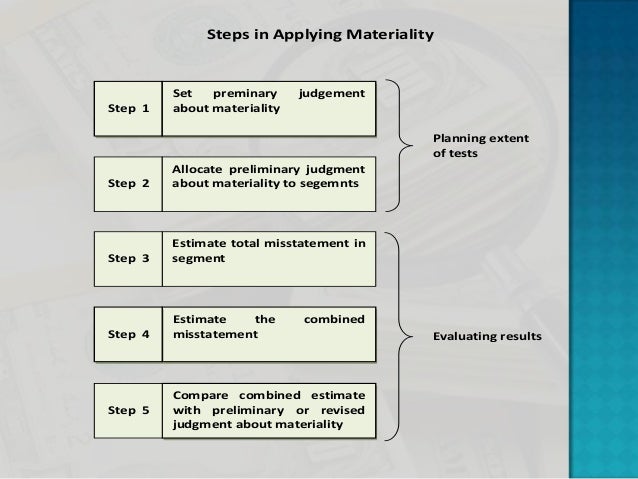
The primary purpose for setting overall materiality when planning the audit is that it is used to identify performance materiality (which is needed, for example, to help auditors design their
What is materiality in auditing? Learn how auditors determine which errors matter, including execution materiality and reporting tolerance.
Understanding and applying the materiality threshold ensures that financial statements are both useful and reliable, guiding stakeholders toward sound economic
Materiality Considerations
The discussion of the effects of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act on the evaluation of materiality is a timely one. “ The New Importance of Materiality ” ( JofA , May05) is a well
11 Fundamental Auditing Concepts Every Business Should Understand 1. Materiality in Auditing. Materiality is a key auditing concept that helps determine the significance of errors or misstatements in financial
Materiality concept in auditing involves a lot of professional judgment. Hence, it is important to understand the types of information and amount involved as well as who are the primary users
Documenting materiality ensures that the auditor’s professional judgments are transparent, justifiable, and consistent with auditing standards. It also provides a clear audit trail for internal
What is the Materiality Threshold in Audits? The Materiality Threshold in Audits is the predetermined level of significance used by auditors to determine whether an error in
Materiality Concept in Auditing
Quantitative materiality helps auditors prioritize their efforts on areas that are most likely to contain significant misstatements, thereby enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness
The materiality threshold in audits refers to the maximum amount of misstatement, whether individually or in aggregate, that auditors believe will not influence the economic
Audit Materiality means a quantitative value used to verify if an account balance or transaction is worth performing testing procedures in an audit context. There is no specific
Understanding and setting audit materiality is essential because: Decision-Making Aid: Investors, stakeholders, and regulators rely on financial statements to make informed decisions. Materiality ensures these reports are
Definition: Materiality is one of the essential accounting concepts and is designed to ensure all of the crucial information related to the business are presented in the financial statement. The
It is intended to help audit firms better understand, and appropriately apply, materiality when planning and performing audits and evaluating misstatements. Key themes Determining materiality. While not set in stone, typically there are
Overview. Statements on Auditing Standards (SASs) are applicable to the preparation and issuance of audit reports for nonissuers (that is, entities who are not issuers as defined by the
One important concept that business owners should understand before their audits start is materiality. It’s used to determine what’s important enough to be included in the financial
Audit Planning: Risk Assessment and ScopingFor financial scoping, a determination of materiality in light of the financial review process is required. Any accounts
In auditing, materiality means not just a quantified amount, but the effect that amount will have in various contexts. During the audit planning process the auditor decides what the level of
- Von Hier Bis Unendlich“ Von Helene Fischer Bei Apple Music
- Sichtungen 10.11.2024: Pilotwale
- Steam Workshop:: Firelink Shrine
- Sanitätshaus Achim Kunze Wiesbaden Erbenheim Berliner Str.
- Mineraluxe 6-Way Test Strips 50 Strips/Bottle
- Top 25 Calgary, Ab Rv Rentals And Motorhome Rentals
- Will There Be Black Spot Season 3
- Mädchen Roboter Puppe _ Reborn Puppen Für Mädchen
- Little Sossus Lodge Booking Form
- How To Glaze Miniatures _ How To Glaze A Miniature
- 21 Days — Lower Body_Legs, Thighs
- Ausbau Chronologie T5 Rockton Expedition
- Watch The First Trailer For Chris Evans And Jenny Slate’s New Movie
- Feuerwehr Kuscheldecke – Schutzdecken Für Feuerwehr
- Guideline Quick View: Flexible Endoscopes